Power Supply Basics: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=Art of Electronics Notes= | =Art of Electronics Notes= | ||
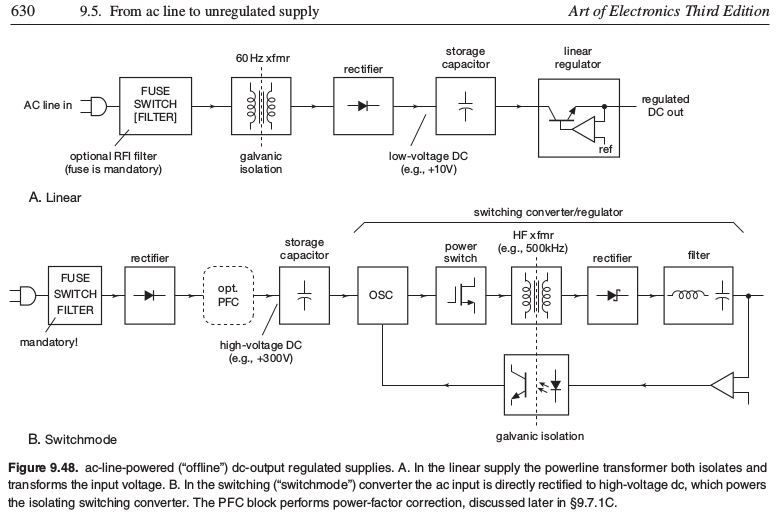
[[File:switchmode.png]] | |||
Switch mode supply requires: | Switch mode supply requires: | ||
*Ch 9 p 630 - Switch and fuse needed at AC side | *Ch 9 p 630 - Switch and fuse needed at AC side | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
*Transient suppressor - a variable resistor - metal oxide varistor - shorts to ground for any high voltage spikes. It's like a high voltage, bidirectional zener diode. | *Transient suppressor - a variable resistor - metal oxide varistor - shorts to ground for any high voltage spikes. It's like a high voltage, bidirectional zener diode. | ||
*Insulate line-voltage connections to prevent shock hazard | *Insulate line-voltage connections to prevent shock hazard | ||
*Storage capacitor - prevents ripple - | |||
Revision as of 23:08, 12 April 2019
- Half wave rectifier, full wave rectifier, and full wave bridge rectifiers - [1]
- Power Supply Cookbook PDF - [2]
- Horowitz and Hill, The Art of Electronics, Ch. 9 - [3]
Art of Electronics Notes
- Ch 9 p 630 - Switch and fuse needed at AC side
- Also, a filter at AC side filters possible RF from power line, using a line voltage capacitor
- Transient suppressor - a variable resistor - metal oxide varistor - shorts to ground for any high voltage spikes. It's like a high voltage, bidirectional zener diode.
- Insulate line-voltage connections to prevent shock hazard
- Storage capacitor - prevents ripple -