Stepper Motor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
A stepper motor (or step motor) is a brushless, electric motor that can divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The motor's position can be controlled precisely without any feedback mechanism (see Open-loop controller), as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application. | A stepper motor (or step motor) is a brushless, electric motor that can divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The motor's position can be controlled precisely without any feedback mechanism (see Open-loop controller), as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application. | ||
=How Stepper Motors Work= | =How Stepper Motors Work= | ||
| Line 12: | Line 9: | ||
*https://www.motioncontroltips.com/faq-what-are-stepper-drives-and-how-do-they-work/ | *https://www.motioncontroltips.com/faq-what-are-stepper-drives-and-how-do-they-work/ | ||
=Holding Torque vs Moving Torque= | |||
*125 oz in hold for nema 17, example - [https://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/sparkfun-electronics/ROB-13656/1568-1376-ND/5995079?&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIvZKS_-jK3wIVBi1pCh0n5Qx7EAQYASABEgL2GvD_BwE] | |||
=Gecko Drives Tutorial= | =Gecko Drives Tutorial= | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 15 April 2019
Overview
A stepper motor (or step motor) is a brushless, electric motor that can divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The motor's position can be controlled precisely without any feedback mechanism (see Open-loop controller), as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application.
How Stepper Motors Work
- See good overview of 2-rotor stepper motors - [1]
- Difference between 2 phase and 5 phase stepper motors - [2]
Holding Torque vs Moving Torque
- 125 oz in hold for nema 17, example - [3]
Gecko Drives Tutorial
Good start.
Voltage
Running steppers at higher voltage produces more torque. 20x rated voltage is ok. [4]
Gecko Drives Tutorial
Good start.
Voltage
Running steppers at higher voltage produces more torque. 20x rated voltage is ok. [5]
Lifetime
The typical lifetime for a stepper motor is 10,000 operating hours. This approximates to 4.8 years; given the stepper motor operates one eight-hour shift per day. The lifetime of a stepper motor may vary in regards to user application and how rigorous the stepper motor is run.[6]
See Also
- Open Source Stepper Motor
- Stepper Motor Controller
- Rotary Encoder
- Open Source Stepper Motor Controller
- Open Source Stepper Motor Controller Problem Statement
- Torch Table Bill of Materials
- Motor
- Wikipedia: Stepper Motor
- [7]
- Stepper Overview Youtube Video
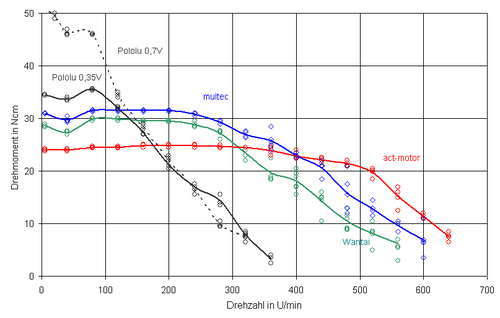
Torque Tests
Test 1
This test used Nema17 stepper motors driven by A4988 driver boards http://reprap.org/wiki/Stepper_torque
Summary: All motors perform well at speeds < 100 revs/min. Dynamical torque starts to drop off at speeds higher than 300 rev/min. The higher the rated current and the lower the inductance, the better the performance at high speeds.
inside a stepper motor
- http://www.homemodelenginemachinist.com/index.php?topic=6748.0
- http://www.robotgear.com.au/Cache/Files/ProductImageOriginals/676_The%20inside%20of%20a%20bipolar%20stepper%20motor.jpg
- http://www.bg-cnc.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/631.jpg
- http://www.designworldonline.com/articles/5409/267/New-Stepper-Motors-Beat-Corrosion-Without-Seals.aspx
- https://www.cdli.ca/courses/isys1205/unit02_org05_ilo07/b_activity.html
- http://electronics-control.info/Stepper_types.htm
- http://electronic-schematic.blogspot.com/2011/04/circuit-for-driving-stepper-motors.html
- http://www.cibomahto.com/2008/02/thing-a-day-day-20-dissecting-stepper-motors/
Types of Stepper Motors
- 17PM-K402 - Hybrid 2 and 4 phase - 6 volts rated - [8] - RAMPS wouldn't run it.
- 12 V rated - [9] - RAMPS wouldn't run it
Sourcing
NEMA 34
Driver
Small
By Origin
- MAE Ametek - made in eu
- Oriental Motor - made in japan