PV Panel Grounding: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→More) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=More= | =More= | ||
*{{check}}Solar PV standards and certifications - [https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introduction-solar-pv-standards-certifications-asif/]. Class II means frames grounded, no system ground. | *{{check}}Solar PV standards and certifications - [https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introduction-solar-pv-standards-certifications-asif/]. Class II means frames grounded, no system ground. | ||
[[File:pvstandards.png| | [[File:pvstandards.png|200px]] | ||
*{{Check}} Paper on PV grounding, 1984. Fire safety and personnel safety are typically tradeoffs? [https://zenodo.org/record/1282867/files/article.pdf] | *{{Check}} Paper on PV grounding, 1984. Fire safety and personnel safety are typically tradeoffs? [https://zenodo.org/record/1282867/files/article.pdf] | ||
**Solidly grounded means neutral is connected to earth electrode. [https://www.google.com/search?sxsrf=ALeKk026QG9BbsZl0rNsBS9KmerMgczY_w%3A1602863734253&source=hp&ei=dsKJX6q8DJDYsAXHkpG4Cw&q=what+does+solidly+grounded+mean&btnK=Google+Search&oq=how+to+configure+nvidia+geforce+gtx+1650+super+on+linux+mint&gs_lcp=CgZwc3ktYWIQAzIFCCEQoAEyBQghEKsCMgUIIRCrAjoOCAAQ6gIQtAIQmgEQ5QI6DgguELEDEMcBEKMCEJMCOggILhDHARCvAToLCC4QsQMQxwEQowI6CAgAELEDEIMBOggILhCxAxCDAToFCAAQsQM6AggAOgQIABAKOgYIABAWEB46CAghEBYQHRAeOgcIIRAKEKABUMsQWOmzAWD8tAFoBnAAeACAAeQGiAGhS5IBDTExLjQ3LjMuMi42LTGYAQCgAQGqAQdnd3Mtd2l6sAEG&sclient=psy-ab&ved=0ahUKEwiqz4DcvLnsAhUQLKwKHUdJBLcQ4dUDCAk&uact=5] | **Solidly grounded means neutral is connected to earth electrode. [https://www.google.com/search?sxsrf=ALeKk026QG9BbsZl0rNsBS9KmerMgczY_w%3A1602863734253&source=hp&ei=dsKJX6q8DJDYsAXHkpG4Cw&q=what+does+solidly+grounded+mean&btnK=Google+Search&oq=how+to+configure+nvidia+geforce+gtx+1650+super+on+linux+mint&gs_lcp=CgZwc3ktYWIQAzIFCCEQoAEyBQghEKsCMgUIIRCrAjoOCAAQ6gIQtAIQmgEQ5QI6DgguELEDEMcBEKMCEJMCOggILhDHARCvAToLCC4QsQMQxwEQowI6CAgAELEDEIMBOggILhCxAxCDAToFCAAQsQM6AggAOgQIABAKOgYIABAWEB46CAghEBYQHRAeOgcIIRAKEKABUMsQWOmzAWD8tAFoBnAAeACAAeQGiAGhS5IBDTExLjQ3LjMuMi42LTGYAQCgAQGqAQdnd3Mtd2l6sAEG&sclient=psy-ab&ved=0ahUKEwiqz4DcvLnsAhUQLKwKHUdJBLcQ4dUDCAk&uact=5] | ||
Revision as of 02:01, 16 September 2023
NEC 690 - Covers PV Systems
- 690.41 - Equipment Grounding Conductor requirements [1]
- 690.41(B) also requires ground fault protection except if there are no more than 2 strings (PV source circuits [2])
- Since NEC 2020, ground fault indicator must be readily visible (but not necessarily readily accessible?) [3]
- 690.45 - size of PV equipment grounding conductors - Table 250.122 + no less than 14 ga.
- 690.41(B) also requires ground fault protection except if there are no more than 2 strings (PV source circuits [2])
- 690.9(A) says that we don't need overcurrent device for PV if the wires can handle short current capacity of PV. But good luck trying to convince a code official.
- PV Grounding PDF [4]. Although the NEC does not specifically require all equipment to be certified/listed, many local jurisdictions and many AHJs establish requirements that all equipment be certified/listed because they feel unqualified to examine uncertified/unlisted equipment for safety as the NEC requires.
- Good overview doc. Read it from p. 6 on to understand equipment ground, system ground.
- Additional issue for PV is that in cloudy conditions, if you get a fault, a breaker may not trip because current is too low. For this reason, extra ground fault protection devices may be required.
- Is earth ground of a PV system connected to DC negative, or to AC neutral?
Ground Faults - System Grounding Howto
- Article says that a common ground fault protection device (GFPD) is a fuse to ground - [5]
- NEC Article 690.41 states that grounding for photovoltaic systems includes 2 grounds:
- The first one is system grounding: the PV system with system voltage over 50 volts should be solidly system-grounded. The other one is
the equipment grounding: the exposed non-currentcarrying metal parts of PV module frames, electrical equipment, and conductor enclosures should be grounded [6].
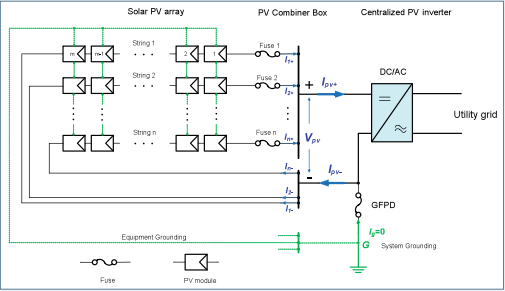
- System Ground Howto: To achieve that, the negative conductor usually is grounded via the GFPD in the PV inverter at point G (see Fig. 1):
More
 Solar PV standards and certifications - [7]. Class II means frames grounded, no system ground.
Solar PV standards and certifications - [7]. Class II means frames grounded, no system ground.
 Paper on PV grounding, 1984. Fire safety and personnel safety are typically tradeoffs? [8]
Paper on PV grounding, 1984. Fire safety and personnel safety are typically tradeoffs? [8]
- Solidly grounded means neutral is connected to earth electrode. [9]
- Class II system had double insulation and equipment ground, but no earth connection.
- Class I has equipment ground and earth connection.
- Insulation failures between current-carrying conductors and the ground are known as ground faults.
 Classic video by Mike Holt. Equipment Grounding + system grounding - Ground and grounding electrode conductor basic with Mike Holt - [10]
Classic video by Mike Holt. Equipment Grounding + system grounding - Ground and grounding electrode conductor basic with Mike Holt - [10]
- Do not earth ground frames with a ground rod like this - [11]
Equipment Grounding
- PV panels should follow electrical grounding conductor sizes - [12]
- Ie, for 30A DC, we need 10 ga ground.
- PV frames must be connected to PV system equipment grounding conductor [13]
- After leaving the PV array, the equipment ground must run together with the power wires. [14]
What Size Grounding Conductor on PV Panels?
- Australia rules - appear to say 6 ga for lightning protection, and 12 ga for frame grounding [15]
- 6 ga USA if 'subject to damage'?