Vegetable growing: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{Breadcrumb|Food and Agriculture|Growing plants}} This page discusses how to make vegetable beds more productive. *Plant the vegetables in waves rather than in rows. This allow...") |
(I'm experimenting with using software to find guilds quickly) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
*Plant the vegetables in waves rather than in rows. This allows you to fit more plants in a bed without reducing the space between plants. | *Plant the vegetables in waves rather than in rows. This allows you to fit more plants in a bed without reducing the space between plants. | ||
*Use mulch or living mulch such as clover. Clover will also | *Use mulch or living mulch such as clover. Clover will also improve the soil. | ||
*[[Biochar]] | *[[Biochar]] | ||
*[[Worms]] | *[[Worms]] | ||
*[[Mushrooms|Fungal symbiosis]]: | *[[Mushrooms|Fungal symbiosis]]: | ||
**Elm oyster mushrooms (''hypsizygus ulmarius'') or garden giants (''stropharia rugosoannulata'') grown in vegetable beds will raise yields. Scatter some colonized grain, straw or cardboard into the beds. | **Elm oyster mushrooms (''hypsizygus ulmarius'') or garden giants (''stropharia rugosoannulata'') grown in vegetable beds will raise vegetable yields while also producing edible mushrooms. Scatter some colonized grain, straw or cardboard into the beds. | ||
**There is plenty of research showing that mycorrhizal spores increase yields. Liquid spore solution can be added to seeds. It is available quite cheaply [http://www.fungi.com/mycogrow/index.html here]. ''Mycelium Running'' say: "Mycorrhizologists harvest spores from wild or greenhouse-cultivated mycorrhizal puffball- or truffleshaped mushrooms from fungi like Glomus, Pisolithus, and Rhizopogon. Mature mushrooms are selected, pulverized into a powder, and then shaken through varied-size mesh screens until the fine spores fall through the bottommost screen (with the smallest openings)." | **There is plenty of research showing that mycorrhizal spores increase yields. Liquid spore solution can be added to seeds. It is available quite cheaply [http://www.fungi.com/mycogrow/index.html here]. ''Mycelium Running'' say: "Mycorrhizologists harvest spores from wild or greenhouse-cultivated mycorrhizal puffball- or truffleshaped mushrooms from fungi like Glomus, Pisolithus, and Rhizopogon. Mature mushrooms are selected, pulverized into a powder, and then shaken through varied-size mesh screens until the fine spores fall through the bottommost screen (with the smallest openings)." | ||
**Endophytic fungi (fungi that grow within plants) can boost yields | **Endophytic fungi (fungi that grow within plants) can boost yields | ||
*Companion planting - see Wikipedia's [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_companion_plants list of companion plants] | *Companion planting - see Wikipedia's [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_companion_plants list of companion plants] | ||
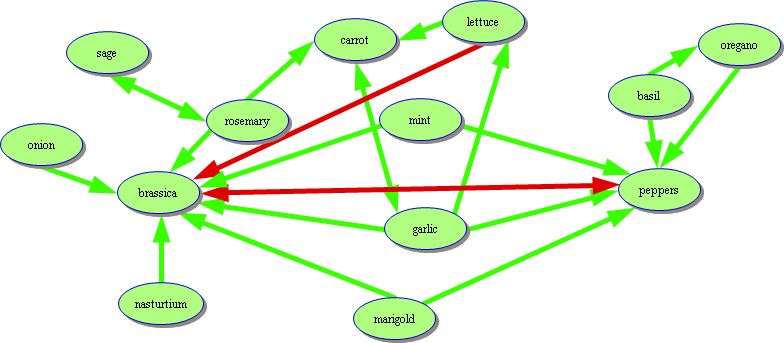
[[File:Companion_planted_vegetable_bed.jpg|900px|thumb|center|An example of companion planting suitable for a vegetable bed. Green arrows show plants that benefit each other and red arrows show plants that harm each other. Note that the harmful interaction of brassicas and peppers is offset by planting mint, garlic and marigold between them, while the harmful effect of lettuce on brassicas is solved by putting carrot and rosemary between them. This is an example of a [[permaculture]] guild.]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:06, 5 June 2011
Main > Food and Agriculture > Growing plants
This page discusses how to make vegetable beds more productive.
- Plant the vegetables in waves rather than in rows. This allows you to fit more plants in a bed without reducing the space between plants.
- Use mulch or living mulch such as clover. Clover will also improve the soil.
- Biochar
- Worms
- Fungal symbiosis:
- Elm oyster mushrooms (hypsizygus ulmarius) or garden giants (stropharia rugosoannulata) grown in vegetable beds will raise vegetable yields while also producing edible mushrooms. Scatter some colonized grain, straw or cardboard into the beds.
- There is plenty of research showing that mycorrhizal spores increase yields. Liquid spore solution can be added to seeds. It is available quite cheaply here. Mycelium Running say: "Mycorrhizologists harvest spores from wild or greenhouse-cultivated mycorrhizal puffball- or truffleshaped mushrooms from fungi like Glomus, Pisolithus, and Rhizopogon. Mature mushrooms are selected, pulverized into a powder, and then shaken through varied-size mesh screens until the fine spores fall through the bottommost screen (with the smallest openings)."
- Endophytic fungi (fungi that grow within plants) can boost yields
- Companion planting - see Wikipedia's list of companion plants

An example of companion planting suitable for a vegetable bed. Green arrows show plants that benefit each other and red arrows show plants that harm each other. Note that the harmful interaction of brassicas and peppers is offset by planting mint, garlic and marigold between them, while the harmful effect of lettuce on brassicas is solved by putting carrot and rosemary between them. This is an example of a permaculture guild.