Coupling Selection
A coupling can be selected by following the six steps described in this article:
Step 1) Select Coupling Type
Step 2) Determine the Service Factor
Step 3) Calculate Torque
Step 4) Calculate the Minimum Coupling Rating
Step 5) Note shaft sizes
Step 6) Select Coupling from a product catalog
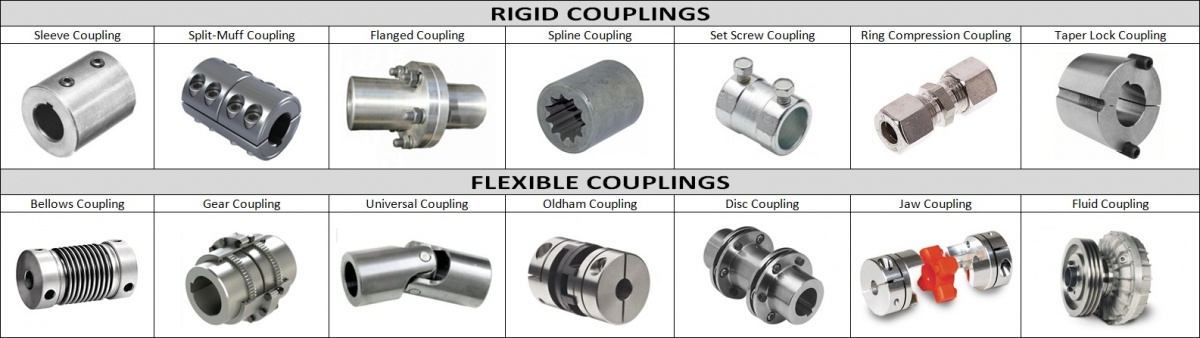
Step 1) Select Coupling Type
There are two main categories of coupling types:
- Rigid couplings
- Flexible couplings
Rigid couplings possess the following attributes:
- Suitable for high torque
- Suitable for high Speed
- Suitable for high Bearing Loads
- Inexpensive
Flexible couplings possess the following attributes:
- Dampens vibrations
- Compensates for Angular Misalignment
- Compensates for Parallel Misalignment
- Suitable for Axial Motion
The table below shows to which degree different couplings possess certain attributes and their respective suitability with regards to specific conditions.
| Zero Backlash |
Constant Velocity |
Torsional Rigidity |
Torque | Bearing Loads |
Inertia | Dampening | Angular Misalignment |
Parallel Misalignment |
Axial Motion |
Maintenance Required |
Electrically Isolating |
Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Six Beam Coupling, Aluminum | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | Low- Mid |
Mid | High- Mid |
Mid | Mid | No | No | Mid |
| Six Beam Coupling, Stainless | Yes | Yes | Mid | Mid | High- Mid |
High | Low- Mid |
High- Mid |
Mid | Mid | No | No | High |
| Four Beam Coupling, Aluminum | Yes | Yes | Low | Low | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | No | No | Low- Mid |
| Four Beam Coupling, Stainless | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | High | Low- Mid |
High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | No | No | High |
| Bellows Coupling, Short | Yes | Yes | High | High | Mid | Low | Low | Low- Mid |
Low | Low- Mid |
No | No | High |
| Bellows Coupling, Long | Yes | Yes | High- Mid |
High | Low- Mid |
Low | Low | High- Mid |
Mid | High- Mid |
No | No | High |
| Controlflex Coupling, Double Disc | Yes | Yes | Low | Low- Mid |
Low | Low | Low | Mid | High- Mid |
High- Mid |
Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
| Controlflex Coupling, Single Disc | Yes | Yes | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Mid | High- Mid |
High- Mid |
Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
| Double Disc Coupling | Yes | Yes | High- Mid |
High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Mid | Low- Mid |
Mid | No | Available | High- Mid |
| Single Disc Coupling | Yes | Yes | High- Mid |
High- Mid |
Mid | Low | Low | Low- Mid |
0 | Low- Mid |
No | No | High- Mid |
| Jaw Coupling, 85 Shore A Blue | Yes | Yes | Low | Low | Low | Low- Mid |
High | Low- Mid |
Low | High | Yes | Yes | Mid |
| Jaw Coupling, 92 Shore A Yellow | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Mid | Low- Mid |
Low | High | Yes | Yes | Mid |
| Jaw Coupling, 98 Shore A Red | Yes | Yes | Mid | High | High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | High | Yes | Yes | Mid |
