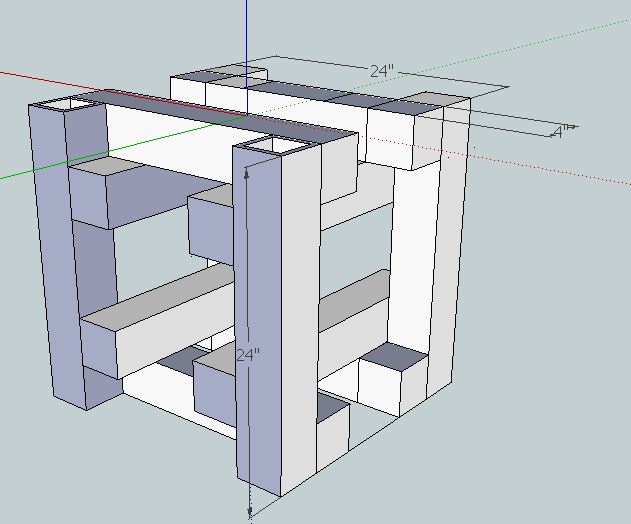
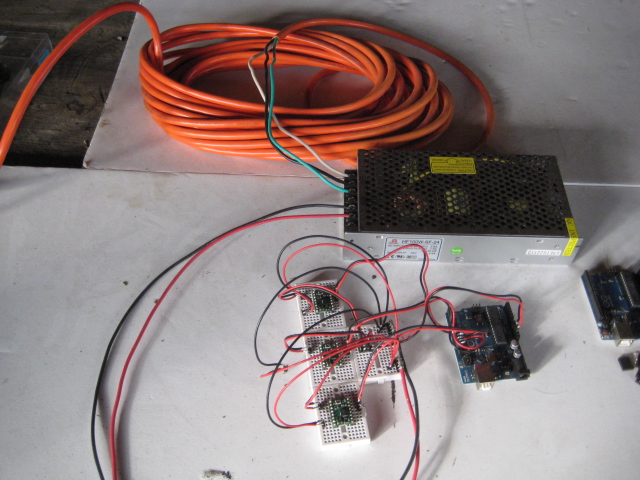
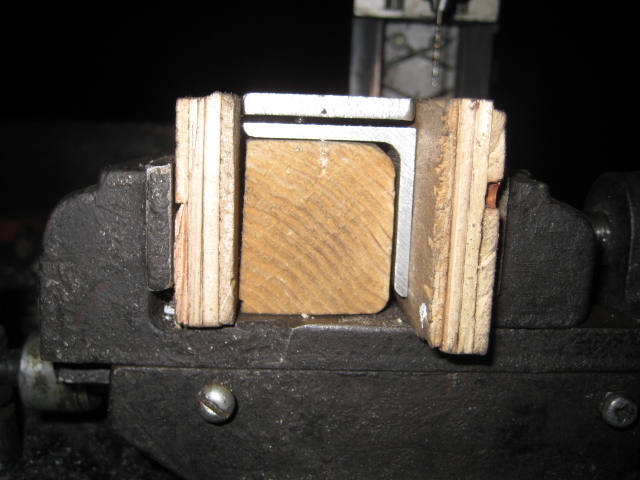
CNC Circuit Mill/Manufacturing Instructions
1 Categorization Key
- The numbers left of each category refer to category strength, low-high being strong-weak. For example, 1 is stronger than 2.
- Stronger categories cover all weaker categories below it until a stronger or equally strong category is established. Examine the following.
1 Tools
2 Drill Bits
1 Materials
2 Bolts
2 Nuts
- The category Drill Bits is contained within Tools; the categories Bolts and Nuts are contained within Materials. Note that neither Materials nor Bolts nor Nuts are a part of Tools; Nuts is not a part of Bolts.
1 Replication
- Information resources required to construct different versions of the CNC Circuit Mill are saved in this section.
- Version 1 (not recommended, near-complete spreadsheet, poor instructions on webpage)
http://opensourceecology.org/wiki/CNCCMV1
1 Prototyping
2 Preparation
- The following active spreadsheet is for prototyping purposes only.
- To edit or download the spreadsheet, click on the following link.
