Hole Puncher Calculations: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "=Overview= {{Ironworker}} Hole puncher calculations. =Calculations= ==Force Required to Shear the metal== Using the shear tonnage calculator at [http://multicyl.biz/calculations...") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=Calculations= | =Calculations= | ||
==Force Required to Shear the metal== | ==Force Required to Shear the metal== | ||
According to an Ironworker Blade manufacturer (he prefers not to be mentioned by name) with a 6 degree rake in the blade, you can '''shear 1"x10" steel''' with '''100 tons''' of force. | |||
No data has been found regarding how much force to shear 1"x12" as is desired, so we will assume that there is a direct relaitonship between length of cut and force to shear it. Following this logic, '''100T/10"=xT/12"''' Solving for x, we get Force to shear ''' 1"x12"=120T.''' | |||
We will include a safety factor to account for any errors we have made. A force of 130T or more should suffice. | |||
==The required moment to act on blade== | ==The required moment to act on blade== | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 2 November 2011
Overview
 Ironworker Hole puncher calculations.
Ironworker Hole puncher calculations.
Calculations
Force Required to Shear the metal
According to an Ironworker Blade manufacturer (he prefers not to be mentioned by name) with a 6 degree rake in the blade, you can shear 1"x10" steel with 100 tons of force.
No data has been found regarding how much force to shear 1"x12" as is desired, so we will assume that there is a direct relaitonship between length of cut and force to shear it. Following this logic, 100T/10"=xT/12" Solving for x, we get Force to shear 1"x12"=120T.
We will include a safety factor to account for any errors we have made. A force of 130T or more should suffice.
The required moment to act on blade
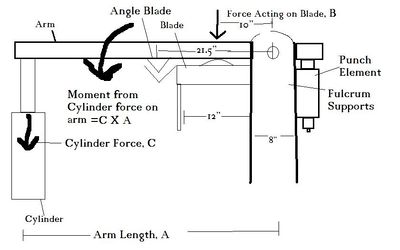
To find this, we must make a few basic assumptions:
- The fulcrum supports are 8" wide
- The blade is 12" wide and placed as close as possible to the fulcrum supports.
- The force will be applied at the center of the blade and distributed evenly.
- The required moment will be whichever is highest for a particular design, the blade force, or the angle shear force.
- In design 1, the angle shear is between the blade and the cylinder
- In design 2, the angle shear is between the cylinder and the fulcrum supports.
- As the distance of the blade to the fulcrum doesn't change, the blade moment is the same for design 1 and design 2.
Blade moment
Since the force on the blade(B) is known, as is its distance from the fulcrum, we can calculate the necessary moment, M. M=Force(B) x Distance from the pivot(d) (10")
For the capability of cutting 1"x12", B=480 tons.
- M=480 tons x 10" = 4800 inch tons
For the capability of cutting 1"x10", B=400 tons.
- M=400 tons x 10" = 4000 inch tons
Angle Shear moment
B=240 tons
Design 1, 6x6 angle: d=21.5"
- M=240 tons x 21.5" = 5160 inch tons
Design 1, 4x4 angle:
- M=160 tons x 21.5" = 3440 inch tons.
Design 2: d= 9"
- M=240 tons x 9" = 2160 inch tons
Required Moments
Design 1, 6x6: As the angle moment is the highest, this value is the requirement, or M=5160 inch tons. This means this machine would have the capacity for 1"x12" flat cuts.
Design 1, 4x4: The blade moment is highest, so for the 12" cut, M=4800 inch tons. For the 10" cut, M=4000 inch tons.
Design 2: The Blade moment is highest, so for the 12" cut, M=4800 inch tons. For the 10" cut, M=4000 inch tons.
Calculating the arm length and cylinder size
There are two possible designs for this; the blade being between the cylinder and the fulcrum supports(Design 1), or the blade being on the other side, along with the punch (Design 2)
- If building an ironworker whose max cutting ability is under 1" x 10", you could scale the cylinder size down according to your desires.
Since the such high force is required to shear the desired metal, we will use the largest available cylinder with an 8" stroke available at surplus center.
To calculate the arm length using this cylinder, we must set the cylinder force (C) multiplied by the lever arm (A) equal to the required moment (M), so A X C = M. Solving for A, we get A=M/C
Design 1
In this particular design, the cylinder will be contracting while shearing, which means the cylinder tonnage we are using must be on the contracting side. See Cylinder Tonnage Calculations for how to find the contracting strength. The calculated contracting tonnage (C) for this specific cylinder is 56.52 tons.
6x6 M=5160 inch tons, so A=5160 inch tons / 56.52 tons = 91.30 inches.
4x4, 12" M=4800 inch tons, so A=4800 inch tons / 56.52 tons = 84.93"
4x4, 10" M=4000 inch tons, so A=4000 inch tons / 56.52 tons = 70.77""
Design 2
In this design, the cylinder is expanding while shearing the 1"x12", so we use the expanding cylinder tonnage for the 8" bore cylinder, or 75.36 tons.
A=M/C For the capability of cutting 1"x12", M=4800 Inch tons.
- A=4800 inch tons/ 75.36 tons = 63.69 inches
For the capability of cutting 1"x10", M= 4000 inch tons
- A=4000 inch tons / 75.36 tons = 53.08 inches
We should also double check to make sure the punch still has enough power We must find the required punch moment, and insure it is less than the required blade moment.
- M= Punch force (P) x distance (d). P= 150 tons, d=23"
M= 150 tons x 23" = 3450 inch tons. This is less than the blade moment, so we are OK.
Design analysis
As we can see, both designs are going to require really long overall arms. Here are the calculated lengths:
Design 1 will require A+6", including the end amounts (this depends on how close the cylinder attaches to the end, and how far the punch is away from the end).
- 6x6= 91.3"+6" = 97.3 inches
- 4x4, 12"= 84.9"+6" = 90.9" including the end amounts.
- 4x4, 10"= 70.7"+6" = 76.7", including the end amounts.
Design 2 will require A+23", including the end amounts.
- For 12": 63.36+23"= 96.36", including the end amounts.
- For 10": 53.08+23"= 66.08", including the end amounts.
Calculation of the size of the pin
To find the size of the pin, we must first find how much force is acting on it when it is most stressed. In this case, it is when we are cutting thru the 1"x10" metal.
Since the arm is not accelerating upwards, we can do a statics calculation, and assume the sum of all the forces is zero. So: -31.5T+400T+P=0 Solving for P, we get P=368.5T.
Now, we must use this to find the necessary cross sectional area of the pin to prevent it from warping.
- At each side, where the pin goes thru the pin holders, a force of P/2 is applied to it via the fulcrum supports. This means that there is a shear force of P/2, or 184.25T acting on the pin.
- The allowable shear for A36 steel is 7.2TSI.
- To calculate the radius of the pin, we must set the product of the cross sectional area (A) and the allowawble shear (S) equal to the shear force (P/2). or, AxS=P/2
- We can replace A with PixR^2, since the cross sectional area is a circle. So PixR^2xS=P/2. Solving for R, we get R=Root[(P/2)/Pi/S]
- Plugging it all in, we get R=Root[184.25T/3.14/7.2TSI]=2.86"
- To find the diameter of the pin, we simply multiply Rx2. so D=5.71
Now that's a big pin!