Steam Engine Build/Piston Head
Main > Energy > Steam Engine
Steam Engine Build Instructions
Description
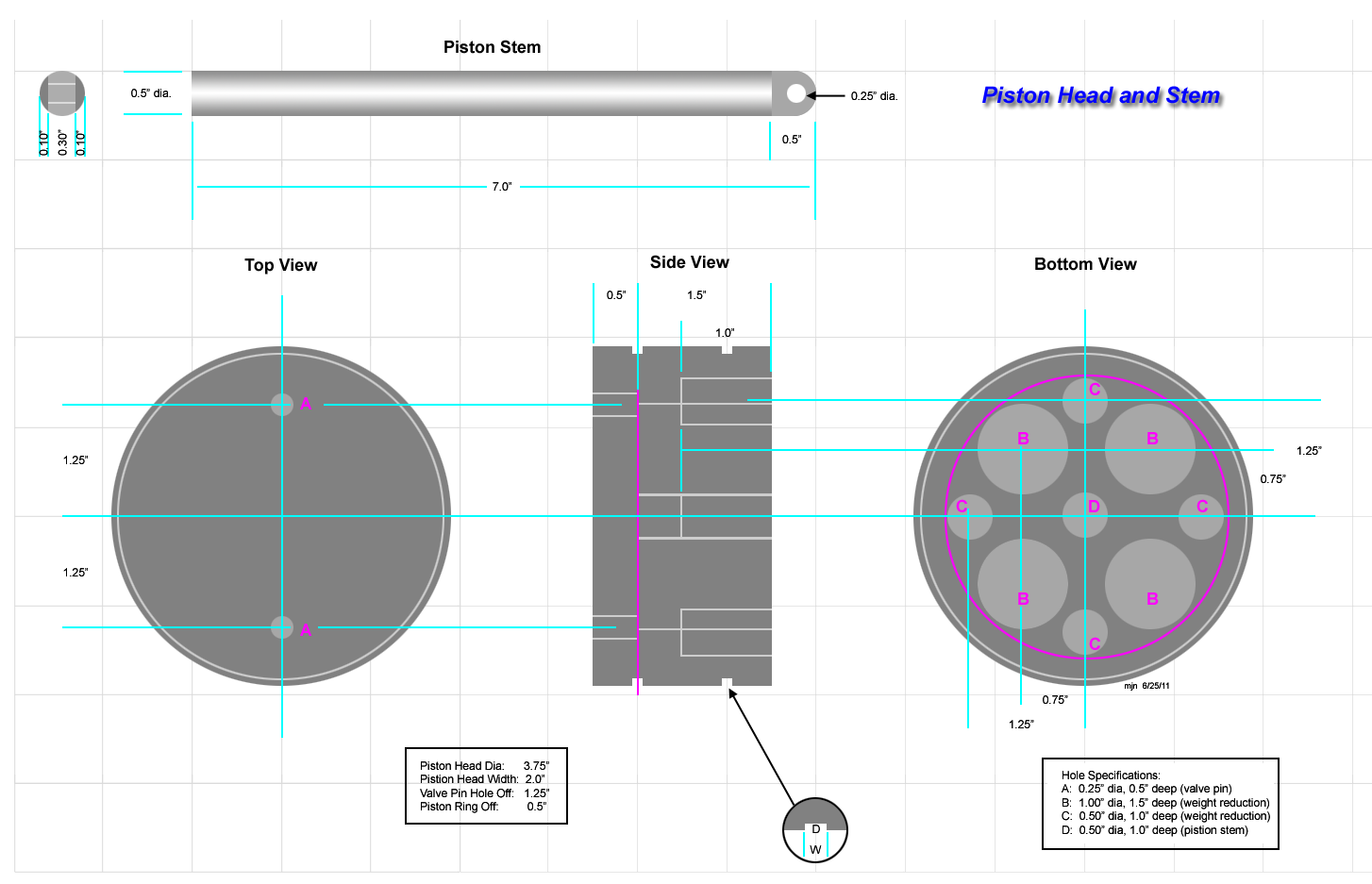
The piston head converts energy stored in steam pressure to motion. As steam in the cylinder expands, it pushes against the piston head, which is connected to a connecting rod, and then to a crank on a crankshaft. The crankshaft converts linear motion in rotary motion. The piston is built from two pieces: the piston head and the piston stem, welded together. On the face of the piston head are two threaded holes that receive the bump valve pins (see Steam Engine Build/Bump Valve Pin). A series of holes are bored in the piston head from the bottom to reduce weight. Two rectangular grooves are turned into the piston face to receive piston rings.
