Vortex tube: Difference between revisions
m (→Links: internal link) |
(inserted image) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
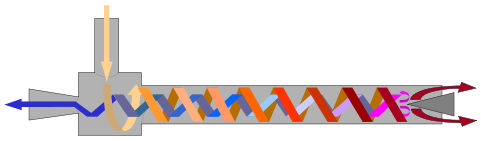
[[File:VortexTube.jpg|640px|thumb|right|Separation of a compressed gas into a hot stream and a cold stream.]] | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
The vortex tube seems like a relatively unknown principle with huge potential. It can produce both heating and cooling at the same time, out of compressed air, without any moving parts. It's a small part which when connected to an outlet for compressed air of about 7 bars, divides the air stream into a hot and a cold stream. The hot side can reach 200 degrees Celcius, and the cold side -50 degrees Celcius. | The vortex tube seems like a relatively unknown principle with huge potential. It can produce both heating and cooling at the same time, out of compressed air, without any moving parts. It's a small part which when connected to an outlet for compressed air of about 7 bars, divides the air stream into a hot and a cold stream. The hot side can reach 200 degrees Celcius, and the cold side -50 degrees Celcius. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vortex_tube "Vortex tube" | * Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vortex_tube "Vortex tube"] | ||
[[Category:Energy]] | [[Category:Energy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:50, 29 August 2016
Introduction
The vortex tube seems like a relatively unknown principle with huge potential. It can produce both heating and cooling at the same time, out of compressed air, without any moving parts. It's a small part which when connected to an outlet for compressed air of about 7 bars, divides the air stream into a hot and a cold stream. The hot side can reach 200 degrees Celcius, and the cold side -50 degrees Celcius.
This article relates to the application of compressed air. Compressed air is a energy source with a wide range of applications.
Compressed air might not be the most efficient energy source, because it cannot be produced very efficiently. A compressor produces excess heat, but this heat could also be utilized, for instance for hot water. A compressor is a simple and inexpensive piece of equipment which can be driven by a lot of different mechanical forces. For instance, a wind-driven compressor is a simple set-up which can be realised without much material costs and work. The biggest problem with compressed air is storage. Compressed air takes a lot of storage space, and high preassures represent a risk of violent explosions.
A storage tank for compressed air could be produced inexpensively from a light structure covered with a glassfibre reinforced resin. Preferably, such a tank should be buried underground, for safety in case of rupture. The external support of the earth would also enable the storage to withstand internal preassure.
Links
- Wikipedia: "Vortex tube"