| Oldham Coupling, Aluminum, Acetal Disk | Yes | Yes | High- Mid |
Mid | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
| Oldham Coupling, Aluminum, Nylon Disk | No | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Low | Low- Mid |
Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
| Oldham Coupling, Aluminum, PEEK Disk | Yes | Yes | High | Mid | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | High |
| Oldham Coupling, Stainless Steel, Acetal Disk | Yes | Yes | High- Mid |
Mid | Low | High- Mid |
Low | Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | High |
| Oldham Coupling, Stainless Steel, Nylon Disk | No | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | High |
| Oldham Coupling, Stainless Steel, PEEK Di | Yes | Yes | High | Mid | Low | High- Mid |
Low | Low | High | Low | Yes | Yes | High |
| Rigid Coupling, Aluminum | Yes | Yes | High | High | High | Mid | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | No | No | Low |
| Slit Coupling, Short Clamp | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Mid | High | High- Mid |
High | No | No | Mid |
| Slit Coupling, Long Clamp | Yes | Yes | Mid | Low- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Mid | High | High- Mid |
High | No | No | Mid |
| Slit Coupling, Short Set | Yes | Yes | Low- Mid |
High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Mid | High | Low | Low | No | No | Mid |
| Slit Coupling, Long Set | Yes | Yes | Mid | High- Mid |
Low- Mid |
Low | Mid | High | High- Mid |
High | No | No | Mid |
Step 2) Determine the Service Factor
In a Service Factor table such as the one below, find the application in which the coupling shall be used and note the corresponding SF-value.
| Application | SF |
|---|---|
| AERATOR | 2,0 |
| AGITATORS | |
| Vertical and Horizontal Screw, Propeller, | 1,0 |
| BARGE HAUL PULLER | 1,5 |
| BLOWERS | |
| Centrifugal | 1,0 |
| Lobe or Vane | 1,25 |
| CAR DUMPERS | 2,5 |
| CAR PULLERS | 1,5 |
| CLARIFIER or CLASSIFIER | 1,0 |
| COMPRESSORS | |
| Centrifugal | 1,0 |
| Rotary, Lobe or Vane | 1,25 |
| Rotary, Screw | 1,0 |
| With Flywheel and Gear between Compressor and Prime Mover |
|
| 1 Cylinder, single acting | 3,0 |
| 1 Cylinder, double acting | 3,0 |
| 2 Cylinders, single acting | 3,0 |
| 2 Cylinders, double acting | 3,0 |
| 3 Cylinders, single acting | 3,0 |
| 3 Cylinders, double acting | 2,0 |
| 4 or more cylinders, single acting | 1,75 |
| 4 or more cylinders, double acting | 1,75 |
| CONVEYORS | |
| Apron, Assembly, Belt, Chain, Flight, Screw | 1,0 |
| Bucket | 1,25 |
| Live Roll, Shaker and Reciprocating | 3,0 |
| CRANES and HOIST | |
| Main Hoist | 1,75 |
| Skip Hoist | 1,75 |
| Slope | 1,5 |
| Bridge, Travel or Trolley | 1,75 |
| DYNAMOMETER | 1,0 |
| ELEVATORS | |
| Bucket, Centrifugal Discharge | 1,25 |
| Gravity Discharge | 1,25 |
| EXCITER, GENERATOR | 1,0 |
| EXTRUDER, PLASTIC | 1,5 |
| FANS | |
| Centrifugal | 1,0 |
| Cooling Tower | 2,0 |
| Forced Draft-Across the Line start | 1,5 |
| Forced Draft Motor driven thru fluid or electric slip clutch |
