Solar Collector Losses Summary: Difference between revisions
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
#Edge Lossses - 10% - from [[Solar_Collector_Calculations#Losses_due_to_edge_effects_only]] - about if we consider the 6 hours of highest sun during the day, or from 9:30 AM - 2:30 PM | #Edge Lossses - 10% - from [[Solar_Collector_Calculations#Losses_due_to_edge_effects_only]] - about if we consider the 6 hours of highest sun during the day, or from 9:30 AM - 2:30 PM | ||
#Reflection from collector tube glass - 4% loss | #Reflection from collector tube glass - 4% loss | ||
#Shading losses from collector tube - 1 slat will be covered by the shadow of the collector tube - at a time, for 6% loss (1 of 16 slats shaded) | |||
(total losses before collector tube are | (total losses before collector tube are 21% = 9.5 kW) | ||
#Radiation losses from collector tube - 7.5 kW with emissivity = .25 selective coating | #Radiation losses from collector tube - 7.5 kW with emissivity = .25 selective coating | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
We assume that all the remaining energy goes into heating the water in the collector tube. | We assume that all the remaining energy goes into heating the water in the collector tube. | ||
The sum of these losses is | The sum of these losses is 24 kW, with 21 kW remaining, or 53% loss. | ||
For general purposes, we will say that the collector is slightly | For general purposes, we will say that the collector is slightly under 50% efficint. | ||
=Conduction Losses= | =Conduction Losses= | ||
Latest revision as of 22:20, 1 February 2009
Introduction
When considering the overall performance of linear slat collectors for a linear Fresnel solar concentrator system oriented in the E-W direction, several losses must be considered. For the case of a 4:1 aspect ratio array, such as a 15 foot wide array that stretches for 60 feet in the E-W direction. For this case, if we use 6" slats, we can fit about 16 slats in this area, or a total of 480 square feet (45 sq meters) of solar intercept. We have about 5 kWhr/day per square meter in Maysville, Missouri - from [1]. We summarize our losses. This includes air mass losses and averages over the seasons - because we are taking empirical data. We are assumining a collector tube with a single layer of insulating glass on the surface. We are considering a case where we are letting the collector tube heat up to 650K.
- Reflection losses from mirrors - 1%, assuming 99% reflective mirrors - and assuming that 4% reflection from glass is reflected back at the collector tube
- Edge Lossses - 10% - from Solar_Collector_Calculations#Losses_due_to_edge_effects_only - about if we consider the 6 hours of highest sun during the day, or from 9:30 AM - 2:30 PM
- Reflection from collector tube glass - 4% loss
- Shading losses from collector tube - 1 slat will be covered by the shadow of the collector tube - at a time, for 6% loss (1 of 16 slats shaded)
(total losses before collector tube are 21% = 9.5 kW)
- Radiation losses from collector tube - 7.5 kW with emissivity = .25 selective coating
- Absorptance losses at collector tube - 4 kW
- Conduction losses of conductor tube - 2.7 kW
We assume that all the remaining energy goes into heating the water in the collector tube.
The sum of these losses is 24 kW, with 21 kW remaining, or 53% loss.
For general purposes, we will say that the collector is slightly under 50% efficint.
Conduction Losses
assuming a 60 ft x .5ft rectangular absorber box with an open bottom (11.3 square meters, we'll just ignore the complexity of corners). The area of 3 sides like this is 90 sq feet (8.4 sq meters).
using 3 inch of rigid fiberglass of R-value [2] 4 (in SI units) and assuming a temperature difference of 300 degree Celsius (400C - 100C).
Power lost due to conduction = 1/R * A * (delta T)[3] = 1/12 * 8.4 * 300 = 210 W
Add the conduction through glass - 8.4*300 = 2520W
Absorptance Loss
Assume that for the absorptance of 90% using Solkote selective coating, the 10% not absorbed is lost through conduction through the glass. The incoming radiation is the 45 kW of available radiation minus 15% of the collector losses, or 38 kW available. About 4 kW is lost due to imperfect absorption.
Radiation Loss Calculation
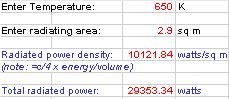
Blackbody radiation calculator shows the following losses for a 60' tube:
This takes a 650K optimal collector temperature, with a 2" tube, 20m long. This collector tube area = 2.9 sq meters.
- 30 kW losses mean 2/3 of the incoming 45 kW of solar gain.
- Reduce this by selective coating of emissivity = 0.25 for Solkote, and we get 7.5 kW of radiation loss
Setting the temperature to 650K gives us