Embodied Energy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Genearal - record for time, energy, and optimization of workflow on GVCS and related projects | Genearal - record for time, energy, and optimization of workflow on GVCS and related projects | ||
=Foundations= | |||
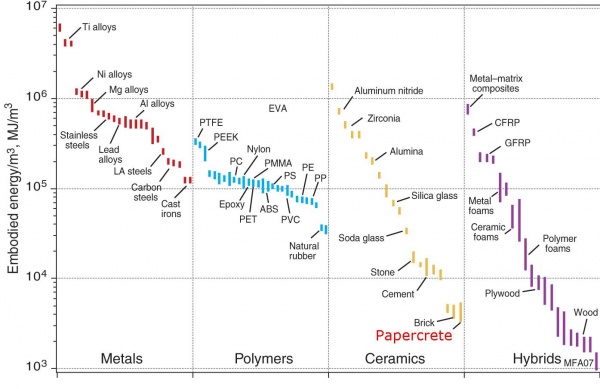
How much energy does it take to produce materials? https://papercrete.wordpress.com/2011/09/06/embodied-energy/ | |||
[[File:embodied1.jpg|600px]] | |||
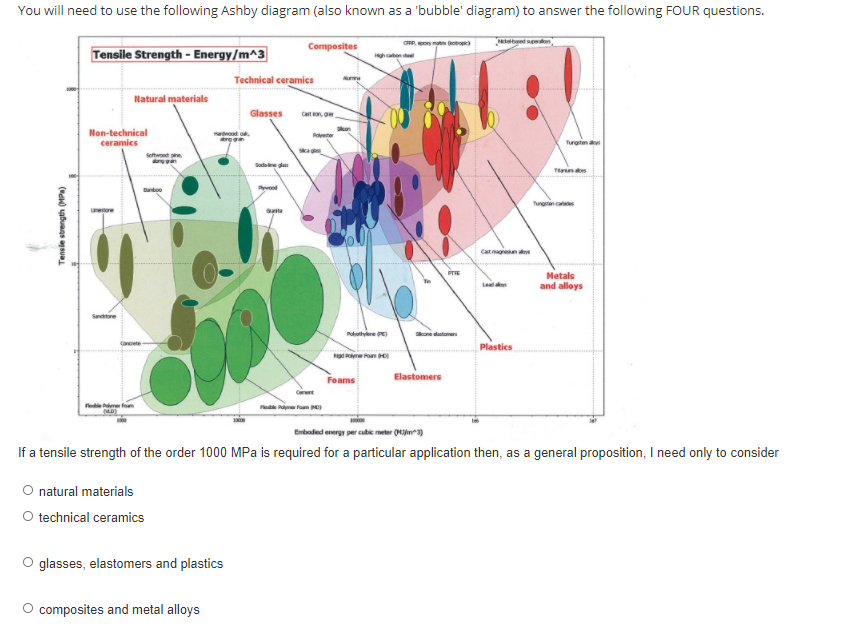
See Ashby Diagram - strength vs embodied energy. [[Image Search]] it for similar. | |||
[[File:embodied2.png]] | |||
=Wikipedia= | =Wikipedia= | ||
Latest revision as of 15:06, 25 May 2022
Genearal - record for time, energy, and optimization of workflow on GVCS and related projects
Foundations
How much energy does it take to produce materials? https://papercrete.wordpress.com/2011/09/06/embodied-energy/
See Ashby Diagram - strength vs embodied energy. Image Search it for similar.
Wikipedia
- Table of common materials - [1]
- Common building materials - [2]
- Geopolymer - says 48% higher embodied energy than Portland? [3]
Materials
- Wood - 8.5MJ/kg
Specific - Energy of Production
- 14-17 kWhr are used for producing 1 kg of PLA plastic 3D printing filament! See excellent industrial ecology paper, p. S84 at [4]
- Note that this is the same amount of energy as that required to smelt 1 kg of aluminum from aluminum oxide!
Enthalpy
- Energy Density - [5]