Prebiotics: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(inserted image) |
(inserted section: Related Pages on this Wiki) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*inulin (sources: [[Jerusalem Artichoke]], chicory, dandelions, onions, etc.) | *inulin (sources: [[Jerusalem Artichoke]], chicory, dandelions, onions, etc.) | ||
*ginger | *ginger | ||
* | |||
==Related Pages on this Wiki== | |||
*[[Fermentation]] | |||
*[[Silage]] | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 5 May 2016

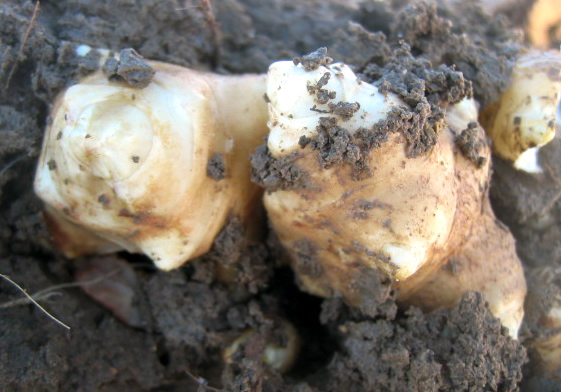
The Jerusalem Artichoke contains high levels of inulin in their roots.
From Wikipedia: "Prebiotics are substances that induce the growth or activity of microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) that contribute to the well-being of their host. The most common example is in the gastrointestinal tract, where prebiotics can alter the composition of organisms in the gut microbiome. As the role of the microbiome is better understood, prebiotics as well as probiotics can be useful tools for the management of microbial populations in livestock. The maintenance of a beneficial microbiome may result in benefits to animal health, less stress, faster growth, less need for antibiotics, less odor, and even potentially better composting."
Sources
- inulin (sources: Jerusalem Artichoke, chicory, dandelions, onions, etc.)
- ginger