500 Factor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Source: [https://www.ucdavis.edu/climate/definitions/how-is-solar-power-generated]] | Source: [https://www.ucdavis.edu/climate/definitions/how-is-solar-power-generated]] | ||
Every 100k years, we go through ice age. [https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Global-mean-temperatures-over-the-last-500-000-years-11_fig3_356606430] | Every 100k years, we go through ice age and hot age - where mean temperature of the earth fluctuates up to 7C. [https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Global-mean-temperatures-over-the-last-500-000-years-11_fig3_356606430] | ||
Revision as of 01:41, 12 August 2024
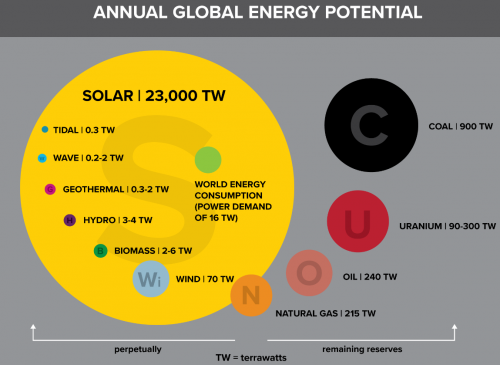
The 1000 factor is a factor calculated theoretically as the limit of possible increase of energy by humans, without suffering from ecocide.
This number is a number that allows for solar energy to power all natural processes such as weather phenomena, natural life, along with human-made processes such as the conversion of solar energy into useful power for industrial processes, indoor heating/cooling, transportation, etc.
Plants are the largest users of solar energy. Plants use only 1-2% of the incoming solar spectrum [1], and the earth's coverage with plants is about 30% [2]. Since only plants can use solar energy, and animals build ecosystems upon plant energy - the plant energy is the primary energy important to overall solar energy usage. Ie, animals do not use solar energy, outside of the heat - a component of weather. Bottom line - the amount of total energy required to sustain the ecosphere is under 1% of the total incoming radiation.
Source: [3]]
Every 100k years, we go through ice age and hot age - where mean temperature of the earth fluctuates up to 7C. [4]