Assembly Mechanisms: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "Physical Compression Mate (ex. Riveting) Fluid Compression Mate (ex. Hydroformed Assembly) Thread Compression (ex. Bolts and Nuts, C-Clamp) Magnetic Attraction (ex. Electromag...") |
(→README) |
||
| (89 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=README= | |||
There's only so many ways things are attached together. Whenever you see a mechanical connection, try to find what assembly mechanism it uses! | |||
*One piece, like a continuous block of steel. | |||
*Soldered, brazed, or welded, like connecting copper to copper using molten-then-cooled tin-copper alloy. | |||
*Adhered, like glue sticking paper to paper | |||
*Fastened with thread, like with a machine screw or a bolt and nut. | |||
*Pressure differential, like with suction cups. | |||
*Plain contact, like a picture frame mounted on the head of a screw in the wall. | |||
*Friction, like a semi-compressed spring holding itself inside a round tube. | |||
*Weave, like a uniform cotton fabric pattern. | |||
*Magnetic, like with 2 magnets attracting each other. | |||
*Buoyant, like with a piece of wood floating on top of a tub of water. | |||
*Gravity, like with a steel weight holding down a length of wire. | |||
=Intermolecular= | |||
<gallery perrow=6> | |||
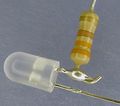
File: molecularassy4.jpg|LED Soldered to Resistor | |||
File: molecularassy5.jpg|Brazed Bicycle Frame | |||
File: molecularassy6.jpg|TIG Welded Pipes | |||
File: molecularassy9.jpg|Friction Welded Pipes | |||
File: molecularassy7.jpg|Pressure Welded Wire Mesh | |||
File: molecularassy10.jpg|Motors Epoxied to Plastic | |||
File: molecularassy11.jpg|Glued Wood Endtable | |||
File: molecularassy12.jpg|Thermoplastic Heat-layer 3D Printing | |||
File: molecularassy13.gif|Ink Heat-layer 2D Printing | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Thread= | |||
<gallery perrow=6> | |||
Weight | File: lspic6.jpg| Light Screen C-Clamped to Steel Tube | ||
File: Machinescwguit.jpg| Screwed Guitar Cover | |||
File: threadassy3.jpg| Wood Fastened by Nut and Bolt | |||
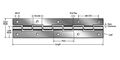
File: threadassy4.jpg| Thread as Linear Guide to Nut | |||
File: ballscrew111.jpg| Ballscrew and Ballscrew Nut | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Tension= | |||
<gallery perrow=6> | |||
File: tensionassy.jpg|Discrete Electronics Tension-Held by Breadboard | |||
File: setscrew111.jpg| Small Rod Connected to Large Rod with Setscrew Coupling | |||
File: clampshaftcollar.gif|Clamp-on Shaft Collar | |||
File: wormscrewhoseclamp.jpg|Worm Screw Hose Clamp | |||
File: springhoseclamp.jpg|Spring Hose Clamp | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Plain Contact= | |||
<gallery perrow=6> | |||
File: holdassy.jpg|2 Carabiners holding Rope | |||
File: rivet.jpg|Plate Riveted to Plate | |||
File: hinge111.jpg|Piano Hinge | |||
File: roundlinearslide.jpg|Round Linear Slide | |||
File: dovetailassy.jpg|Dovetail Linear Slide | |||
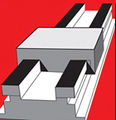
File: boxedassy.jpg|Boxed Way Linear Slide | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Rolling Contact= | |||
<gallery perrow=6> | |||
File: rollerwheellinear.jpg|Roller Wheel Slide | |||
File: ballbearing11.jpg|Ball Bearing | |||
File: taperrollerbearing11.jpg|Tapered Roller Bearing | |||
File: slewingbearing111.jpg|Slewing Bearing | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Magnetic= | |||
<gallery> | |||
File: magassy.jpg|Magnets Repelled and Attracted by Magnets | |||
File: magnet2.JPG|Electromagnet Attracting Iron-containing Paperclips | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Pressure Differential= | |||
<gallery> | |||
File: plungerassy.jpg|Plunger Assembled with Suction on Computer Screen | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Weight= | |||
<gallery> | |||
File: Leather-book-weight.jpg|Weight Holding Book Paper Down | |||
</gallery> | |||
=Woven= | |||
<gallery> | |||
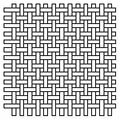
File: wovenassy.jpg|Plain Weave | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:44, 6 January 2013
README
There's only so many ways things are attached together. Whenever you see a mechanical connection, try to find what assembly mechanism it uses!
- One piece, like a continuous block of steel.
- Soldered, brazed, or welded, like connecting copper to copper using molten-then-cooled tin-copper alloy.
- Adhered, like glue sticking paper to paper
- Fastened with thread, like with a machine screw or a bolt and nut.
- Pressure differential, like with suction cups.
- Plain contact, like a picture frame mounted on the head of a screw in the wall.
- Friction, like a semi-compressed spring holding itself inside a round tube.
- Weave, like a uniform cotton fabric pattern.
- Magnetic, like with 2 magnets attracting each other.
- Buoyant, like with a piece of wood floating on top of a tub of water.
- Gravity, like with a steel weight holding down a length of wire.