ISO to USB: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
= Alternative way for console= | |||
You can install the .iso file to a usb using just one command from the Terminal: | You can install the .iso file to a usb using just one command from the Terminal: | ||
*sudo dd if=[iso file] of=[destination device] | *sudo dd if=[iso file] of=[destination device] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Example: | Example: | ||
* sudo dd if=/media/Downdloads/ubuntu-16.04.1-2017.02.10v2-desktop-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb1 | * sudo dd if=/media/Downdloads/ubuntu-16.04.1-2017.02.10v2-desktop-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb1 | ||
=Unetbootin= | |||
[[Unetbootin]] did not work either. | |||
=Links= | =Links= | ||
*[[OSE Linux]] | *[[OSE Linux]] | ||
Revision as of 02:06, 1 March 2017
- Instructions from [1] for Ubuntu Linux are shown here
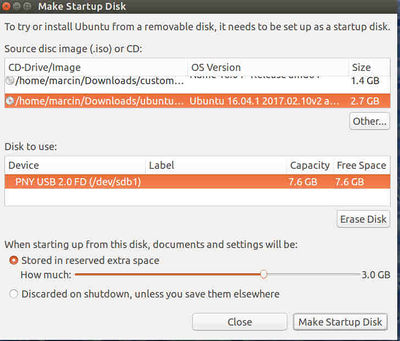
- Use Startup Disk Creator to make a bootabl USB disk from an ISO File.
- If USB disk is not formatted, use Disks utility to format it. I formatted an 8GB disk to ext4, which is linux compatible only.
- Screenshots:
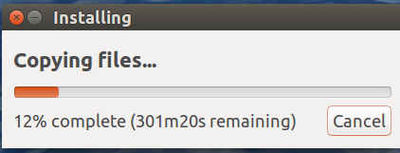
Everything looked ok until this point:
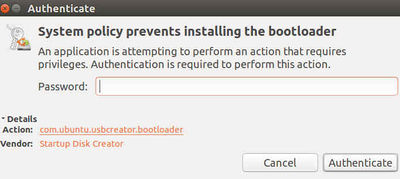
After I typed in my root password, I got an error message that the bootloader failed to install.
I tried running the USB anyway. Got to the boot choices screen, selected to boot from USB, but the new system did not load. Got a blank screen, nothing further happened.
Alternative way for console
You can install the .iso file to a usb using just one command from the Terminal:
- sudo dd if=[iso file] of=[destination device]
where "iso file" is the source .iso file, and "destination device" is the file that was attached to the USB for example /dev/sdc1. If you do not know the device file, you can check it with the command "dmesg".
Example:
- sudo dd if=/media/Downdloads/ubuntu-16.04.1-2017.02.10v2-desktop-amd64.iso of=/dev/sdb1
Unetbootin
Unetbootin did not work either.