Functional Block Diagram F.4 Global Village Facilities
Diagrams
(Note: This page is new, diagram is in work)
Notes
(1) Put numbered notes aside from description here
Description
Facilities includes land, buildings, and outdoor modifications/additions. Generally items permanently attached to the ground are included as facilities. A device such as a wind turbine could also be counted as equipment, so the distinction is somewhat arbitrary. The important thing is to only list a given item in one place, and track the flows going in and out of it.
Total land required is based on the total number of people, what percentage of their needs the land will support, the productivity and geology of the land, and land needed for individual buildings and other facilities. An allowance for future expansion may be included. Not everything can be built at once, so time phased use of land should be considered. For example, an area may be used for an outdoor garden at first, and later converted to a more productive greenhouse. Mixed or multiple use land should also be considered, but the component area needs can be summed up by type.
For comparison, United States average values are 3 acres of farmland + 1.5 acres forest and resource land + 0.5 acres homestead = 5 acres/person total required. An optimized village design should use much less.
Facilities Functions
F4.1 Prepare Land for Use - This includes clearing, leveling, earth-moving, ditching, digging (for wells and posts), tilling, harrowing, extracting materials, adding materials.
F4.2 Provide Water - For drinking, watering plants, washing
F4.3 Provide Stationary Energy - This includes electric power, mechanical power (ie windmill direct drive), and process heating
F4.4 Grow Living Things - This includes seeding, transplanting, watering, fertilizing, harvesting, animal husbandry.
F4.5 Provide Human Shelter - This includes provide living volume, protection from water, wind, earth movement, animals, and insects, provide fresh air, and temperature control
F4.6 Provide Workspace - For indoor machines, assembly areas
F4.7 Provide Storage - For equipment, food, water, chemicals, raw materials, and wastes (recycling or final waste)
F4.8 Provide Human Comforts - This includes furniture, lighting, soundproofing, entertainment, and communications.
Facilities Types
Facility types carry out the above functions. A partial list of facility types and initial estimates for sizing are:
Managed Forest - Land primarily used for growing timber, but with other shared uses when possible. Standard home construction uses about 6 board-feet wood per square foot of floor area. Median US home size is 750 square feet per person. Total US timberland is 750 million acres, with 1 trillion board feet of commercial sawtimber volume (which is only 11% of total tree volume). Annual growth is 2.8% of volume, of which 100% can be sawtimber volume as smaller trees become large enough to use. Converting to per acre values gives 1333 board feet per acre, adding 38 board feet per year. These are highly variable numbers for any given piece of land. For example, mature (100 year old) forest can have over 60,000 board feet of sawtimber per acre, or 50 times the average.
If we assume 2% growth and 1% maintenance after initial construction, we need 135 board feet per person/year or 3.5 acres per person to be sustainable. This does not count initial construction. This seems high, so there are several ways to reduce the number. Sawtimber only counts the parts of trees over 10 inches in diameter and 8-12 feet long, ie useful for commercial loggers. You can use more of the tree, or smaller trees. Average land is not "fully stocked", meaning having enough trees to fully use the light that falls on it. So selecting fully stocked land or planting additional trees can increase the growth. The vast majority of forest land is not fertilized like field crops. Trees respond to fertilizer like any other plant. Finally, a house can be built using less wood.
Crop Fields - Land primarily used for growing field crops. For estimating purposes the following chart can be used and compared to the calorie needs for the number of people. Field crops require a lot of land area, mechanization to grow efficiently, and is highly competitive in the developed world. So strong consideration to alternatives to having them be the primary internal food source should be made. Having said that, each person needs 876,000 kCal per year. Allowing for spoilage and waste, assume 1 million kCal harvested. The field crops in the chart below average 6 million kCal per acre, so if they provided all food calories (which is not nutritionally sound), then 1/6 acre per person would be required. The difference between that number and the 3 acres farmland per person in the US is due to variable land productivity, feeding some crops to animals, and not using 100% of land area for crops.
