Melt Blown Plastic: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
#Near-sonic air flow | #Near-sonic air flow | ||
#Hot air generation | #Hot air generation | ||
=SME Search= | |||
As a first step - contact researchers in the field for rapid learning on the technology. | |||
=Specifications= | |||
#Melt blowing produces 3 micron- size fibers. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/melt-blowing] | |||
=Machines= | =Machines= | ||
Revision as of 23:18, 23 March 2020
Basics
- A Process for Manufacturing Nonwoven Fabric of a very fine nature
- Used mainly for filters, but also has many other applications
- Not to be confused with Blow Molding
- Uses fine nozzles for plastic which are surrounded by high velocity air to essentially atomise it
- Melt-blown plastic is a material for making N95 masks, or HEPA filters as well.
- Similar Processes are used for Fiberglass, Basalt Fiber...And Cotton Candy, although this is typically done with a linear, rather than radial output (see the patent section)
Patents
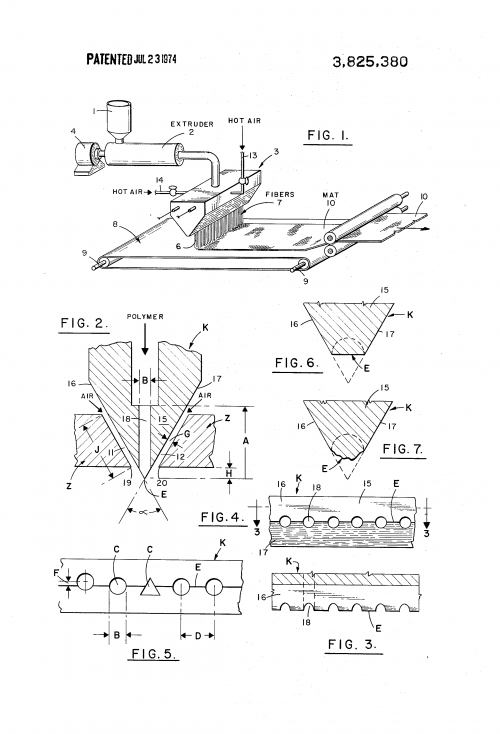
- Melt-blown plastic, original Exxon patent - [1]
Feasibility Study
What level of technology is required to produce the machine?
- Precision die with small holes
- Near-sonic air flow
- Hot air generation
SME Search
As a first step - contact researchers in the field for rapid learning on the technology.
Specifications
- Melt blowing produces 3 micron- size fibers. [2]