CEB 3D Printer: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
<u>'''Calculate Length Function:'''</u> Now that desire gripper position & all 4 current lengths are known, desired length for each cable can be calculated. | |||
<html> | |||
<pre> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> px, py, pz; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// p (x,y,z) is the current position of the gripper</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> dpx, dpy, dpz; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// p (x,y,z) is the desired position of the gripper</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> Bheight = 12.0, Blength = 18.0, Bwidth = 12.0; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Base dimensions at 12'x18'x12'</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> B1x = 0.0, B1y = 0.0, B1z = Bheight; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// top point of base rod 1</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> B2x = 0.0, B2y = Blength, B2z = Bheight; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// top point of base rod 2</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> B3x = Bwidth, B3y = Blength, B3z = Bheight; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// top point of base rod 3</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> B4x = Bwidth, B4y = Blength, B4z = Bheight; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// top point of base rod 4</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> L1,L2,L3,L4, dL1,dL2,dL3,dL4; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Current and desired length variables</span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// This function calculates the length that each of the cables</span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// must be in order to attain the desired gripper position.</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">void</span> get_lengths() | |||
{ | |||
| |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Lengths are determined from top of base rod to gripper,</span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// so this does not include length from motor to pulley </span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// at the top of the rod.</span> | |||
| |||
L1 = dist3d(B1x, B1y, B1z, px,py,pz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Length of cable 1 in feet</span> | |||
L2 = dist3d(B2x, B2y, B2z, px,py,pz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Length of cable 2 in feet</span> | |||
L3 = dist3d(B3x, B3y, B3z, px,py,pz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Length of cable 3 in feet</span> | |||
L4 = dist3d(B4x, B4y, B4z, px,py,pz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Length of cable 4 in feet</span> | |||
| |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Desired lengths calculated the same way.</span> | |||
| |||
dL1 = dist3d(B1x, B1y, B1z, dpx,dpy,dpz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Desired length of cable 1</span> | |||
dL2 = dist3d(B2x, B2y, B2z, dpx,dpy,dpz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Desired length of cable 2</span> | |||
dL3 = dist3d(B3x, B3y, B3z, dpx,dpy,dpz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Desired length of cable 3</span> | |||
dL4 = dist3d(B4x, B4y, B4z, dpx,dpy,dpz); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Desired length of cable 4</span> | |||
| |||
} | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">//____________CALCULATE_THE_3-D_DISTANCE_(L-3_NORM)________________//</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> dist3d(<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p1x, <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p1y, <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p1z, <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p2x, <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p2y, <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> p2z) | |||
{ | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> dist3 = <span style="color: #CC6600;">sqrt</span>((p2x-p1x)*(p2x-p1x) + (p2y-p1y)*(p2y-p1y) + (p2z-p1z)*(p2z-p1z)); | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">return</span> dist3; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
</html> | |||
<u>'''PID Function:'''</u> Now that desired length and current length are known, motor output and direction for each motor can be calculated. | |||
<html> | |||
<body> | |||
<pre> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[] err = <span style="color: #CC6600;">new</span> <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[4]; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// error array</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[] dir = <span style="color: #CC6600;">new</span> <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[4]; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// direction array</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[] out = <span style="color: #CC6600;">new</span> <span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span>[4]; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// output array</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> kp = 500; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// this gain is arbitrary, but must be positive</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> Prop; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Variable used for proportional gain.</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">float</span> max_output = 100; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Saturate the output at 100, also arbitrary</span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">//___________________PID_FUNCTION______________________//</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">void</span> pid() <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Actually just P for simplicity's sake</span> | |||
{ | |||
| |||
Prop = kp*err[motorIndex]; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// P = const*(desired_length - current_length)</span> | |||
out[motorIndex] = Prop; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// output = P;</span> | |||
| |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">if</span> (out[motorIndex] > 0) dir[motorIndex] = 1; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// Get direction either 1</span> | |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">else</span> dir[motorIndex] = 0; <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// or 0</span> | |||
| |||
<span style="color: #CC6600;">constrain</span>(out[motorIndex], -max_output, max_output); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// saturate output</span> | |||
out[motorIndex] = <span style="color: #CC6600;">abs</span>(out[motorIndex]); <span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// now that we know direction, we</span> | |||
<span style="color: #7E7E7E;">// just need the absolute output</span> | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
</body> | |||
</html> | |||
Revision as of 08:03, 20 December 2011
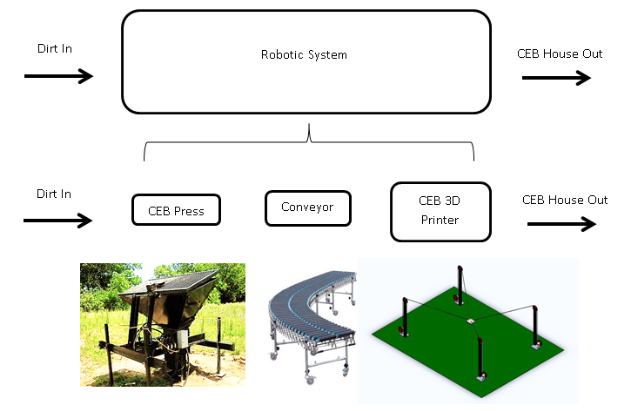
Concept (Illustrated Below): This idea is to develop an automated brick-laying system that can build homes from the ground up, literally. Using a combination of the CEB Press, a conveyor belt, gripper, and a common machine configuration (TBD), the machine acts like a large 3D printer which picks and places compressed bricks robotically.
