Cold Saw/Understand2: Difference between revisions
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
The Cold Saw's blade rotation will be powered by a hydraulic motor because hydraulic motors require no gear reduction and are simpler to control at constant torque than AC motors. | The Cold Saw's blade rotation will be powered by a hydraulic motor because hydraulic motors require no gear reduction and are simpler to control at constant torque than AC motors. | ||
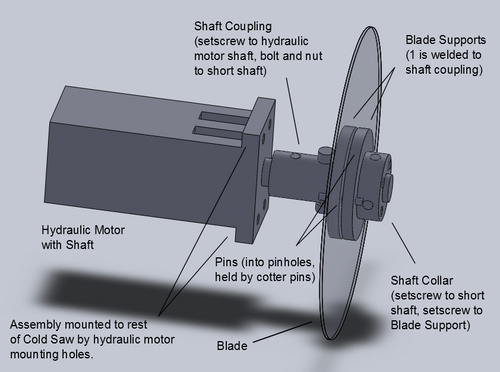
= | =Rotation Diagram= | ||
[[Image: ColdSawV1DriveAssembly.jpg|500px]] | [[Image: ColdSawV1DriveAssembly.jpg|500px]] | ||
Revision as of 00:51, 23 June 2012
Starting the Design with the Right Focus
How the blade will be rotated and how the material will be held are the 2 major considerations.
Following that, how to combine the rotation and holding mechanism into a single assembly while allowing the blade to move into and swivel at an angle to the material.
Rotating the Blade
Cold Saw rotation must let the material be chipped away. The rotation speed must be low so as to avoid producing dust. The torque must be high so as to ensure a consistent cutting process without stalling (the rotation stopping because not enough power was transmitted to the blade teeth to chip away the next layer of material).
Conventionally, Cold Saws use an AC motor (alternating current) that rotates at extremely high speeds with low torque. A multi-stage gearbox (multi-stage means a lot of gear reduction steps) is typically used to change the kinetic power output into low speed and high torque. Controlling the speed of an AC motor at a constant torque involves relatively complex electronics.
Hydraulic motors rotate at low speeds with exceptionally high torque; as such, no gearbox is required. Controlling the speed of a hydraulic motor at a constant torque involves a simple hydraulic flow splitter.
The Cold Saw's blade rotation will be powered by a hydraulic motor because hydraulic motors require no gear reduction and are simpler to control at constant torque than AC motors.
Rotation Diagram
Standard Dimensions
The standard outside diameter of Cold Saw blades: 200mm, 225mm, 250mm, 275mm, 300mm, 315mm, 325mm, 350mm, 370mm, 400mm, 450mm
The standard thickness of Cold Saw blades: 2mm, 2.5mm, 3mm, 3.5mm, 4mm
The standard inside diameter of Cold Saw blades: 32mm, 38mm, 40mm, 50mm
Selected Cold Saw Blade: 350mm OD x 3mm Thk x 32mm ID
For 32mm ID Cold Saw Blades, the pinhole pattern is 2 holes of diameter 8mm, each spaced 45mm from the center; the second pinhole pattern is 2 holes of diameter 12mm, each spaced 64mm from the center.
Selected pinhole pattern: 2 holes x 8mm Dia x 45mm blade center-to-pin center spacing
The mounting rectangle dimensions of the hydraulic motor are 40mm x 100mm, with 12.7mm diameter holes.
Selected Fastener Thread: M12x1.75
For uniformity, the selected setscrew thread is also M12x1.75.
The hydraulic motor shaft is 31.8mm diameter. For uniformity, the selected short shaft diameter is also 31.8mm.