Pelton Wheel: Difference between revisions
m (various minor edits, links) |
(→Links) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
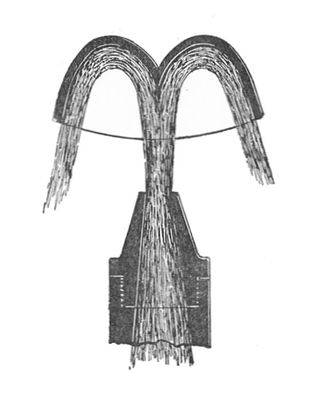
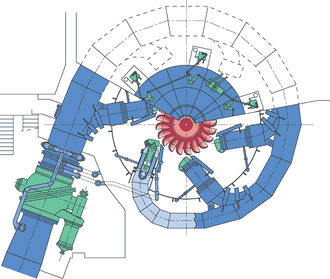
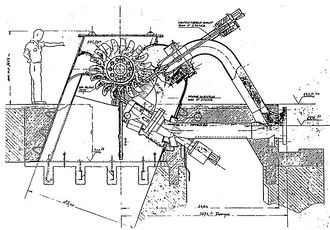
The Pelton wheel is an impulse type water turbine: extracting energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's weight. The design extracts almost all of the impulse energy, allowing for a very efficient turbine. It was invented by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lester_Allan_Pelton Lester Allan Pelton] in the 1870s. | The Pelton wheel is an impulse type water turbine: extracting energy from the '''impulse''' of moving water, as opposed to water's weight. The design extracts almost all of the impulse energy, allowing for a very efficient turbine. It was invented by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lester_Allan_Pelton Lester Allan Pelton] in the 1870s. This wheel is the most widely used water turbine across the world. It is the preferred turbine for hydropower when the available water source has relatively high hydraulic head at low flow rates. In this situation, the Pelton wheel geometry is most suitable. Pelton wheels are made in all sizes: the largest units can be over 400 megawatts, while the smallest ones are only a few inches across. The wheel acts as a kind of [[Flywheel Energy Storage|flywheel]]. | ||
==Gallery== | ==Gallery== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 14: | ||
</gallery></div> | </gallery></div> | ||
== | ==Small-Scale Pumped Storage== | ||
Possibility of using | Possibility of using one or multiple [[windpump|windpumps]] to lift water up to a reservoir that acts as a "battery" of potential energy. Then a micro hydro power plant (with Pelton turbine) can convert that stored potential energy to electricity on demand. This system does not need to be attached to a natural water flow (river, stream), it can be isolated. | ||
See related OSE Wiki page: [[Pumped Hydroelectric Storage]]. | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelton_wheel Pelton Wheel] | * Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelton_wheel Pelton Wheel] | ||
* Mother Earth News (1972) [http://www.motherearthnews.com/renewable-energy/pelton-wheel-zmaz72jmazraw.aspx "Water Power: Building a Pelton Wheel"] | * Mother Earth News (1972) [http://www.motherearthnews.com/renewable-energy/pelton-wheel-zmaz72jmazraw.aspx "Water Power: Building a Pelton Wheel"] | ||
* [http://www.doradovista.com/DVPower2.html "DoradoVista - Small Hydro Power Project"] | * [http://www.doradovista.com/DVPower2.html "DoradoVista - Small Hydro Power Project"] | ||
* [http://www.renewablesfirst.co.uk/hydropower/hydropower-learning-centre/pelton-and-turgo-turbines/ "Pelton and Turgo Turbines"] | * [http://www.renewablesfirst.co.uk/hydropower/hydropower-learning-centre/pelton-and-turgo-turbines/ "Pelton and Turgo Turbines"] | ||
* Low-Tech Magazine:[http://www.lowtechmagazine.com/2013/09/power-from-the-tap-water-motors.html "Power from the Tap: Water Motors"] | |||
[[Category:Energy]] | [[Category:Energy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:13, 13 September 2016
The Pelton wheel is an impulse type water turbine: extracting energy from the impulse of moving water, as opposed to water's weight. The design extracts almost all of the impulse energy, allowing for a very efficient turbine. It was invented by Lester Allan Pelton in the 1870s. This wheel is the most widely used water turbine across the world. It is the preferred turbine for hydropower when the available water source has relatively high hydraulic head at low flow rates. In this situation, the Pelton wheel geometry is most suitable. Pelton wheels are made in all sizes: the largest units can be over 400 megawatts, while the smallest ones are only a few inches across. The wheel acts as a kind of flywheel.
Gallery
Small-Scale Pumped Storage
Possibility of using one or multiple windpumps to lift water up to a reservoir that acts as a "battery" of potential energy. Then a micro hydro power plant (with Pelton turbine) can convert that stored potential energy to electricity on demand. This system does not need to be attached to a natural water flow (river, stream), it can be isolated.
See related OSE Wiki page: Pumped Hydroelectric Storage.
Links
- Wikipedia: Pelton Wheel
- Mother Earth News (1972) "Water Power: Building a Pelton Wheel"
- "DoradoVista - Small Hydro Power Project"
- "Pelton and Turgo Turbines"
- Low-Tech Magazine:"Power from the Tap: Water Motors"