Two video animations, originally made as Java applets, illustrate two such designs:
Animation (Gantry Design)
Animation (Cable Design)
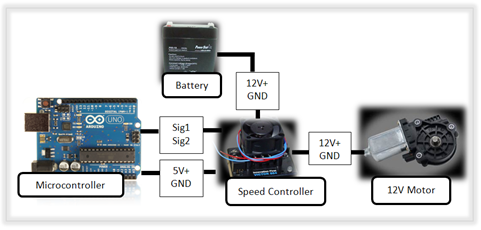
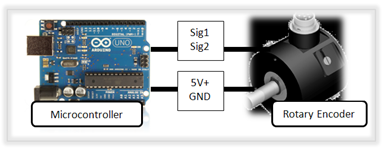
High-Level Actuator Architecture:
High-Level Feedback Architecture:
Sample Source Code:
|
Pseudo Code
|
Arduino Code |
| DECLARE VARIABLES & FUNCTIONS Initialize Output Channels // Tell microcontroller which pins are output Initialize Input Channels // Tell microcontroller which pins are input MAIN LOOP For Motors 1 to 4: Read Encoder Values Calculate Motor Output to Achieve Desired Position Write to Motor Output Channel // Note: the motor signal is sent to a speed controller // to be amplified END FOR LOOP END MAIN LOOP |
void setup() { pinMode(2, OUTPUT); // to Base motor 1 pinMode(3, OUTPUT); // to Base motor 2 pinMode(4, OUTPUT); // to Base motor 3 pinMode(5, OUTPUT); // to Base motor 4 pinMode(6, INPUT); // from digital Encoder 1 pinMode(7, INPUT); // from digital Encoder 2 pinMode(8, INPUT); // from digital Encoder 3 pinMode(9, INPUT); // from digital Encoder 4 } void loop() { for (int motorIndex = 0; motorIndex < 3; motorIndex++) { read_encoders(); pid(); write_to_motors(); } } |
Calculate Length Function: Now that desire gripper position & all 4 current lengths are known, desired length for each cable can be calculated.
float px, py, pz; // p (x,y,z) is the current position of the gripper float dpx, dpy, dpz; // p (x,y,z) is the desired position of the gripper float Bheight = 12.0, Blength = 18.0, Bwidth = 12.0; // Base dimensions at 12'x18'x12' float B1x = 0.0, B1y = 0.0, B1z = Bheight; // top point of base rod 1 float B2x = 0.0, B2y = Blength, B2z = Bheight; // top point of base rod 2 float B3x = Bwidth, B3y = Blength, B3z = Bheight; // top point of base rod 3 float B4x = Bwidth, B4y = Blength, B4z = Bheight; // top point of base rod 4 float L1,L2,L3,L4, dL1,dL2,dL3,dL4; // Current and desired length variables // This function calculates the length that each of the cables // must be in order to attain the desired gripper position. void get_lengths() { // Lengths are determined from top of base rod to gripper, // so this does not include length from motor to pulley // at the top of the rod. L1 = dist3d(B1x, B1y, B1z, px,py,pz); // Length of cable 1 in feet L2 = dist3d(B2x, B2y, B2z, px,py,pz); // Length of cable 2 in feet L3 = dist3d(B3x, B3y, B3z, px,py,pz); // Length of cable 3 in feet L4 = dist3d(B4x, B4y, B4z, px,py,pz); // Length of cable 4 in feet // Desired lengths calculated the same way. dL1 = dist3d(B1x, B1y, B1z, dpx,dpy,dpz); // Desired length of cable 1 dL2 = dist3d(B2x, B2y, B2z, dpx,dpy,dpz); // Desired length of cable 2 dL3 = dist3d(B3x, B3y, B3z, dpx,dpy,dpz); // Desired length of cable 3 dL4 = dist3d(B4x, B4y, B4z, dpx,dpy,dpz); // Desired length of cable 4 } //____________CALCULATE_THE_3-D_DISTANCE_(L-3_NORM)________________// float dist3d(float p1x, float p1y, float p1z, float p2x, float p2y, float p2z) { float dist3 = sqrt((p2x-p1x)*(p2x-p1x) + (p2y-p1y)*(p2y-p1y) + (p2z-p1z)*(p2z-p1z)); return dist3; }
PID Function: Now that desired length and current length are known, motor output and direction for each motor can be calculated.
float[] err = new float[4]; // error array float[] dir = new float[4]; // direction array float[] out = new float[4]; // output array float kp = 500; // this gain is arbitrary, but must be positive float Prop; // Variable used for proportional gain. float max_output = 100; // Saturate the output at 100, also arbitrary //___________________PID_FUNCTION______________________// void pid() // Actually just P for simplicity's sake { Prop = kp*err[motorIndex]; // P = const*(desired_length - current_length) out[motorIndex] = Prop; // output = P; if (out[motorIndex] > 0) dir[motorIndex] = 1; // Get direction either 1 else dir[motorIndex] = 0; // or 0 constrain(out[motorIndex], -max_output, max_output); // saturate output out[motorIndex] = abs(out[motorIndex]); // now that we know direction, we // just need the absolute output }
IRC Experimental Meeting Test Chart: This chart is used to display group meeting times on the OSE Internet Relay Chat (IRC) http://opensourceecology.org/wiki/Irc where groups can discuss project ideas and progress with realtime feedback. Group member names, IRC chat usernames, and status of sub-projects are listed.
| Task | Name/Pseudonym | IRC Username | Status of Project | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Testing | vc_nepo | vc_nepo | 10 % | Link |
| Encoder | User B | userBonIRC | 20 % | |
| Material Spec | User C | userConIRC | Complete |