Microfluidics: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "500px|thumb|right|Microfluidic Chip Analytical devices can be produced at very low cost from simple materials. Applications are vast revolutionary, ...") |
m (categorized) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* [http://www.rsc.org/Publishing/ChemTech/Volume/2008/01/Shrinky-Dink_microfluidics.asp Shrinky Dink® microfluidics] - academic paper [http://shrink.eng.uci.edu/papers/2008_Grimes.pdf here] | * [http://www.rsc.org/Publishing/ChemTech/Volume/2008/01/Shrinky-Dink_microfluidics.asp Shrinky Dink® microfluidics] - academic paper [http://shrink.eng.uci.edu/papers/2008_Grimes.pdf here] | ||
* Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfluidics Microfluidics] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lab_on_a_chip Lab-on-a-chip] | * Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microfluidics Microfluidics] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lab_on_a_chip Lab-on-a-chip] | ||
[[Category:Health]] | |||
Revision as of 00:38, 6 February 2011
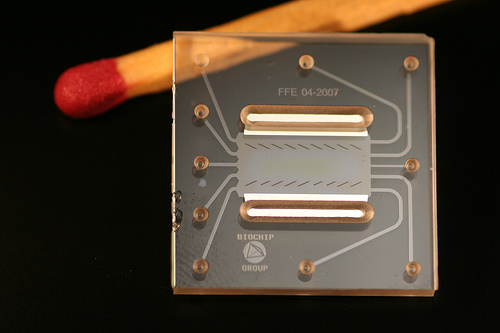
Analytical devices can be produced at very low cost from simple materials. Applications are vast revolutionary, and include medical tests, environmental sensing, agriculture, soil science and many more. Microfluidics refers to a set of technologies that control the flow of minute amounts of liquids or gases—typically measured in nano- and picoliters — in a miniaturized system. With these "chips", room-sized diagnostic testing equipment can be shrunk down to the size of a postage stamp.
Materials Used
blotter paper, regular paper, wax paper, shrinky-dink, transparency film, cotton thread, sewing needles,
Applications
- medicine (immediate testing), genetic research
- agriculture and soil science
- environmental sensing, toxins, pathogens
George Whitesides, MIT
In his legendary career in chemistry, George Whitesides has been a pioneer in microfabrication and nanoscale self-assembly. Now, he's fabbing a diagnostic lab on a chip.
Further Reading
- Disposable microfluidic devices created using regular wax paper
- Shrinky Dink® microfluidics - academic paper here
- Wikipedia: Microfluidics and Lab-on-a-chip