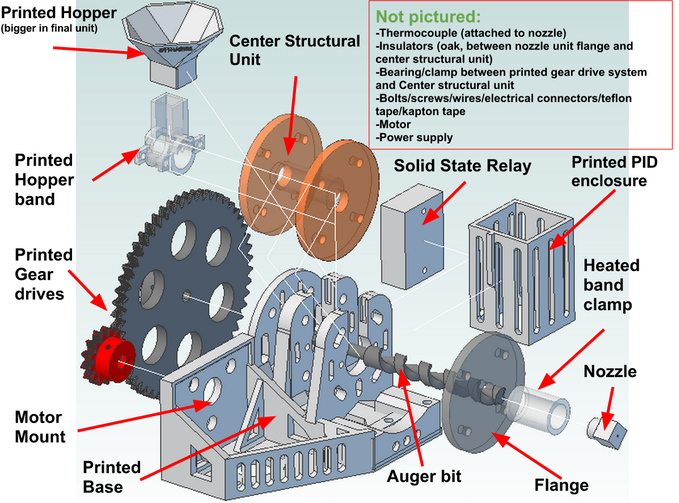
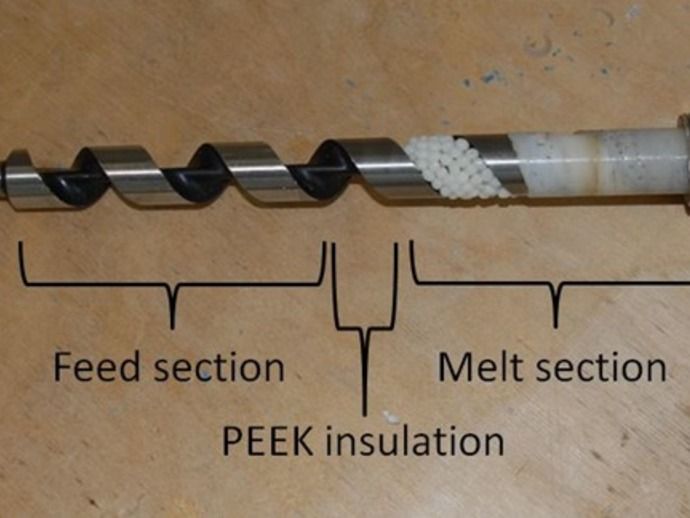
Filament extruder
Development
Principle
Concept Draw
Detail of Feeding Screw
Industry solution
- 140-180 meter per second
- +-0.001 mm size precision
Open Source Extruder Projects
Lyman Filament Extruder V6
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Lyman filament extruder is a device for making 3-D printer filament suitable for use in 3-D printers like the RepRap. It is named after its developer Hugh Lyman and was the winner of the Desktop Factory Competition.
It is open source hardware and all of the plans can be downloaded from Thingiverse
The goal of the Desktop Factory Competition was to build an open source filament extruder for less than $250 in components can take ABS or PLA resin pellets, mix them with colorant, and extrude enough 1.75 mm diameter ± 0.05 mm filament that can be wrapped on a 1 kg spool. The machine must use the Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-SA 3.0).
The use of DIY filament extruders like the Lyman can significantly reduce the cost of printing with 3-D printers. The Lyman filament extruder was designed to handle pellets, but can also be used to make filament from other sources of plastic such as post-consumer waste like other RecycleBots. Producing plastic filament from recycled plastic has a significant positive environmental impact.
Project files on thingiverse.com: [1]
Precision of Filament
Non-commercial optical Filament Sensor -- http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:454584
DIY Filament Extruder
http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-Filastruder/
Precious Plastics Extrusion Machine
https://preciousplastic.com/en/videos/build/extrusion/
MOST lab's Recyclebot
External Sources
http://www.appropedia.org/Recyclebot
Commercial Filament Extruders
- Filabot
- Price: $950—original, $2500—EX2 - proprietary, .05 mm accuracy, 1 kg/hr production rate
- STRUdittle
- Filastruder
- Price: $300
- Webpage
Filament Extruders Using Non-commercial Copyright Clauses on Design Files
Non-commercial copyright clauses prevents people from selling copies of the design files. Copyright does not regulate who makes and who sells physical machines. For OSE's view on the licences the machines below use, see Why OSE Doesn't Support the Use of Creative Commons Non-Commercial Licenses.
- Felfil
- Felfil Evo
Previous work within OSE
Filament Winders
From Tobben - The windings on the spools depicted on Filawinder's home page is not as ordered as Lyman manages to get them. Ordered windings are important to avoid tangles and print failures.
This video shows Filawinder's very simple approach anyways: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2rnxNLFvuD4
This video shows that Lyman gives windings tension using Latex rubber pinch rollers to get ordered windings. https://youtu.be/H6h1yDzoPMU?t=1m10s
Filawinder uses an optical sensor where Lyman uses a pair of microswitches. Optical gives more resolution. I don't know if it makes a practical difference.
Helix loopers can be used to place the filament orderly on the spool. Video of Russ' helix looper in operation: https://youtu.be/vdEXPOo4v64?t=12m42s Hugh Lyman has a helix looper (called "Worm Gear") published under a CC-BY licence in this repo: http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:380987 .
I don't know how Lyman and Russ regulates helix rotation speed. It should depend on current spool radius (how much filament is already winded up).
Calculations
- 600 feet per minute for professional extruder lines
- One kg spool of filament - 1000 feet long for 1.75 mm, 1/3 that for 3 mm
- One kg/hr for filabot. This one is 4 feet per minute - [4]
- Filastruder - 6hr/kg, 60W usage, 3 feet per minute max production - [5]
List of Open Source Versions
- Lyman - complete with winder.
- Recyclabot
- Instructables - [6]. No winder.
List of Others
- Ouroboros - [7]. Ouroboros v3 2019 update - looks promising - [8]
- Reflow - [9]
- Open source branded RWG - [10]
See Also
Links
- List of open and closed projects - [11]
- List of open projects plus intro to extrusion - http://3dprintingforbeginners.com/how-to-make-diy-filament-for-your-3d-printer/