Drip Irrigation: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
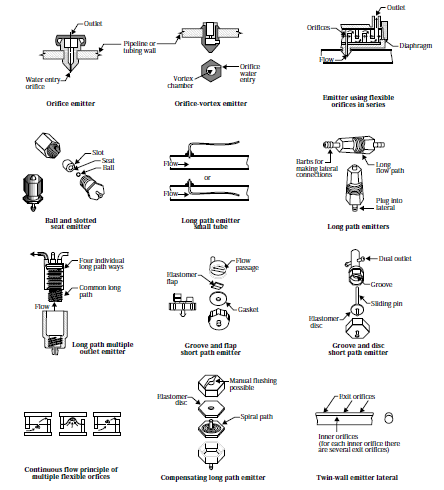
[[Image:emitter_types.png|thumb|left|upright=3|Emitter types, U.S. Department of Agriculture.]] | [[Image:emitter_types.png|thumb|left|upright=3|Emitter types, U.S. Department of Agriculture.]] | ||
=Calculations= | |||
*1/4 GPH per emitter | |||
*6-12" space between emitters for rows | |||
[[Category:Food and Agriculture]] | [[Category:Food and Agriculture]] | ||
Revision as of 16:24, 30 May 2022
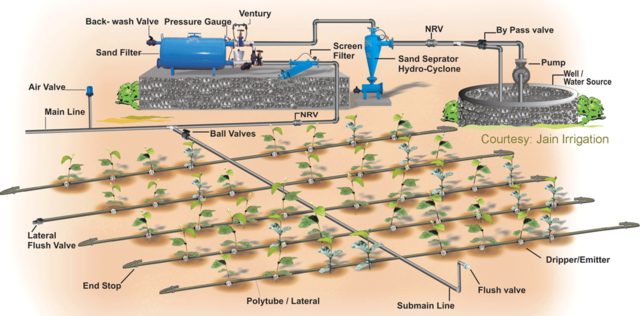
Drip irrigation is the targeted delivery of water to plants along water distribution lines emanating from a central water reservoir. Drip irrigation saves water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants.
Typical components for a micro irrigation system include the reservoir, control valve, filter, main pipe, lateral pipe, and micro-tube/emitter. This type of system covers an area between 20 m2 and 1000 m2. The layout of each drip irrigation system is highly variable, dependent on the crop and field. Many emitters exist with different methods of water impedance, including vortex, tortuous path, long path, and groove and disk short path.
Other Pages
- Related: Subsurface Drip Irrigation
- Appropedia: Drip Irrigation
- Appropedia: CCAT Gravity fed drip irrigation
Calculations
- 1/4 GPH per emitter
- 6-12" space between emitters for rows