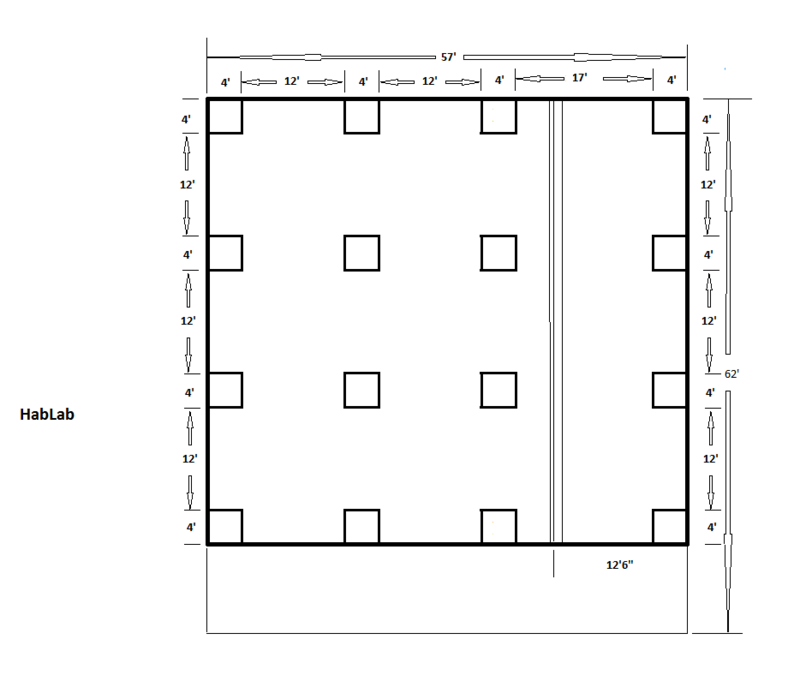
Hab Lab
The need for all-weather housing to shelter year-round members of the community, located where summers can be unpleasantly hot and winters unpleasantly cold, can be met with superinsulated designs. Here we will examine some possible options and our progress in bring them into existence. Planning tools, instructions, modifications, etc. will be included.
The Design Page is a good place to see what has been offered and to post any of your own great ideas. More ideas are great for everybody!
Survey & Design
The area on the property for the first group habitation was on a noticeable slope. OSE staff members worked with a home-made water level to take measurements over a 100' square area.
How to make a water level: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nAcT_1T25LM
Ideas submitted for this project are located on the Hab Lab Design Gallery page.
Building Orientation
Planning
Kitchen/Bath Water
Utility/Storage Area
Heating
Source Material
http://dnr.mo.gov/pubs/pub781.pdf
Site Preparation
The Hab Lab is designed to be supported by columns built of CEB (Compressed Earth Block)which are constructed on a reinforced concrete pad. Due to the slope of our site, we designed a lowered section which requires a low retaining wall. Included here are instructions for preparing the site with adequate footings.
Here is a picture with a preliminary excavation layout for the column pad sites and the retaining wall in the Hab Lab.
- When you are laying out the excavation site, be sure to add 5' in each direction for the excavator to work to.
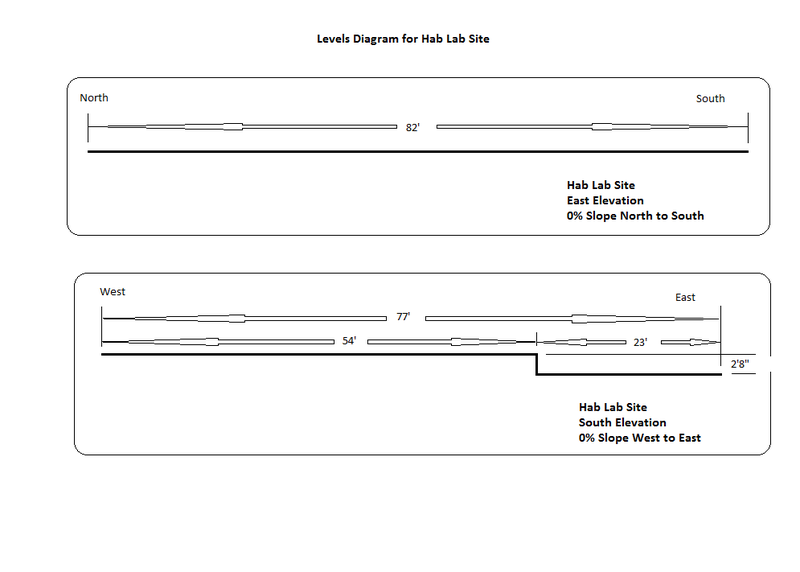
This levels diagram is from our theoretical measurements - we actually wound up with a 2' drop, not a 2'8" drop. That will make only a minor difference in raising the building - changing the size of the retaining wall and removing one or two CEB's at the top of the lower columns to maintain the planned roof pitch.
