Eco-Industrial Park: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→Links: +link) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
* [http://www.indigodev.com/AEIP_HB.html "Agro-eco-industrial parks (AEIP)"] (Ernest Lowe), chapter taken from: | * [http://www.indigodev.com/AEIP_HB.html "Agro-eco-industrial parks (AEIP)"] (Ernest Lowe), chapter taken from: | ||
* (older, ca. 2001) Handbook: [http://www.indigodev.com/Handbook.html "Eco-Industrial Park Handbook for Asian Developing Countries" (Ernest Lowe)] | * (older, ca. 2001) Handbook: [http://www.indigodev.com/Handbook.html "Eco-Industrial Park Handbook for Asian Developing Countries" (Ernest Lowe)] | ||
* also from Indigo Development: [http://www.indigodev.com/Defining_EIP.html "An Eco-Industrial Park definition for the Circular Economy"] | |||
[[Category:Housing and construction]] | [[Category:Housing and construction]] | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 23 April 2016
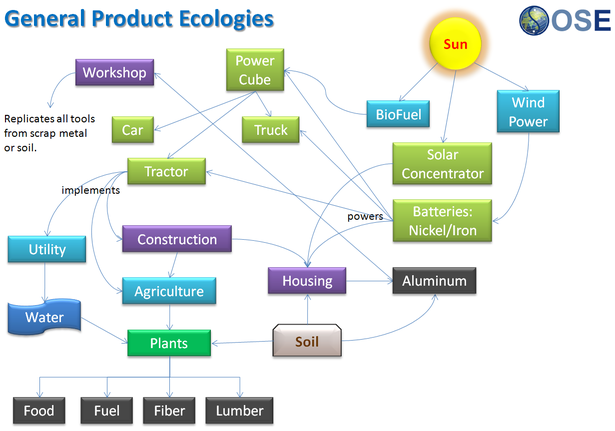
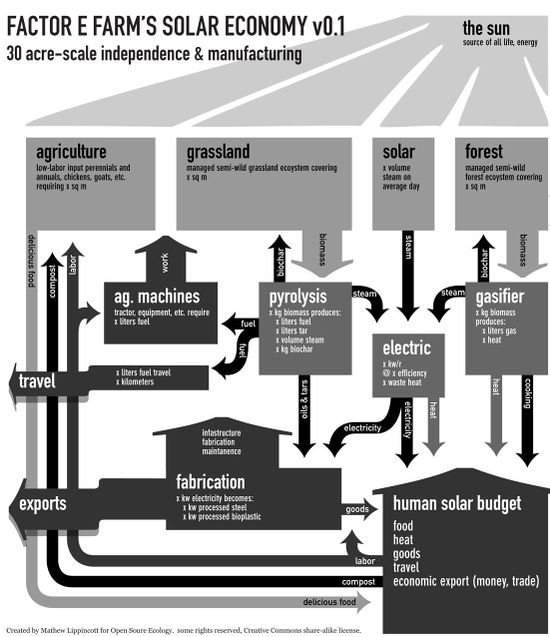
In an Eco-Industrial Park, the use of energy and materials is optimized in such a way that the output of one process is the input into another ("industrial ecosystem"). These arrangements may result in cost savings and waste reduction. The design of the industrial infrastructure attempts to maximize economic and environmental efficiencies. When there is a strong agricultural component, the name Agro-Eco-Industrial Park is sometimes used.
Benefits of eco-industrial parks include:
- monetary benefits to companies (lower production costs / bargain prices, lower energy consumption, less transportation, less waste)
- environmental benefits (less demand on natural resources, less waste in all forms, transportation via pipes instead of trucks)
- societal benefits (jobs, cheap heating, better air quality, better health)
System Design
Design options include site design, park infrastructure, individual facilities, and shared support services. System components include natural systems (e.g. solar, wind, biomass, water resources etc.), energy (e.g. steam), material flows (e.g. co-locating brewery + mushroom farm + pig farm), water flows (different grades of water, e.g. processed/used water), management and support services (e.g. training center, cafeteria, day care center, offices, transportation logistics).
Possible Tenants
The following list was excerpted with modifications from this page, which contains a lot of specific examples and business models. Tenants on an agro-eco-industrial estate may include:
1. Suppliers of equipment, energy, materials, and services to farmers (field equipment, equipment for monitoring of nutrients, co-generation of energy for food processing, biomass by-products, ethanol fermentation, bioenergy crops, integrated pest management services, consulting and training firms, agricultural extension agencies,...)
2. Food processing and distribution firms (distribution center for fruits and vegetables, community supported agriculture, dairy processing, meat/fish/poultry processing)
3. Firms utilizing by-products from any part of the system (energy generators, manufacturers using biomass by-products, ethanol/methane, animal feed processors, greenhouses and aquaculture ponds, composting yard)
4. Intensive food production located in or near an agro-estate (landscaping, greenhouses and aquaculture ponds, integrated brewery, etc.)
5. Other potential recruitment targets (manufacturers using primary biomaterials such as kenaf, hemp, or bamboo, etc.)
Agro-Eco-Industrial Park as the core of a farming community
A rationally designed farming community may have an eco-industrial park as its center. The surrounding farms would be suppliers of raw materials such as biomass. The core park would would be the central hub with processing facilities and other specialized services.
Related pages on this wiki
Links
- "Agro-eco-industrial parks (AEIP)" (Ernest Lowe), chapter taken from:
- (older, ca. 2001) Handbook: "Eco-Industrial Park Handbook for Asian Developing Countries" (Ernest Lowe)
- also from Indigo Development: "An Eco-Industrial Park definition for the Circular Economy"