Motor selection: Difference between revisions
| Line 255: | Line 255: | ||
N: Speed | N: Speed | ||
==Step X.X) Calculate Input Power== | ==Step X.X) Calculate Input Power== | ||
Revision as of 10:52, 7 August 2022
THIS INSTRUCTION IS NOT COMPLETED AND NOT READY FOR USE.
The selection of motor includes the following steps (which are described in further detail on this page):
Step 1) Select the motor type
Step 1.1) Identify application and desired motor attributes
Use the table below to select one of four motor types that correspond to your application and the desired motor attributes.
| Attribute | Stepper motors | Servo motors | Brushed DC motors | Brushless DC motors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area of use | Positioning by incremental steps. Low speed and low acceleration. | High speed and high acceleration. | Continuous rotation at high RPMs and constant torque across the motor’s speed range. | Continuous rotation at high RPMs and constant torque across the motor’s speed range. |
| Suitable applications |
• floppy disk drives • flatbed scanners • computer printers • plotters • slot machines • image scanners • compact disc drives • intelligent lighting • camera lenses • CNC machines and 3D printers • Textile machines • Printing presses • Medical imaging machinery • Small robotics • Welding equipment |
• Automated manufacturing • Robotics • CNC machinery • Telescopes • Elevators • Conveyor Belts • Camera Auto Focus • Solar Tracking System • Metal Cutting & Metal Forming Machines • Antenna Positioning • Printing Presses/Printers • Automatic Door Openers |
• Home appliances • toys • electrical propulsion • cranes • paper machines • steel rolling mills |
• Drones • Electric cars • Washing machines • Air Conditioners • Cordless tools • Computer • Fans • Disk drives |
| Accuracy | High | High (achieved by adding encoder to the system.) | None | Varies |
| Torque at low speeds | High | High | - | - |
| Torque at high speeds | Low (can lose up to 80% torque at high speeds) | High | - | - |
| Cost efficiency | High | Lower (uses rare-earth magnets, may need encoder or gearbox.) | High | Lower |
| Lifespan | Long life | Shorter | Shorter | - |
| Size | Compact | High output power relative to size and weight. | Compact | - |
| Load capacity | Low (might skip steps at high loads.) | High | - | - |
| Efficiency | Low (constantly draw maximum current independent of load.) | High (80–90% efficiency.) | High | - |
| Ease of use | • Easily controlled (can be controlled with micro controllers such as the ATmega chips that are readily available on Arduino development boards.) Can stall or lose position without a control loop. | • Higher maintenance if gearbox and encoder is included.
• Limited range of motion; positional rotation servos are limited to 180 degrees of motion. • Works in AC or DC drive. |
• Torque to Speed Ratio can be altered (exclusive to brushed motors.)
• High maintenance requirements due to easily worn out as a result of continuous moving contact. |
• Some brushless motors are difficult to control and require a specialized regulator.
• Low maintenance. |
Step 1.2) Confirm Load characteristic
Look at the Load characteristics type in the table below and identify which Load characteristic corresponds to your application. Then confirm that the motor type you selected from the table above corresponds to the identified Duty cycle.
| Load characteristic | Application examples |
|---|---|
| Torque that is constant | conveyors, extruders, bulk material conveyors, extruders, positive displacement pumps |
| Torque that changes abruptly | elevators, compactors, punch presses, saws, and batch conveyors |
| Torque that change gradually over time | centrifugal pumps, fans, blowers, compressors with unloaders |
Step 1.3) Confirm Duty cycle type
Look at the Duty cycle types in the table below and identify which Duty cycle corresponds to your application. Then confirm that the motor type you selected from the table above corresponds to the identified Duty cycle.
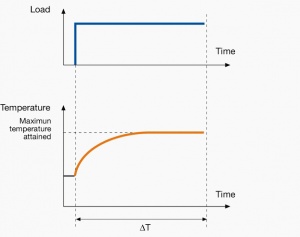
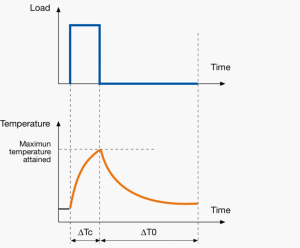
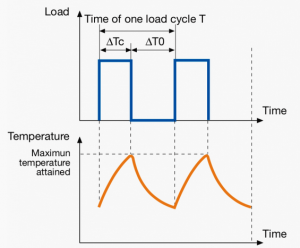
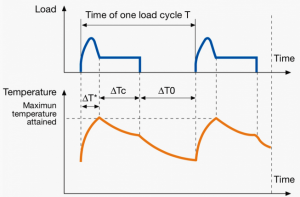
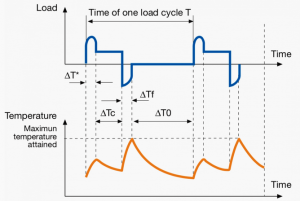
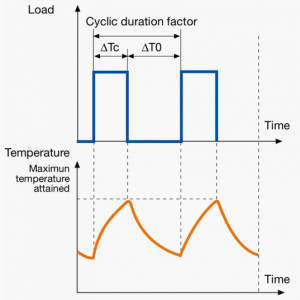
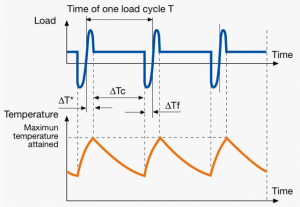
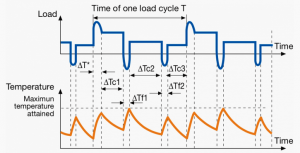
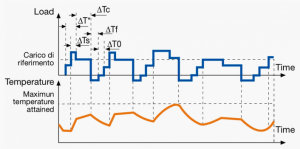
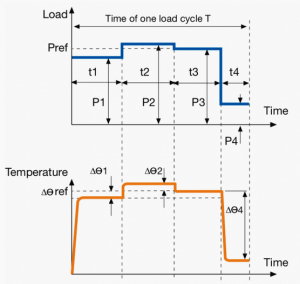
A duty cycle type specifies the sequence and time duration the motor operation including Starting, Running with no load, Running with a full load, Electric braking, and Rest. How the operations affect motor temperature determines whether increased cooling is needed or whether another motor is suitable.