Foundations & Column Slabs
Laying out the Hab Lab excavation site to be square
Collect equipment and supplies needed
- Blueprint of site plan
- (2) 100’ Measuring tapes
- 4 3-4’ stakes
- Hammer
- Bright spray paint
Steps for Staking out the excavation site.
- Choose a spot approximately 5 feet to the North and 5 feet to the West of the area to be excavated.
- Pound in a stake and spray paint the top foot or two of it.
- Measure due East a distance 10’ longer than the foundation width (total 67’).
- Place and paint another stake.
- Calculate a distance 10’ longer than the foundation length (total 62’).
- Calculate the diagonal measurement of the excavation site [Length(squared) x Width(squared) = Diagonal(squared)] (91'4").
- Measure due South from the Northwest stake the distance calculated in step 6.
- Set the second tape measure on the Northeast stake and measure the diagonal calculated in step 7 going Southwest.
- Set your third stake where the two measured lengths meet each other.
- Paint the stake.
- Measure due South from the Northeast stake the distance calculated in step 6.
- Set the second tape measure on the Northwest stake and measure the diagonal calculated in step 7 going Southeast.
- Set your fouth stake where the two measured lengths meet each other.
- Paint the stake.
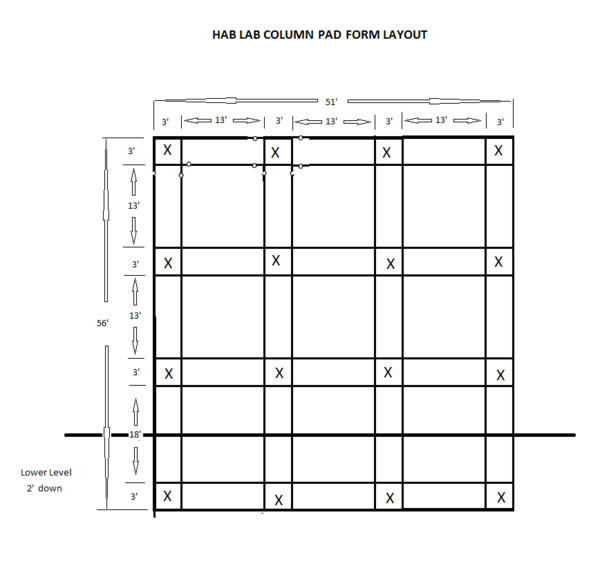
- With the site leveled, the foundation holes for the column slabs must be laid out.
- After excavation, the stone fill for the foundation goes into the holes.
- At the same time, the 6" stone floor foundation is spread.
Concrete forms and rebar reinforcing assemblies
These can be built well ahead of need whenever volunteers are available.
- You could set up an assembly line effect to do them all at once with several people working together.
- An individual might do one unit at a time.
- An individual might do all the wood cutting at one time, another do all the rebar cutting at another time, another do all the rebar bending at another time.
- A couple of people might work together to get some wooden forms assembled once the pieces are cut, another time, a couple of people might work together to get some rebar assemblies welded.
The following step-by-step instructions are provided for building the forms and the reinforcing rebar assemblies.
[Assembly sheet for column pad forms]
[Rebar plan for column footings]
Laying out the locations for the forms on top of the foundation stone
After doing this in real life - More comments on that to come!
Here is the layout diagram to place the column forms.
