Ziggurat: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
(Added some more links under the "Internal Links" section) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Breadcrumb|Housing and construction}} | |||
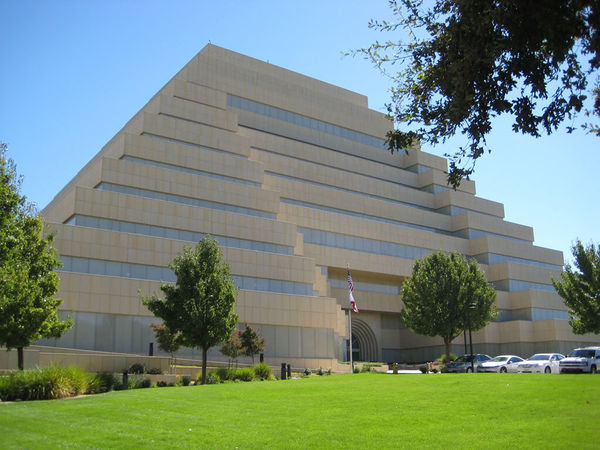
The Ziggurat ("rising building" in Akkadian zaqâru, "to rise high") is the Mesopotamian equivalent of the Egyptian pyramids: large artificial square mountains of stone. Ziggurats played a role in the cults of many cities in ancient Mesopotamia and were always built by kings. Modern Ziggurat-like artificial mountains with stepped terraces could be used for agriculture while at the same time offering residential and commercial space inside. These structures could play an important role in urban agriculture and food security. | |||
[[Image:zigmodel.jpg]] | [[Image:zigmodel.jpg]] | ||
[[ | ([http://www.panacea-bocaf.org/lionkuntz.htm source]) | ||
[[Image:ziggurat.jpg|600px]] | |||
[[Image:zigtop.jpg|300px|2 storey ziggurat from above]] | |||
=Modern Examples= | |||
*[[SEH 2]] can be turned into a ziggurat | |||
*UK dorms - [https://www.themodernhouse.com/journal/my-favourite-building-the-uea-ziggurats/] | |||
=Internal Links= | |||
*[[OBI Aesthetics]] | |||
*[[Green Roof]] | |||
*[[Carbon Pyramid]] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:50, 14 February 2022
Main > Housing and construction
The Ziggurat ("rising building" in Akkadian zaqâru, "to rise high") is the Mesopotamian equivalent of the Egyptian pyramids: large artificial square mountains of stone. Ziggurats played a role in the cults of many cities in ancient Mesopotamia and were always built by kings. Modern Ziggurat-like artificial mountains with stepped terraces could be used for agriculture while at the same time offering residential and commercial space inside. These structures could play an important role in urban agriculture and food security.
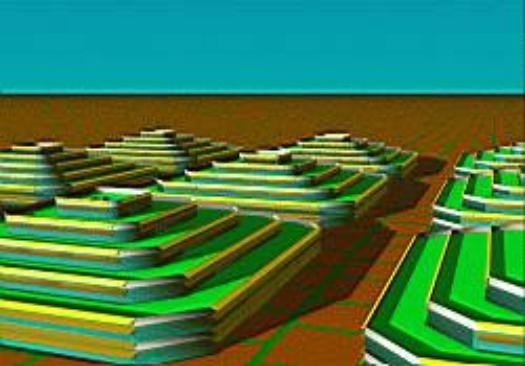 (source)
(source)