Refrigeration
Main > Food and Agriculture > Food Storage and Processing
Einstein fridge
Albert Einstein invented a refrigerator with no moving parts. It is powered by applying heat to one of the chambers; no electricity is required. The expired patent gives basic plans of how it works. This should be developed into a full open-source design with building instructions, bill of materials etc. It fulfils all the criteria for an Open Ecology product: it is in the public domain, it should last a lifetime and be cheap to build, it would be extremely useful to an off-grid community, it could help alleviate poverty .
Thermal mass fridge
Described in Volume III of the Earthship manual. Basically uses the coolness of the earth in summer to keep cool.
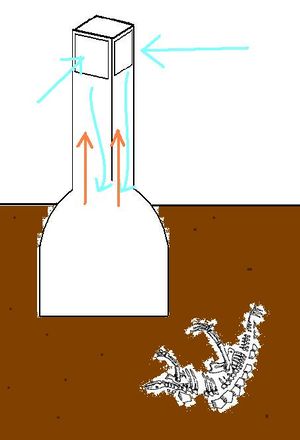
Persian windcatchers
A windcatcher is a tower rising up to catch high winds and funnel them down into an area to be cooled. Simultaneously, it acts as a chimney letting hot air rise out.
Concept for combined thermal mass/ windcatcher system
possible Fridge Efficiency methods
fullness: If a fridge has more space it thus has more air to cool to keep food below room temperature, So keeping space occupied in a fridge leads to energy savings. Shape: Simply put it should be a box with a lid that holds the cold air in when it opened like a deep-freeze. [1]
As the Earthships manual points out, it is wasteful to put a fridge in a heated room (as most homes do). If you want to keep the fridge cool, allow it access to cool outside air.
