Rammed Earth: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:CEB2.jpg|540px|thumb|right|Rammed earth at | [[File:CEB2.jpg|540px|thumb|right|Rammed earth buildings at Escuela de Artes Visuales de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, México.]] | ||
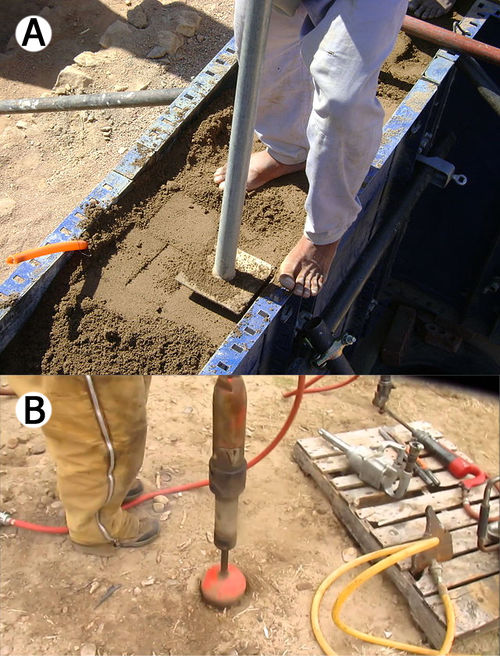
[[File:Tamp RammedEarth.jpg|500px|thumb|right|(A) Picture showing manual ramming of earth in metallic shutters. | [[File:Tamp RammedEarth.jpg|500px|thumb|right|(A) Picture showing manual ramming of earth in metallic shutters. This technique is quite labor intensive (photo taken in Sinai, Egypt). (B) Pneumatic tamper.]] | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rammed_earth Rammed earth] is an ancient building method that has seen a revival in recent years. It produces noncombustible, thermally massive, strong, and durable buildings. However, walls can be labour-intensive to construct without machinery (powered tampers). Structures are susceptible to water damage if not adequately protected or maintained. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rammed_earth Rammed earth] is an ancient building method that has seen a revival in recent years. It produces noncombustible, thermally massive, strong, and durable buildings. However, walls can be labour-intensive to construct without machinery (powered tampers). Structures are susceptible to water damage if not adequately protected or maintained. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Open Source Hardware Needs== | ==Open Source Hardware Needs== | ||
* powered (pneumatic) tamper; this may require an air compressor | |||
* temporary frame, i.e. formwork (usually wood, plywood, steel) | |||
==Related Pages== | ==Related Pages== | ||
* [[Lime]] may be used as a stabilizer, and in fact historically a lot of rammed earth construction has used lime | * [[Lime]] may be used as a stabilizer, and in fact historically a lot of rammed earth construction has used lime | ||
* [[Earthco Megablock]] - not actually rammed earth but somewhat related | * [[Lime]] plaster as an external covering for protection | ||
* [[Earthco Megablock]] - not actually rammed earth but a somewhat related technique | |||
* Reinforcement: [[hemp]] fibers, [[bamboo]], steel | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* Nice overview - [http://webs.ashlandctc.org/jnapora/hum-faculty/syllabi/trad.html] | * Nice overview - [http://webs.ashlandctc.org/jnapora/hum-faculty/syllabi/trad.html] | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 20 July 2016
Rammed earth is an ancient building method that has seen a revival in recent years. It produces noncombustible, thermally massive, strong, and durable buildings. However, walls can be labour-intensive to construct without machinery (powered tampers). Structures are susceptible to water damage if not adequately protected or maintained.
Building a rammed-earth wall involves compressing a damp mixture of earth that has suitable proportions of sand, gravel and clay (sometimes with an added stabilizer) into an externally supported frame or mould. The construction of an entire wall begins with a temporary frame (formwork).
Open Source Hardware Needs
- powered (pneumatic) tamper; this may require an air compressor
- temporary frame, i.e. formwork (usually wood, plywood, steel)
Related Pages
- Lime may be used as a stabilizer, and in fact historically a lot of rammed earth construction has used lime
- Lime plaster as an external covering for protection
- Earthco Megablock - not actually rammed earth but a somewhat related technique
- Reinforcement: hemp fibers, bamboo, steel
Links
- Nice overview - [1]