Steel Production: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Recycling of steel from scrap at 1kWhr/kg | *Recycling of steel from scrap at 1kWhr/kg | ||
energy input. See [[Solar Steel]]. | energy input. See [[Solar Steel]]. | ||
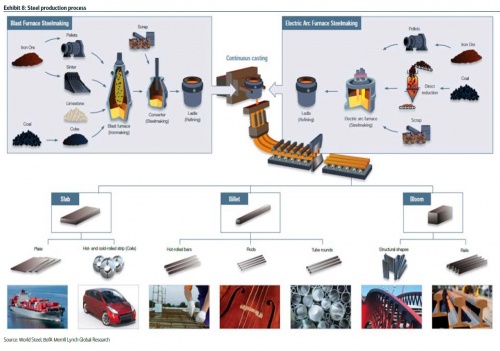
*Another route is reduction of ore using hydrogen. | *Another route is reduction of ore using hydrogen. See [[Hydrogen Reduction Smelting]] | ||
*OSE's case would be to produce steel from direct reduction, which is more efficient and lower temperature than a blast furnace. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_reduced_iron | *OSE's case would be to produce steel from direct reduction, which is more efficient and lower temperature than a blast furnace. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_reduced_iron | ||
*Iron mining in the USA - [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron_mining_in_the_United_States] | *Iron mining in the USA - [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron_mining_in_the_United_States] | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 21 August 2023
https://edge.alluremedia.com.au/uploads/businessinsider/2017/11/iron-ore-steel.jpg
OSE Case
- Recycling of steel from scrap at 1kWhr/kg
energy input. See Solar Steel.
- Another route is reduction of ore using hydrogen. See Hydrogen Reduction Smelting
- OSE's case would be to produce steel from direct reduction, which is more efficient and lower temperature than a blast furnace. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_reduced_iron
- Iron mining in the USA - [1]
- Chromium mining (for stainless steel) - Chromite (FeCrO) is reduced to Ferrochrome (FeCr) via carbothermic reduction. Chromite in Oregon, Montana, California - [2]
OSE Workflow
Sourcing
- Recycling
- Ore?
Refining
- Froth Floatation and other ore methods?
- Direct Reduction , and Charcoal Blast Furnace