Drive mechanism selection
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Linear motion
To achieve motion in a straight line, consider the following solutions in relation to the factors that are relevant to your application.
| Application factors | Belt drives | Chain drives | Rack/Gear and pinion | Roller Pinon/rack | Leadscrews | Ballscrews | Linear Motors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Low | Low | Low-High | High | Low | Low-High | High |
| Backlash/Vibration | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero | A consideration | A consideration | Near Zero |
| Acceleration | Medium | Low | High | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Speed | Medium | Low | Medium | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Load capacity | Low | Medium | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| Length | Shorter | Shorter | Long | Long | Shorter | Shorter | Moderate |
| High wear and short life | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Long life | A consideration | A consideration | Long life |
| Maintenance | A consideration | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none | A consideration | A consideration | Low to none |
| Noise level | Medium | High | Medium | Low | High | Medium | Low |
| Dust and dirt emissions | High | High | Moderate | Low to none | Moderate | Moderate | Low to none |
Rotary motion
For applications with heavy loads and slow turning, such as rotation of a crane, slewing bearings are suitable.
For applications with several, or several thousand, rotations per minute, rolling bearings are suitable.
Rolling bearings
Main article: Bearing selection
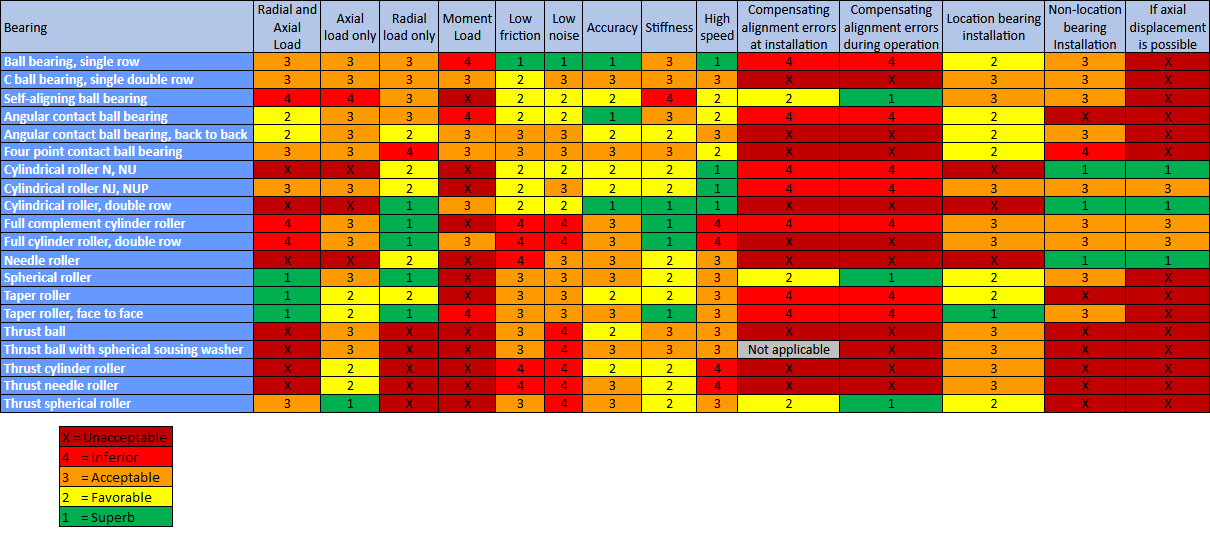
The table below shows level of suitability of different bearing types for different conditions.
This section is based on a table found in SKF handbooks and on the Engineers Edge website.
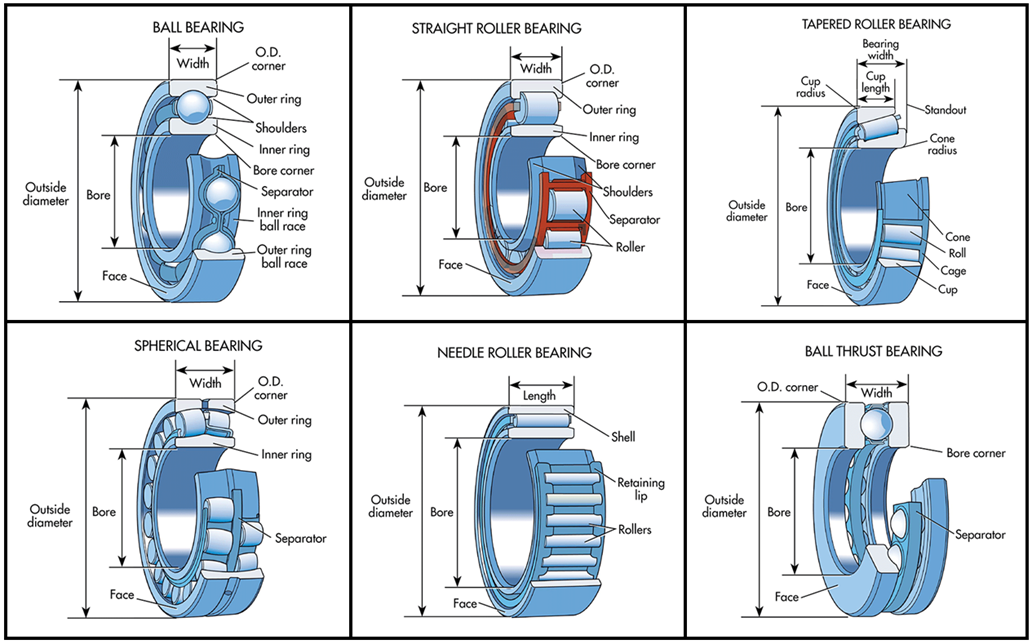 Image source: https://www.machinedesign.com/learning-resources/whats-the-difference-between/article/21831901/whats-the-difference-between-bearings
Image source: https://www.machinedesign.com/learning-resources/whats-the-difference-between/article/21831901/whats-the-difference-between-bearings