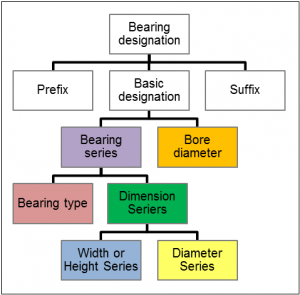
Bearing designation
To identify a bearing, it’s assigned a standardized code referred to as a designation. The designation is made up of one to three parts;
- Prefix
- Basic designation
- Suffix
Prefixes and suffixes, which provide additional information to the designation, are not always included.
Basic designation
A basic designation contains three to five digits that always represent these three pieces of information:
- Bearing type,
- Dimension series, and
- Bore size (inner diameter).
Note: the Bearing type and Dimension series put together is called Bearing series.
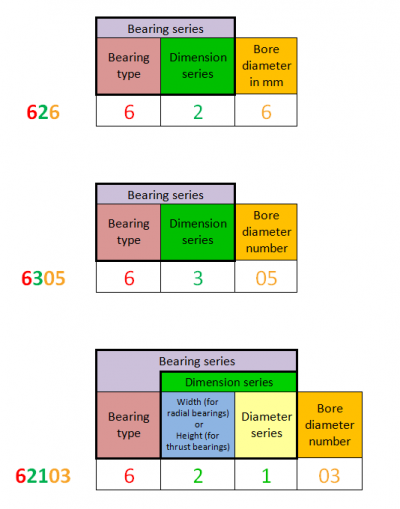
Let’s take the following three designations as examples
- 626 (3 digit designation)
- 6305 (4 digit designation)
- 62103 (5 digit designation)
626
- The first digit always tells us the Bearing type (6 = Single row deep ball groove bearing.)
- The second digit (2) tells us the Dimension series (2 = Light).
- In a three digit designation, the third digit (6) tells us the Bore size in mm. So in this case, the Bore diameter is 6 mm.
6305
- Again, the first digit tells us the Bearing Type (6 = Single row deep ball groove bearing.)
- The second digit (3) tells us the Bearing series (3 = Medium.)
- The third and fourth digit (05) tells us the Bore size (05 = 25 mm.)
62103
- The first digit is for Bearing type.
- The second and third digit tells us the Dimension series where
- the second digit (2) is the width code and
- the third digit (1) is the diameter series
- The fourth and fifth digits (03) tells us the bearing Bore size (03 = 17 mm.)
Prefixes and suffixes
A bearing code can also be made longer to include additional information such as;
- Shield code
- Contact angle code
- Matched pair or stack code
- Internal design code
- External configuration code
- Bearing ring shape code
- Internal clearance code
- Tolerance class code
Codes and their meanings are listed in the section Code tables.
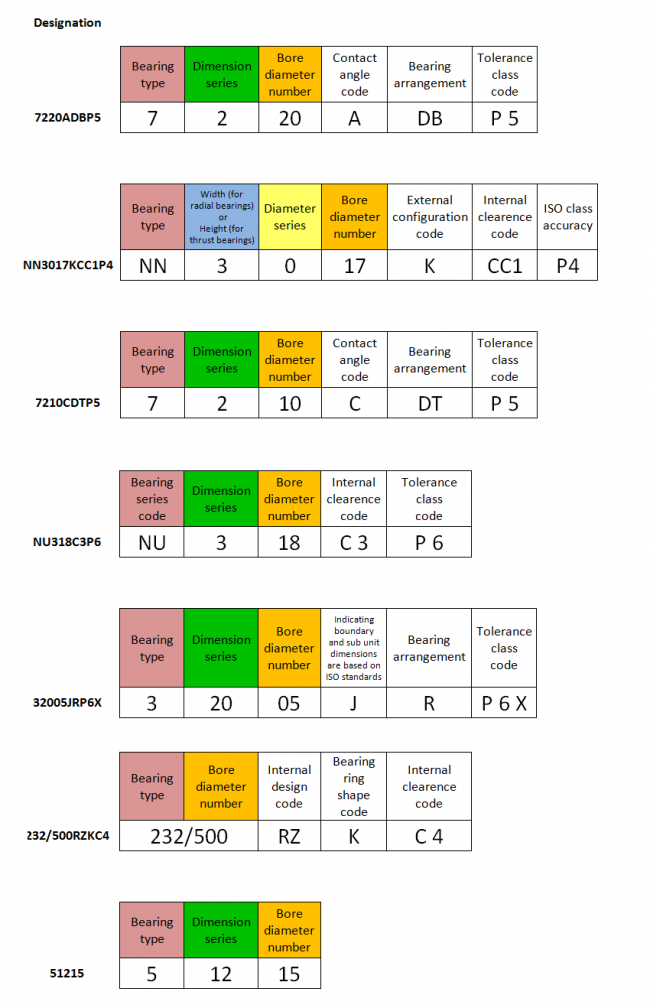
Additional designation examples
Here are some examples what bearing designations can look like. The meaning of the codes is found in section Code tables.
