CEB Press/Manufacturing Instructions/Controller Box/FeF Liberator Controller
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
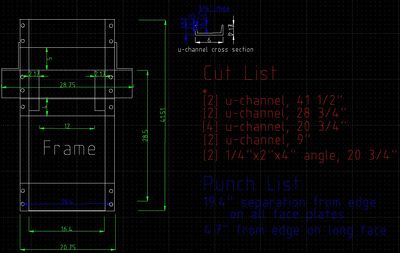
Step 1
- Source 7/16" thick, 6" wide u-channel: 20 feet of it.
- Pieces needed: (click on image to enlarge)
- Torch or cold-cut channel to size
- Punch holes
Step 2
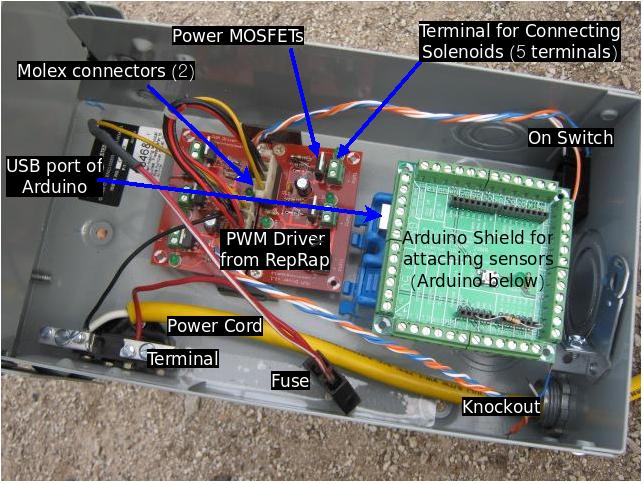
Source the electronics. Here is a diagram of the controller box
Here is the complete controller installed:
Gross Electronics:
- Electronics Box - local hardware store
- Extension Cord
- Or house wiring with Female Plug and Male Plug.
- 2 alligator clips for battery connection - auto parts store
- House wiring box (blue box in picture above below the Arduino Shield - hardware store
- Fuse holder - car parts store
- 12v quick connect plugs - 5 pairs - for quick-coupling to solenoids out of controller box - car parts store
- Stranded 5A wire for solenoid connections
- Spade terminals (10) for connection to solenoid terminals
- Underground phone cable - makes very tough connectors for sensors
- Potting compound
- PVC pipe - with 1 end capped
- Stranded Cat 5 wire for sensor connections
- [5] Supermagnets -
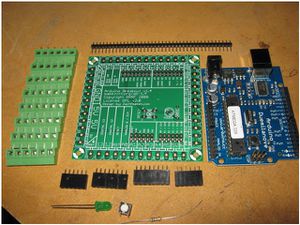
Microelectronics:
- [2] Hall Effect Sensors - Sparkfun
- [1] Arduino shield kit - Makerbot
- [1] Arduino - Makerbot
- [2] RepRap PWM Driver Boards
Components for PWM Driver Boards
- [1] Replacement MOSFETS -
- []
Step 3
Shopping list for items which are shipped:
- [1] Arduino breakout shield - $25, Makerbot
- Assembly instructions - [1]
- [1] Arduino (Duemilanove) - $30, Makerbot
- [2] Solenoid drivers -$13 ea., Makerbot
- Assembly instructions - [2].
- total cost with shipping - $88.25
- [4] MOSFET replacements (see discussion) for solenoid drivers, VNP35N07-E - $3.34, Future Electronics (if not available, search at Octopart) (grate shaker is automated, no sensors needed for it)
- Notes: The cheaper version recommended by Nophead from RepRap was this [3]. See discussion.
- Total $25.70 (for 5)
- [2] Hall Effect sensors - $0.95 ea, Sparkfun
- Total $9.16 (for 5)
- [4] 3/8" V-groove bearings - $7.77 ea, VXB
- Total $42.47
- [6] Supermagnets - $0.48, Gaussboys
- Total $11.11 (for 12)
Grand total for electronics, magnets, and bearings - $176.69
- [1] Potting Compound - $22 for 48 oz, Polymer Composites
- Molex connector for powering solenoid drivers - [4]
- [1] Fuse holder - [5]
Step 4
Put together control box and test sensors
- Assemble entire Control Box
- Blue spacer box - Arduino attached on top with 2 small screws. Slightly slanted attachment to make screw holes fit on blue spacer box
- Terminal in electrical outlet box cut in half on metal cutoff saw to create + and - terminals
- Plastic mount on bottom of electrical box was shaved to allow 2 solenoid drivers to fit
- Test Arduino on laptop - for example by blinking Channel 13 output on Duemilanove.
- Test sensors by passing magnets over them. See this sample code.
- Data Sheet
- Supply voltage is 5V from the Arduino breakout shield
- The pins are +,-, OUT reading from top (printed / smaller face)
- The output is "Open Drain" - this means you need a "pull up" resistor on the output (10K connected to +)
- This model is "latching" which means it turns on from one pole, and off by the other, remembering its state in the meantime.
Controller checklist (ie, So you don't burn your components, check these):
- Arduino powers on with USB cord? Check.
- Arduino works - ex. blink Channel 13 with an LED? Check. Atmega 328 Duemilanove - on Ubuntu 10.04.
- Controller main power switch light red when battery is connected and switch is turned on? Check.
- With Molex connectors disconnected, 12V appears at pins 1 and 2?
- With Molex connectors plugged into solenoid driver boards, main power switch turns the drivers on?
- Arduino powers on with battery supply after flipping main switch on?
- Solenoid drivers are turned on with main switch?
- Solenoids turn all of their MOSFETS as seen via indicator lights?
- Solenoids can cycle the solenoid valves?
C
Step 5
- Test solenoid valves by attaching power to battery and running this sample code for 2 solenoid channels.
- Note we can reduce 3 solenoid channels to 2 by running both the shaker motor and the drawer cylinder from the same channel - the shaker is activated at every stroke of the drawer, as there is ample hydraulic fluid flow available in that part of the overall CEB operation cycle.
Step 6
Build sensor and magnet mounts, attach to the machine
Step 7
Mount control box and solenoid valve on the machine
Step 8
Test the entire machine
- Test motion of main cylinder with this code
- Test motion of soil drawer cylinder with this code.
- Test motion of both cylinders, and machine is ready to run.