Conflict Management Styles: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
=Conflict and Collaboration= | =Conflict and Collaboration= | ||
*Want collaboration? Accept and actively manage conflict - [https://hbr.org/2005/03/want-collaboration-accept-and-actively-manage-conflict]. ''But despite the billions of dollars spent on initiatives to improve collaboration, few companies are happy with the results.'' | *Want collaboration? Accept and actively manage conflict - [https://hbr.org/2005/03/want-collaboration-accept-and-actively-manage-conflict]. ''But despite the billions of dollars spent on initiatives to improve collaboration, few companies are happy with the results.'' | ||
*The three myths of collaboration - that we need teams, that we can incentivize collab, and that we can structure companies for collab [https://hbr.org/2005/03/want-collaboration-accept-and-actively-manage-conflict] | |||
=Communication in the Real World= | =Communication in the Real World= | ||
*OER text book - [https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/] | *OER text book - [https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/] | ||
Revision as of 05:26, 29 October 2020
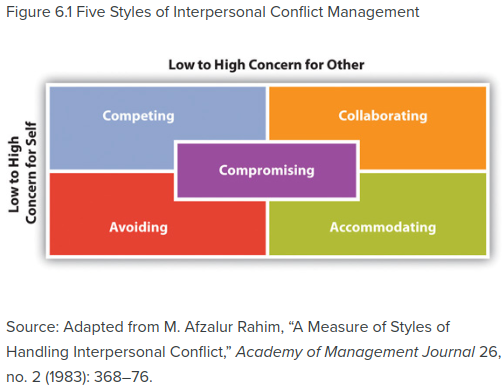
- Five styles of interpersonal conflict management [1]
- Mentions awareness of instrumental, relational, and self-presentation goals in negotiation
- Demand-withdrawal pattern - [2] - ranks among the most destructive and least effective interaction patterns
Conflict and Collaboration
- Want collaboration? Accept and actively manage conflict - [3]. But despite the billions of dollars spent on initiatives to improve collaboration, few companies are happy with the results.
- The three myths of collaboration - that we need teams, that we can incentivize collab, and that we can structure companies for collab [4]
Communication in the Real World
- OER text book - [5]