CAD
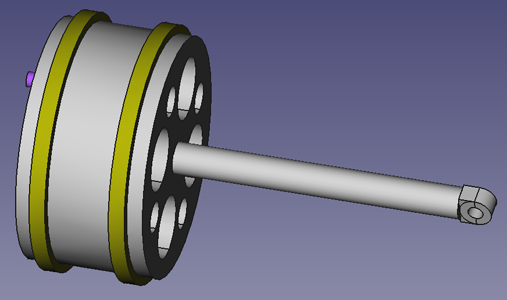
Full Piston Assembly with Rings and Pins
Drawing
Instructions
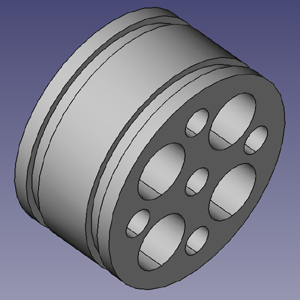
Piston Head
- Mount a 4.0" cast iron rod in a lathe.
- Reduce the outside diameter to 3.75".
- Cut two piston ring grooves at 0.5" (center) offset from the top and bottom of piston (width and depth are TBD).
- Cut off the piston head to a length of 2.0"
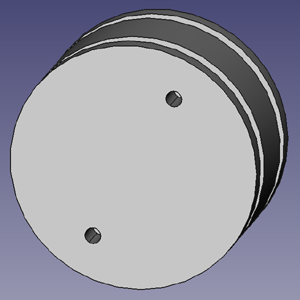
- On the top of the piston head, drill two 0.25" holes, 1.25" from the center (Holes A in drawing).
- From the bottom of the piston head, bore the following holes:
- 4 Holes B: 1.0" dia to a depth of 1.5" (weight reduction).
- 4 Holes C: 0.5" dia to a depth of 1.0" (weight reduction).
- 1 Hole D: 0.5" dia to a depth of 1.0" (piston stem receiving hole).
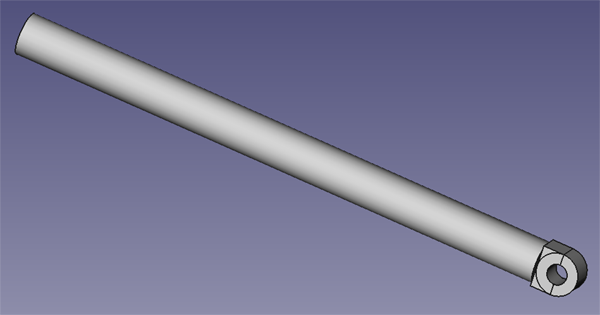
Piston Stem
- Use 0.5" steel rod stock.
- Cut off 0.2" on either side, 0.5" in from end.
- Round off the end (0.5" dia.)
- Drill a 0.25" dia hole
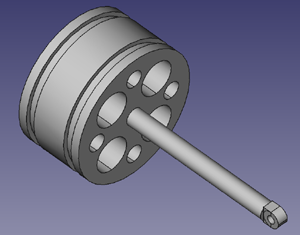
Assembly
- Insert completed piston stem into piston stem receiving hole (Hole D).
- Weld around to secure it.