Hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a strain of the Cannabis sativa plant species that is grown specifically for the industrial uses of its derived products. Consumption of hemp does not lead to intoxication (the THC levels are too low.)
Hemp can be used to make thousands of different products found in different industries such as material, construction, nutrition, energy, etc. For details, see Uses below.
Uses
| Hemp stalk materials | Stalk cross section | Plant anatomy and uses |
|---|---|---|
The sortable table below shows examples of products that can be made from hemp.
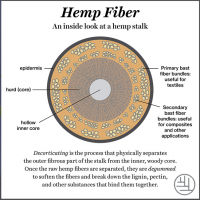
All products below are made from one of these four materials from the hemp plant:
- Seeds
- Hurd (the woody interior off the stalk)
- Bast fiber
- Microfiber
A hemp decorticator can be used to separate the hemp plant into the four materials.
| Hemp material | Product | Product category | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber | bioplastic | Material | Can be used for 3D printing filament, autoparts, biocomposites, etc. a small percentage of hemp was used in what appears to be a composite - rather than bioplastic - car body (70% fiber, of which fiber 10% was hemp, and 30% binder) - [1] |
| Fiber | paper | Material | Including writing paper and toilet paper. |
| Fiber | textile | Material | Used for clothes, bags, shoes, drapes, etc. See the page on spinning and weaving for instructions on what to do with it once harvested. |
| Fiber or hurd | hemp wood | Construction | "HempWood can be used as a construction material. It utilizes bio-mimicry to transform hemp fibers and protein based bonding agents into a viable substitute for anything solid oak can be used for.
Density: 50-55 lbs/ft3 Hardness: 2,000+ Stability: similar to Brazilian Cherry Workability: cuts, sands, and stains. Machining requires testing of speed and blades [2] Hemp grows 100 times as fast as oak and hemp wood is 20% harder. [3] [4]" |
| wax | Material | ||
| Fiber | fibre composites | Material | |
| Fiber | furniture | Miscellaneous | Both cusions and wood-like frameworks can be made from hemp. |
| diapers | Miscellaneous | ||
| Fiber | rope | Miscellaneous | |
| Fiber | surfboard | Miscellaneous | |
| water and soil purification | Miscellaneous | ||
| insulation | Construction | Including flexible and compressible insulation batts, masonry blocks, semi-rigid soundproofing panels, semi-rigid decorative and soundproofing panels, felts for subfloor insulation. [5] | |
| Hurd | hempcrete | Construction | Hurd + lime + water |
| Hurd | fibre board | Construction | |
| Seeds | hemp oil | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | milk | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | butter | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | cheese | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | protein powder | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | flour | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | pasta | Nutrition | |
| beer | Nutrition | ||
| Seeds | nutritional suppliment | Nutrition | |
| Seeds | hemp seeds | Nutrition | 31.56 g of protein per 100 g. Rich in Omega 3 and 6. [6] |
| Seeds | body lotion | Body care | |
| Seeds | hand lotion | Body care | |
| Seeds | soap | Body care | |
| Seeds | shampoo, conditioner, and body wash | Body care | |
| Seeds | lip balm (and other types of balm) | Body care | |
| Seeds | toothpaste | Body care | |
| Seeds | sun screen | Body care | |
| Seeds | wax for hair removal | Body care | |
| Microfiber | water and soil purification | Energy | |
| Fiber, hurd, seeds | biofuel | Energy | Including hemp oil, biodiesel, and cellulosic ethanol. |
| Fiber | batteries and supercapacitors | Energy | |
| serum (for psorasis, eczema) | Medicine | ||
| Microfiber | CBD (oil, spray, lotion) | Medicine | Relief for pain, inflamation, migrain, anxiety, insomnia. |
| heat musle rub | Medicine | ||
| Seeds or seed hulls | animal feed | Agriculture | |
| growing mat (instead of rockwool in hydroponics) | Agriculture | ||
| Hurd | garden bark chippings | Agriculture | |
| Fiber | boat sails | Miscellaneous | Hemp fiber is used in modern boat sails to this day. |
Cultivation, harvest, and processing
Cultivation
Hemp is an annual plant that grows from seed. It is cultivated in a range of soils and in green houses. It can also be grown with Hydroponics.
Beneficial conditions for cultivation in soil
Soil that produces high yields of corn tends to be the most suitable soil for hemp.[7]
The soil must be well drained, rich in nitrogen, and non-acidic.[8]
Soil temperatures must reach a minimum of 42-46°F or 5.5-7.7°C before seeds can be planted.[9]
Hemp prefers a mild climate, humid atmosphere, and a rainfall of at least 25-30 in or 64-76 cm per year.[10]
Harvesting
Harvest timing
The crop is ready for harvesting high quality fiber when the plants begin to shed pollen, in mid-August for North America.[11]
Harvesting for seed occurs four to six weeks later.[12]
Fiber hemp is normally ready to harvest in 70-90 days after seeding.[13]
Equipment for conventional harvesting
Combines are used for harvesting and special machines with rows of independent teeth and a chopper is used for harvesting. To harvest hemp for textiles, specialized cutting equipment is used. [14]
Conventional processing
Retting
After harvest, stalks can be left exposed to the environment for four to six weeks depending on the weather. This is process is called “retting” and removes the pectin binder.[15]
Hemp can also be retted by being submerged in water barrels.
When the hemp has been adequately retted, the soft fiber, encapsulating the hard interior of the stem, will easily peel off, even by hand.
Baling
After retting, stalks are baled with conventional hay harvesting equipment.[16]
Processing for fiber, hurd, and green micro fiber
A hemp decorticator is a machine that separates the hemp plant in to different materials from which the vast array of hemp products are made.
See main article: Hemp decorticator
Hemp seed processing
A dehulling step, which removes the crunchy skin from the seed using a crushing machine, may be required. Modifications to existing equipment may be required to adequately clean the seeds of hull residues.[17]
Hemp oil extraction
Kitchen cold presses for home use that extract oil from seeds are commercially available.
Extraction of oil is normally achieved via mechanical cold pressing; a mechanical expeller press under a nitrogen atmosphere. Solvent extraction methods are also emerging for removing oil since they achieve higher yields. Such methods use hexan, liquid carbon dioxide, or ethanol as the solvent. Refining and deodorizing steps may be required for cosmetics manufacturers.[18]
Paper making
After decortication, it is usually the bast fibers that are used for papers by being put into a spherical tank called a digester with water and chemicals. This mixture is heated for up to eight hours at elevated temperature and pressure until all fibers are separated from each other. Washing with excess water removes the chemicals and the extracted binding components (pectin). The clean fibers can then be fed into a machine called a Hollander beater, which consists of a large tub equipped with a wheel revolving around a horizontal axis. This beating step, which lasts for up to 12 hours, cuts the fibers to the desired length and produces the required surface roughness for proper bonding. Bleaching chemicals are sometimes added during this step or to separate tanks with the fibers. The bleached pulp is then pumped to the paper machine or pressed to a dryness suitable for transportation to a paper mill at another location.[19]
Storage
Hemp bales are stored in dry places like sheds, barns, or other covered storage. The moisture content of hemp stalks should not exceed 15%.[20]
Hemp seeds must be properly cleaned and dried before storing.[21]
Hemp oil must be protected from oxygen, light, and heat for an acceptable shelf-life and good taste.[22]
Links
- Overview publication - [23]
- North American Industrial Hemp Council
- Appropedia: Hemp
- OMAFRA: Growing Industrial Hemp in Ontario
Industry Standards
- Largest hemp processing plant in America - [24]