Drive mechanism selection: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Linear motion= | =Linear motion= | ||
Linear motion is motion in a straight line. It is usually achieved by converting rotational motion to linear motion - such is the case for belt drives, | Linear motion is motion in a straight line. It is usually achieved by converting rotational motion to linear motion - such is the case for belt drives, ball screws, etc. but not for linear motors. | ||
To achieve motion linear motion, consider the following solutions in relation to the factors that are relevant to your application. | To achieve motion linear motion, consider the following solutions in relation to the factors that are relevant to your application. | ||
Revision as of 09:17, 24 May 2021
Linear motion
Linear motion is motion in a straight line. It is usually achieved by converting rotational motion to linear motion - such is the case for belt drives, ball screws, etc. but not for linear motors.
To achieve motion linear motion, consider the following solutions in relation to the factors that are relevant to your application.
| Application factors | Belt drives | Chain drives | Rack/Gear and pinion | Roller Pinon/rack | Leadscrews | Ballscrews | Linear Motors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Low | Low | Low-High | High | Low | Low-High | High |
| Backlash/Vibration | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero |
| Acceleration | Medium | Low | High | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Speed | Medium | Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Load capacity | Low | Medium | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| Length | Shorter | Shorter | Long | Long | Shorter | Shorter | Moderate |
| High wear and short life | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Long life | A consideration | A consideration | Long life |
| Maintenance | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none |
| Noise level | Medium | High | Medium | Low | High | Medium | Low |
| Dust and dirt emissions | High | High | Moderate | Low to none | Moderate | Moderate | Low to none |
Rotary motion
For applications with heavy loads and slow turning, such as rotation of a crane, slewing bearings are suitable.
For applications with several, or several thousand, rotations per minute, rolling bearings are suitable.
Rolling bearings
Main article: Bearing selection
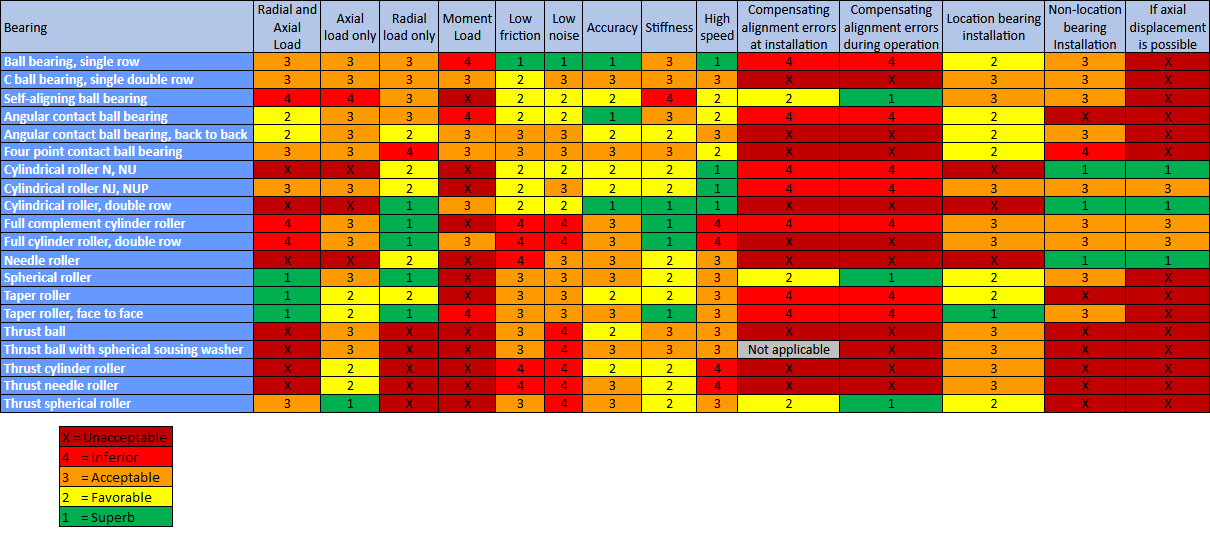
The table below shows level of suitability of different bearing types for different conditions.
This section is based on a table found in SKF handbooks and on the Engineers Edge website.
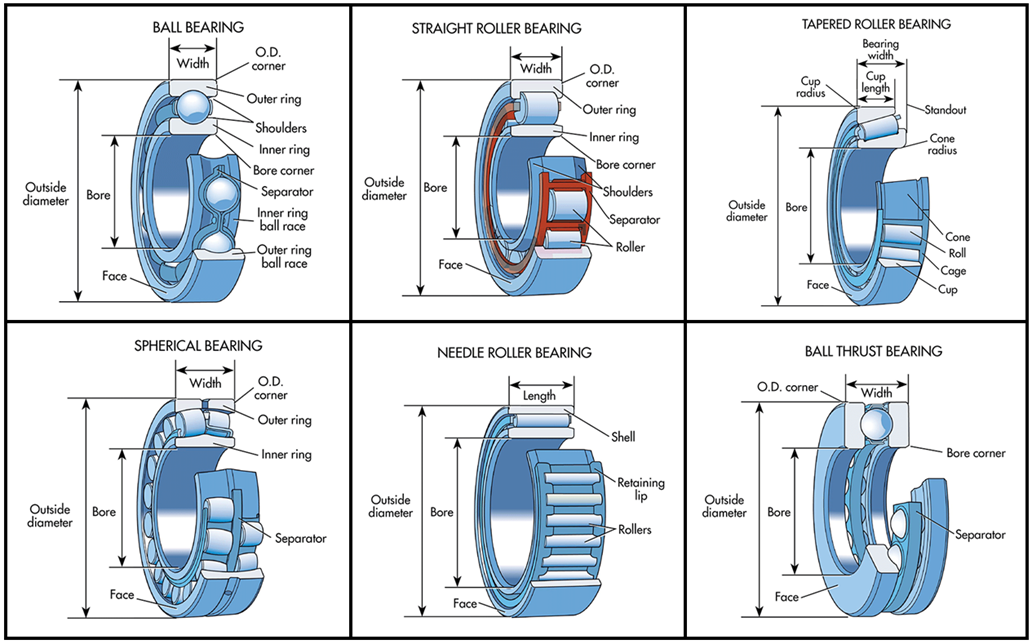 Image source: https://www.machinedesign.com/learning-resources/whats-the-difference-between/article/21831901/whats-the-difference-between-bearings
Image source: https://www.machinedesign.com/learning-resources/whats-the-difference-between/article/21831901/whats-the-difference-between-bearings