Inverter Design Rationale and Specification
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Design Rationale
Specifications
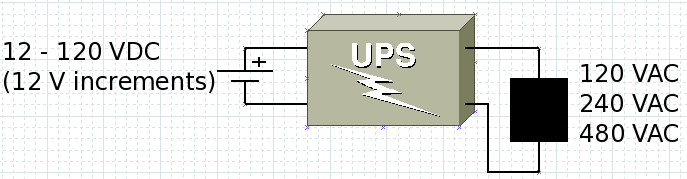
- Input – 12-120V DC using IGBTs that can handle that
- Output - 12-480V AC
- Plug-in transformer modules allow from 1 to 10 amplitude modification
- Use turnkey, plug-in IGBT module of 2.5 kW continuous, 5 kW peak
- Proper heat sinking
- Use turnkey, plug-in gate driver
- Use pure sine wave signal generator
- Stackable up to 10 units for up to 25kW
- Phase cable connects units so power is in phase
Particulars
- Continuous output power: 2500 Watts
- Surge power capability (peak power): 5000 Watts
- dc input / operating voltage: 10 to 120 DC
- Output voltage: 120-480 Volts ac
- Output frequency: 60 Hz +/- 0.5 Hz
- Battery low voltage shutdown: 9.5 +/- 0.5 V
- No load minimum operating temperature: 25 degrees F
- Full load maximum operating temperature: 140 degrees F
- Efficiency: >90%
- No load draw: .6 amps
- AC Output Socket Type: 3 bolt down connectors
- High input voltage protection: 15V
- Low input voltage shutdown: 10V
- Internal fuse protection
Modularity
- Plug-in transformers
Scalability and Modularity Analysis
- Basic unit above provides up to 25kW continuous power with a stack of 10 inverters
- Plug in IGBT module may be scaled for higher power, up to 250 kW for a stack of 10 inverters.
- Modular design retains allowance for different gate drivers, such as high frequency power for induction furnace power supplies and other applications
Links
IGBT Sources
Deployment Strategy
- Ask a vendor for a ready design
- Post on GrabCAD