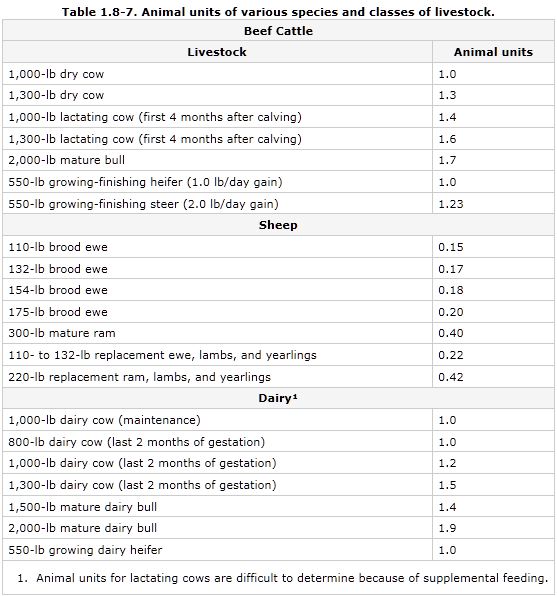
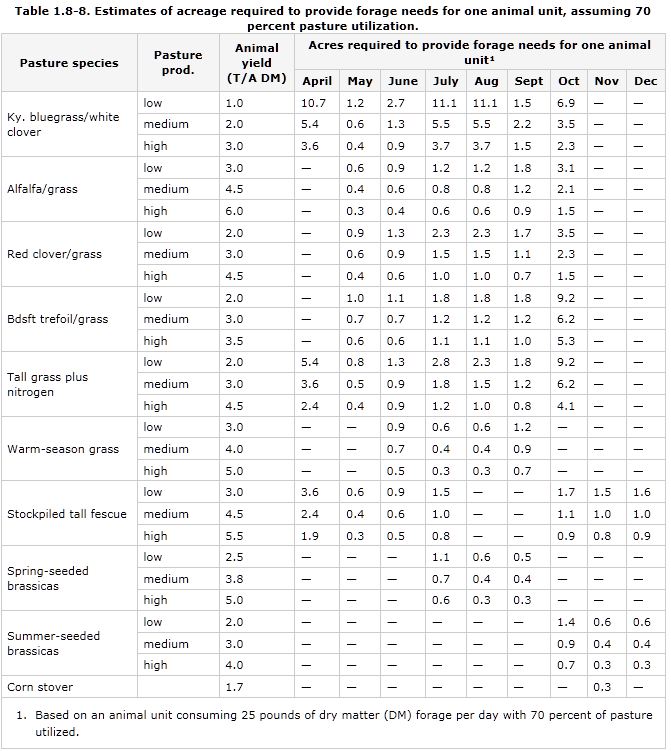
Pastures - Land used for grazing livestock or growing feed for them. The USDA Cooperative Extension service lists tables of acreage required in terms of "Animal Units" equal to one 1,000 lb cow, and land productivity in units of tons/year of dry matter, which is highly variable. The species listed are very limited (cows and sheep), so consider other animal food sources (chicken, fish, etc). Turning plant matter into meat is always inefficient, so consider minimizing meat use if diet preference and nutrition allows.
Livestock Enclosures - Buildings and outdoor structures to contain and protect livestock.
Gardens - Land used for growing specialty plants on a smaller scale than fields
Orchards - Land used for growing trees that provide fruit
Greenhouses - Buildings for growing plants in a controlled environment
Quarries - Land used to extract soil, subsoil, rock, or specialty minerals
Residences - Buildings for people to live in when not working.
Storage Buildings - This includes various subtypes:
- Tool and Equipment Storage
- Parts and materials inventory
- Food storage
Workshop Buildings
- Metal Shop
- Wood Shop
Infrastructure - This includes various subtypes:
- Drainage and irrigation channels
- Water wells, outdoor ponds and dams
- Roads and parking
- Utility lines
- Power generation
Links to Related Diagrams
Higher Level: Functional Block Diagram F.0 Global Village System
Inputs: (To be done)
Outputs: (To be done)
Controls: (To be done)
Mechanisms: (To be done)