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheet/ccc?key=0AlpsBarfpPkzdFk5aDY3dHM0eEhfZHNkWVppdV9EelE
2 Process
3 Picture Repository
2 Electronics
2 Detailed Software Guide
3 Ubuntu 10.04 LTS 32-Bit
4 Getting Git
- Open Terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install git-core
4 Getting Arduino Integrated Development Environment
- Go to this webpage:
http://arduino.cc/hu/Main/Software
- Download the Linux 32-bit version of Arduino IDE to a directory of your choosing
4 Compatibilizing Arduino IDE
- The following steps are a summary of the information in this webpage:
http://www.pluggy.me.uk/arduino-ubuntu/
- Open System>Administration>Synaptic Package Manager, then type your password
- In Synaptic Package Manager, search for jre, then mark for installation the item with the following name:
Openjdk-6-jre
- Note: marking these items will bring up other packages also to be marked. Click "mark" during these times.
- In Synaptic Package Manager, search for gcc-avr, then mark for installation the item with the following name:
gcc-avr
- In Synaptic Package Manager, search for avr-libc, then mark for installation the item with the following name:
avr-libc
- In Synaptic Package Manager, click "Apply"
- Restart your computer
4 Getting RUBY Programming Language
- Open Terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install ruby1.9.1
- Restart the computer for the changes to take place
4 Getting GRBL Files
- Open Terminal and type:
git clone https://github.com/damellis/grbl.git grbl
4 Getting Gctrl
- Open Terminal and type:
git clone https://github.com/damellis/gctrl.git gctrl
4 Getting Processing
- Go to this webpage:
http://processing.org/download/
- Download the latest version of Processing to a directory of your choosing
4 Moving RXTX files
- Navigate to the Arduino IDE folder>lib.
- Copy RXTXcomm.jar
- Navigate to the Processing folder>modes>java>libraries>serial>library
- Paste RXTXcomm.jar, replacing the existing version
- Navigate to the Arduino IDE folder>lib
- Copy librxtxSerial.so
- Navigate to the Processing folder>modes>java>libraries>serial>library>Linux32
- Paste librxtxSerial.so, replacing the existing version
4 Modifying Gctrl
- Open the Gctrl folder
- Open gctrl.pde in gedit
- Change a part of the code as annotated in the following:
Serial port = null; //change starts
String portname = "/dev/ttyACM0"; // Linux, Arduino Uno
//change ends
boolean streaming = false;
4 Modifying GRBL Files
- Navigate to the GRBL folder
- Open "Makefile" in gedit
- Edit the PROGRAMMER line as:
PROGRAMMER = -c stk500v1 -P /dev/ttyACM0 -b 115200
4 Flashing GRBL
- Open Terminal and navigate to the GRBL folder (ex. by using the "ls" and "cd" commands)
- In Terminal, type:
make clean
make
- Connect the Arduino Uno to the computer via USB cable
- In Terminal, type:
make flash
- Disconnect the Arduino Uno
4 Running GRBL
- Navigate to the Processing folder
- Open and run Processing, setting the sketchbook folder as the folder in which the gctrl folder exists
- In Processing, open gctrl using File>Sketchbook>
- Connect the Arduino Uno to the computer via USB cable
- In Processing, run gctrl using Sketch>Run
- Note: For certain functions of gctrl, press and hold down the key for the popup windows to populate.
4 Determining GRBL Configuration Changes Required
- Go to the following webpage:
http://dank.bengler.no/-/page/show/5474_configuringgrbl?ref=mst
4 Modifying GRBL Settings
- Navigate to the Arduino IDE folder
- Double-click "Arduino" then click "run" in the popup window
- Note: you may want to create a quick launcher for the Arduino IDE
- Connect the Arduino Uno to the computer via USB cable
- In Arduino IDE, open Tools>Serial Monitor
- Note: the Serial Monitor window should pop up and you should see the following:
Grbl 0.6b
'$' to dump current settings
- In the Serial Monitor, change the left drop-down setting to the following:
Both NL & CR
- In the Serial Monitor, type the following in the command line:
$
- Note: you should now see the following:
$0 = 157.480 (steps/mm x)
$1 = 157.480 (steps/mm y)
$2 = 157.480 (steps/mm z)
$3 = 10 (microseconds step pulse)
$4 = 500.0 (mm/min default feed rate)
$5 = 600.0 (mm/min default seek rate)
$6 = 0.100 (mm/arc segment)
$7 = 0 (step port invert mask. binary = 0)
$8 = 25.0 (acceleration in mm/sec^2)
$9 = 225.0 (max instant cornering speed change in delta mm/min)
'$x=value' to set parameter or just '$' to dump current settings
- In the Serial Monitor, type commands as necessary in the following format, where "X" and "Y" are numbers:
$X = Y