1,0 |
| Gas Recirculating | 1,5 |
| Induced Draft with damper control or blade | 1,25 |
| Indcleaneruced Draft without controls | 2,0 |
| FEEDERS | |
| Apron, Belt, Disc, Screw | 1,0 |
| Reciprocating | 2,5 |
| GENERATORS | |
| Even load | 1,0 |
| Hoist or Railway Service | 1,5 |
| Welder Load | 2,0 |
| Hoist or Railway Service | 1,5 |
| Welder Load | 2,0 |
| HAMMERMILL | 1,75 |
| LAUNDRY WASHER or TUMBLER | 2,0 |
| LINE SHAFTS | |
| Any Processing Machinery | 1,5 |
| MACHINE TOOLS | |
| Auxiliary and Traverse Drive | 1,0 |
| Bending Roll, Notching Press, Punch Press, Planer, | 1,75 |
| Plate Reversing Main Drive |
1,5 |
| METAL FORMING MACHINES | |
| Continous Caster | 1,75 |
| Draw Bench Carriage and Main Drive | 2,0 |
| Extruder | 2,0 |
| Farming Machine and Forming Mills | 2,0 |
| Slitters | 1,0 |
| Wire Drawing or Flattening | 1,75 |
| Wire Winder | 1,5 |
| Coilers and Uncoilers | 1,5 |
| MIXERS | |
| Concrete | 1,75 |
| Muller | 1,5 |
| PRESS, PRINTING | 1,5 |
| PUG MILL | 1,75 |
| PULVERIZERS | |
| Hammermill and Hog | 1,75 |
| Roller | 1,5 |
| PUMPS | 1,5 |
| Boiler Feed | 1 |
| Centrifugal-Constant Speed | 1,25 |
| - Frequent speed changes under Load | 1,25 |
| Descaling with accumulators | 1,25 |
| Gear, Rotary, or Vane | 1,25 |
| Reciprocating, Plunger Piston | |
| - 1 Cylinder, single or double acting | 3,0 |
| - 2 Cylinders, single acting | 2,0 |
| - 2 Cylinders, double acting | 1,75 |
| - 3 or more cylinders | 1,5 |
| Screw Pump, Progressing Cavity | 1,25 |
| Vacuum Pump | 1,25 |
| SCREENS | |
| Air Washing | 1,0 |
| Grizzly | 2,0 |
| Rotary Coal or Sand | 1,5 |
| Vibrating | 2,5 |
| Water | 1,0 |
| STEERING GEAR | 1,0 |
| STOKER | 1,0 |
| TIRE SHREDDER | 1,5 |
| TUMBLING BARREL | 1,75 |
| WINCH, MANEUVERING | |
| Dredge, Marine | 1,5 |
| WINDLASS | 1,5 |
| WOODWORKING MACHINERY | 1,0 |
Step 3) Calculate Torque
Look up the values for the motor (that should have been selected prior to coupling selection, see Motor selection) and input those values into the formula below. Then note the calculated value for the torque.
T = (P * 9550) / RPM
where
T = Motor Torque (measured in Nm)
P = Motor Effect (measured in kW)
RPM = Revolutions per minute
Step 4) Calculate the Minimum Coupling Rating
TKN = T * SF
where
TKN = Minimum Coupling Rating (measured in Nm)
T = Motor torque (calculated in Step 3.)
SF = Service Factor (determined in Step 2.)
Step 5) Note shaft sizes
Step 5.1) Note motor shaft diameter
Note the shaft diameter of the motor (driving) that has been selected prior to coupling selection.
Step 5.2) Note drive shaft diameter
Note the shaft diameter on the side that is driven.
Step 6) Select Coupling from a product catalog
Use a product catalog to identify a coupling corresponding to the following:
- Coupling type (selected in Step 1.)
- Minimum Coupling Rating (calculated in Step 4.)
- Driving shaft diameter (noted in Step 5.1)
- Driven shaft diameter (noted in Step 5.2)
The values of the selected coupling shall be equal to or higher than those determined in the steps listed above.