Inverter Design Rationale and Specification: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Tom Griffing (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=Specifications= | =Specifications= | ||
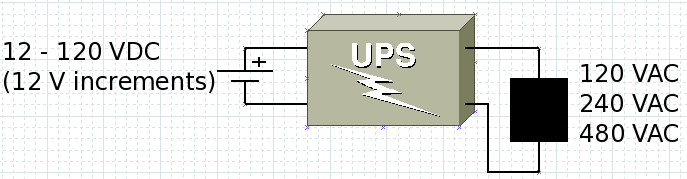
*Input – 12-120V DC | *Input – 12-120V DC using IGBTs that can handle that | ||
*Output - 12-480V AC | *Output - 12-480V AC | ||
*Plug-in transformer modules allow from 1 to 10 amplitude modification | *Plug-in transformer modules allow from 1 to 10 amplitude modification | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*Modular design retains allowance for different gate drivers, such as high frequency power for induction furnace power supplies and other applications | *Modular design retains allowance for different gate drivers, such as high frequency power for induction furnace power supplies and other applications | ||
=Links= | |||
IGBT Sources | |||
*http://www.shaoguang.com.cn/data/sgkj09005.pdf | |||
[[Category:Specifications]] | [[Category:Specifications]] | ||
Revision as of 00:52, 20 January 2012
Design Rationale
Specifications
- Input – 12-120V DC using IGBTs that can handle that
- Output - 12-480V AC
- Plug-in transformer modules allow from 1 to 10 amplitude modification
- Use turnkey, plug-in IGBT module of 2.5 kW continuous, 5 kW peak
- Use turnkey, plug-in gate driver
- Use pure sine wave signal generator
- Stackable up to 10 units for up to 25kW
- Phase cable connects units so power is in phase
Scalability and Modularity Analysis
- Basic unit above provides up to 25kW continuous power
- Plug in IGBT module may be scaled for higher power, up to 250 kW for a stack of 10 inverters.
- Modular design retains allowance for different gate drivers, such as high frequency power for induction furnace power supplies and other applications
Links
IGBT Sources