Setting the column pad forms
Collect equipment and supplies needed
- Supplies
- 16 Pre-built column pad forms
- 80 form stakes (we used 2"x2"x18" wooden stakes)
- Equipment
- Heavy Hammer(s)
- 4'spirit Level
- Water level
- tape measure
- Steps to place Column Pad forms.
- Choose one pad site along the East edge to be the reference pad. (The center of the East side works well.)
- Set a pre-built column pad form in place under the string lines with the inside of the forms under the strings.
- Drive two form stakes next to the outside of one side and one on each of the other three sides. They will need to sit deep enough that the tops of the stakes will be level with (or lower than) the top of the form.
- Level the form.
- Screw one of the stakes (on the side with two) to the side of the form so that the form sits 1/2" above the gravel level with the top of the stake level with (or lower than) the top of the form.
- Use the spirit level to set this side of the form level and screw it in position.
- Use the spirit level to set the opposite side of the form at the same level.
- Check the level on the other two sides and screw them in place.
- Use the water level to set another form in the East row of columns to be level with the reference pad.
- Repeat steps 2 through 5 to complete setting the forms in that row.
- Use the water level to set the level of the center form in the next row of columns (to the West) as a reference form for that row. It should be about 1-1/2" lower than the reference pad in the previous row of columns.
- Repeat steps 2 to 7 two more times.
- Repeat steps 2 to 5 again.
Preparing Column Pad Forms for Reinforced Concrete
Collect equipment and supplies needed
- Supplies
- 16 Pre-built column pad rebar assemblies
- 64 rebar chairs
- Equipment
- Rake(s)
- shovel
- tape measure
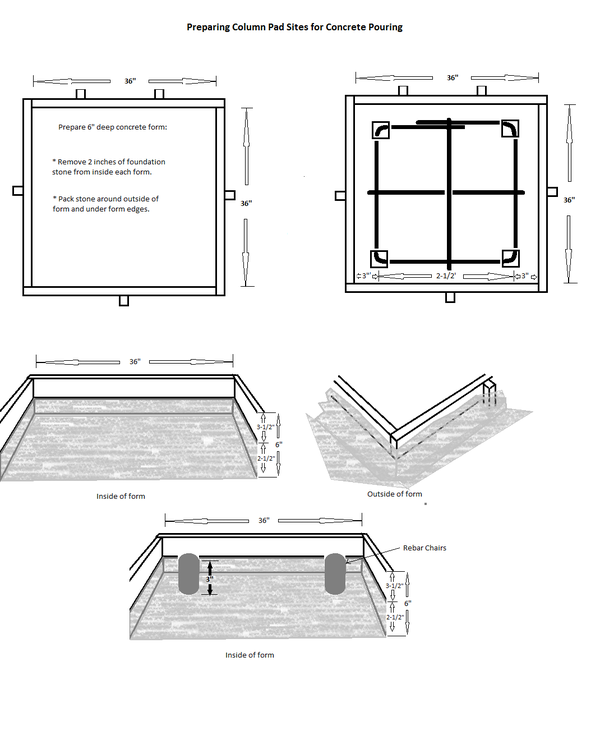
- Use a rake and shovel to remove about 2" of stone from the inside of the form. (until is 6" deep)
- Pack removed stone around outside of forms to create a fully enclosed 6" deep form.
- Use one prebuilt column pad rebar assembly for each column pad site.
- Center the rebar assembly with 3” gap between assembly and form wall on every side.
- Set rebar chairs under corners of prebuilt column pad rebar assemblies.-Put a stone or some gravel under the chairs if needed to center the rebar so it will sit at about the middle of the finished slab (3" off the floor of the form).
Concrete Work
Insulated Outside Wall Support Slabs
We are planning to put concrete the full 3' width of the Column Support Pads all the way around the outside of the building. They will be 3-1/2" (2x4 lumber size) deep and will support the two CEB walls that enclose the hay bale insulation.
Narrow Wall Support Slabs
We will support and stabilize the interior CEB walls with a 12" wide x 3-1/2" deep concrete slab.
Kitchen and Bath Areas
The Kitchen and Bath Floor Areas both have a potential for receiving noticeable amounts of water. We consider it advisable to pave them both with concrete and include a central drain.