In the table below, the term "Load" refers to the electrical current (measured in Ampere) that is supplied. This electrical load, or current, corresponds to the mechanical load, or torque, measured in Newton meter. More torque requires more current. The terms "Temperature equilibrium" or "Steady state temperature" simply mean temperature that remains constant.
Step 2) Select Drive mechanism
Select a type of Drive mechanism that is suitable to your application.
| Application factors | Belt drives | Chain drives | Rack/Gear and pinion | Roller Pinon/rack | Leadscrews | Ballscrews | Linear Motors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Low | Low | Low-High | High | Low | Low-High | High |
| Backlash/Vibration | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero |
| Acceleration | Medium | Low | High | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Speed | Medium | Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Load capacity | Low | Medium | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| Length | Shorter | Shorter | Long | Long | Shorter | Shorter | Moderate |
| High wear and short life | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Long life | A consideration | A consideration | Long life |
| Maintenance | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none |
| Noise level | Medium | High | Medium | Low | High | Medium | Low |
| Dust and dirt emissions | High | High | Moderate | Low to none | Moderate | Moderate | Low to none |
Step 3) Identify the available power supply
The standard for Mains Electricity (also called Utility Power or Wall Power) in most countries is typically around 100 or 200 Volts for residential voltage and around 400 for three-phase voltage.
Lists of Mains Electricity standards by country is readily available on the internet.
Servo motors are available for these voltages: 100, 200 and 400 Volts.
Step 4) Calculate needed Power, Torque, and Speed
Now that have selected the Motor type, we must select the power of the motor. If the motor is under-dimensioned, it won't be powerful enough to perform its intended task. If the motor is over-dimensioned, it's price and operation cost will be too high.
Step 4.1) Calculate Current, Voltage, and Resistance
Power, Torque, and Speed can be calculated partly from Current, Voltage, and Resistance. Ohm’s law states that
I = V / R
where
I – current, measured in amperes (A);
V – applied voltage, measured in volts (V);
R – resistance, measured in ohms (Ω).
This formula can also for example be used to calculate the Resistance of your motor by measuring the consumed current and applied voltage:
R = I * V
From the formula it can be read that the Current can be controlled through applied Voltage for a given resistance of a motor (the resistance of the coil).
Step 4.1 Calculate Power
P = T * ((2 * pi * N) / 60)
where
P: Power
T: Torque
N: Speed
Step X.X) Calculate Input Power
The consumed electrical power of the motor is defined by the following formula:
Pin = I * V
where Pin – input power, measured in watts (W);
I – current, measured in amperes (A);
V – applied voltage, measured in volts (V).
Step X.X) Calculate Output Power
Output mechanical power of the motor can be calculated by using the following formula: Pout = τ * ω where Pout – output power, measured in watts (W); τ – torque, measured in Newton meters (N•m); ω – angular speed, measured in radians per second (rad/s).
Step X.X) Calculate Efficiency
Efficiency of the motor is calculated as mechanical output power divided by electrical input power:
E = Pout / Pin
If the motor has 100% efficiency all electrical power is converted to mechanical energy. However such motors do not exist. Even precision made small industrial motors such as one we use as a generator in generator kit have maximum efficiency of 50-60%. Motors built from our kits usually have maximum efficiency of about 15% (see Experiments section on how we estimated this). Don’t be disappointed with 15% maximum efficiency.
Step 4.2) Calculate the Torque
τ = (I * V * E) / ω
Step 4.3 Calculate Speed
Angular speed can be calculated with the following formula if the rotational speed of the motor in RPM (revolutions per minute) is known:
ω = RPM * 2π / 60
where
ω – angular speed, measured in radians per second (rad/s);
rpm – rotational speed in revolutions per minute;
π – mathematical constant pi (3.14).
60 – number of seconds in a minute.
Step 5) Determine the application's Motion Profile
Select motor
One of the most important things about choosing a new motor is one whose speed torque curve exceed that of the load torque curve.
Step 6) Select gears
Main article: Gear for detailed description and gear calculation.
Gears, just like spurs and sprockets, are mechanisms used to transfer energy by rotary motion.
They can all be used to change the following:
- Speed of rotation
- Direction of rotation
- Amount of torque available to do work