Gas Holder: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(image text added) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_holder Gas Holder] | *Wikipedia: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_holder Gas Holder] | ||
*The Telegraph: [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/energy/oilandgas/10473071/Gasometers-a-brief-history.html "Gasometers: a brief history"] | *The Telegraph: [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/energy/oilandgas/10473071/Gasometers-a-brief-history.html "Gasometers: a brief history"] | ||
[[Category:Energy]] | |||
[[Category:Biofuel]] | |||
Revision as of 19:33, 16 March 2016

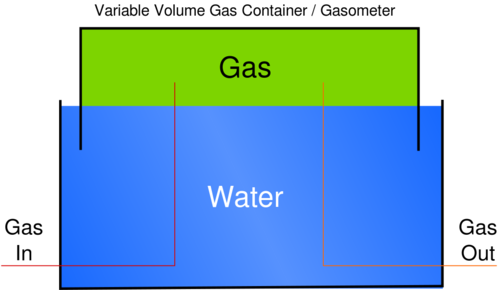
Gas holder with an external fixed frame. Water provides a seal. The whole tank floats in a circular water reservoir, held up by the roughly constant pressure of a varying volume of gas. The pressure is determined by the weight of the structure, and the water providing the seal for the gas within the moving walls. Besides storing the gas, the tank's design serves to establish the pressure of the gas system.
Traditional gas holder. May be used for:
- storage of biogas
- storage of pyrolysis gas
- holding CO2-rich off-gas from combustion (after purification with biofilter) for subsequent use in a greenhouse or in the open field
Links
- Wikipedia: Gas Holder
- The Telegraph: "Gasometers: a brief history"