House Resource Management Software: Difference between revisions
(Add Principles) |
No edit summary |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Hint | Moved to https://github.com/gbroques/ecovillage-resource-management-spec}} | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Software to manage the resources of a house in a cyclical closed-loop system. | Software to manage the resources of a house in a cyclical closed-loop system. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
* Food | * Food | ||
* Energy | * Energy | ||
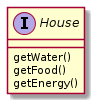
Thus, a <code>House</code>, in the software can be thought of as a generic interface with the following methods: | |||
* <code>getWater()</code> | |||
* <code>getFood()</code> | |||
* <code>getEnergy()</code> | |||
[[File:House-interface-plant-uml-diagram.png]] | |||
<html> | |||
<details> | |||
<summary>Plant UML Source</summary> | |||
<pre> | |||
@startuml | |||
interface House { | |||
getWater() | |||
getFood() | |||
getEnergy() | |||
} | |||
@enduml | |||
</pre> | |||
</details> | |||
</html> | |||
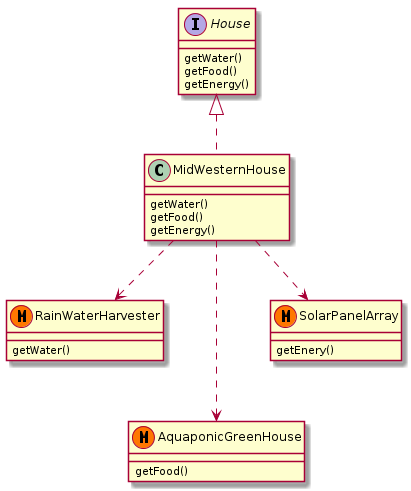
You may have several implementations of this generic <code>House</code> interface to meet the needs of people in different bio-regions. | |||
For example, a mid-western house. | |||
[[File:Mid-western-house-implementation-plant-uml-diagram.png]] | |||
<html> | |||
<details> | |||
<summary>Plant UML Source</summary> | |||
<pre> | |||
@startuml | |||
interface House { | |||
getWater() | |||
getFood() | |||
getEnergy() | |||
} | |||
class MidWesternHouse implements House { | |||
getWater() | |||
getFood() | |||
getEnergy() | |||
} | |||
' Responsible for the collection, storage, and purification of rain-water | |||
class RainWaterHarvester << (M,#FF7700) >> { | |||
getWater() | |||
} | |||
class AquaponicGreenHouse << (M,#FF7700) >> { | |||
getFood() | |||
} | |||
class SolarPanelArray << (M,#FF7700) >> { | |||
getEnery() | |||
} | |||
MidWesternHouse ..> RainWaterHarvester | |||
MidWesternHouse ..-> AquaponicGreenHouse | |||
MidWesternHouse ..> SolarPanelArray | |||
@enduml | |||
</pre> | |||
</details> | |||
</html> | |||
'''TODO:''' In reality, a house would likely have ''multiple'' sources for any one resource. For example, energy may come from solar, wind, and bio-gas digestion. The above diagrams don't account for this yet. Expand this to waterSources, foodSources, and energySources? | |||
==I/O== | |||
A house can be defined in terms of I/O, or '''inputs''' and '''outputs'''. | |||
===Inputs=== | |||
Inputs are unique to a geographic location or bio-region, and result in resource generation. | |||
For example, in the mid-west of the United States, an input to a house may be '''rain-water'''. | |||
The house would have a rain-water harvesting sub-component that adapts the '''input''' of rain-water to the '''resource''' of water. | |||
Other geographic locations may have different inputs that lead to water resource generation such as ground-water, salt-water, river-water, glacier-water, or spring-water -- and each water input would need a different sub-component to adapt it to a water resource ready for human consumption. | |||
===Outputs=== | |||
TODO: Define outputs. | |||
* Human waste | |||
* are there others? | |||
==Principles== | ==Principles== | ||
See | See [[Village Resource Management Software#Principles]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 18:25, 25 July 2020
Introduction
Software to manage the resources of a house in a cyclical closed-loop system.
Sub-component of the Village Resource Management Software.
House resources are defined as:
- Water
- Food
- Energy
Thus, a House, in the software can be thought of as a generic interface with the following methods:
getWater()getFood()getEnergy()
Plant UML Source
@startuml
interface House {
getWater()
getFood()
getEnergy()
}
@enduml
You may have several implementations of this generic House interface to meet the needs of people in different bio-regions.
For example, a mid-western house.
Plant UML Source
@startuml
interface House {
getWater()
getFood()
getEnergy()
}
class MidWesternHouse implements House {
getWater()
getFood()
getEnergy()
}
' Responsible for the collection, storage, and purification of rain-water
class RainWaterHarvester << (M,#FF7700) >> {
getWater()
}
class AquaponicGreenHouse << (M,#FF7700) >> {
getFood()
}
class SolarPanelArray << (M,#FF7700) >> {
getEnery()
}
MidWesternHouse ..> RainWaterHarvester
MidWesternHouse ..-> AquaponicGreenHouse
MidWesternHouse ..> SolarPanelArray
@enduml
TODO: In reality, a house would likely have multiple sources for any one resource. For example, energy may come from solar, wind, and bio-gas digestion. The above diagrams don't account for this yet. Expand this to waterSources, foodSources, and energySources?
I/O
A house can be defined in terms of I/O, or inputs and outputs.
Inputs
Inputs are unique to a geographic location or bio-region, and result in resource generation.
For example, in the mid-west of the United States, an input to a house may be rain-water.
The house would have a rain-water harvesting sub-component that adapts the input of rain-water to the resource of water.
Other geographic locations may have different inputs that lead to water resource generation such as ground-water, salt-water, river-water, glacier-water, or spring-water -- and each water input would need a different sub-component to adapt it to a water resource ready for human consumption.
Outputs
TODO: Define outputs.
- Human waste
- are there others?