Code tables
The tables below provide the symbols that can make up a bearing designation along with their respective meanings.
Prefix codes
| Prefix Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| K | Cage with roller elements |
| L | Removable bearing ring |
| R | Ring with roller set |
| S | Roll body of stainless steel |
| W | Stainless steel deep groove ball bearing |
| H, LM | Tapered Roller Bearings-Inch |
| HJ, IR | Needle Roller Bearings-Inchstvle |
| K | Needle Roller Bearings-Metric |
| N, NJ, NU, NUP | Cvlindrical Roller Bearings-Metric |
| NA, NAO | Needle Roller Bearings with Inner Rings-Metric |
| NK, RNA | Needle Roller Bearings without Inner Rinos-Metric |
| NN | Super Precision Cylindrical Roller Bearings |
Bearing type codes
| Bearing type code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | Self aligning Ball Bearing |
| 2 | Spherical Roller Bearing |
| 3 | Double row Angular contact Ball bearing |
| 4 | Double row Ball Bearing |
| 5 | Thrust Ball bearing |
| 6 | Single row deep groove ball bearing |
| 7 | Single row angular contact bearing |
| 8 | Felt sealbearing |
| 32 / T | Tapered Roller Bearing |
| R | Inch Bearing |
| N | Cylindrical roller bearing |
| NN | Double row roller bearing |
| NA | Needle roller bearing |
| BK | Needle roller bearing with closed end (Drawncup) |
| HK | Needle roller bearing with openends (Drawncup) |
| C | GARB roller bearings |
| K | Needle roller and cage thrust assembly |
| QJ | Four-point contact ball bearings |
| BH | Angular cont-act (15°) |
| BIH | Angular contact (15°)inch series |
| BA | Angular contact (25° or 29°) |
| BT | Angular contact (35"-40") |
| BY | Angular contact (35°-40") |
| BO | Angular contact, double row, radial, non- filling slot |
| BZ | Angular contact,split inner ring |
| BE | Bell bearin& double row,angular contact,filling slot (maximum capacity) |
| BG | Ball bearing, double row, angular contact,non-filling slot |
| BF | Ball bearing,double row, radial,fill ng slot (maximum capacity) |
| BK | Ball bearing, double row, radial,non-filling slot |
| BM | Ball bearing, single row separable |
| 8L | Ball bearing, single row, radial,filling slot (maximum capacity) |
| BC | Ball bearing, single row, radial,non-filling slot (Conrad) |
| BIC | Bell bearing, single row, radial,non-filling slot,inch series (Conrad) |
| BS | Self-aligning ball bearing |
| R | Cylindrical roller |
| S | Self-aligning spherical roller |
| T | Thrust ball or roller |
Dimension series codes
| Dimension series code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Extra light |
| 1 | Extra light thrust |
| 2 | Light |
| 3 | Medium |
| 4 | Heavy |
| 8 | Extra thin section |
| 9 | Very thin section |
Bore size codes
From code 04 and onward, the code multiplied by 5 equals the bore size in millimeters;
04x5 = 20 mm,
05x5 = 25 mm,
06x5 = 30 mm and so on.
| Bore size code | Bore size in millimeters |
|---|---|
| 00 | 10 |
| 01 | 12 |
| 02 | 15 |
| 03 | 17 |
| 04 | 20 |
| 05 | 25 |
| 06 | 30 |
| 07 | 35 |
| 08 | 40 |
| 09 | 45 |
Shielding or sealing code
| Shielding orsealing code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Code | Description |
| z | One side shielded |
| zz | Both sides shielded |
| RS | One side sealed |
| 2RS | Both sides sealed |
| v | One side non contact seal |
| vv | Both sides non contact seal |
| DDU | Both sides contact seals |
| NR | Snap ring and groove |
| M | Brass cage |
Angular contact codes
| Angular contact code for ball bearings | Meaning |
|---|---|
| A | 30° |
| AC | 25° |
| B | 40° |
| C | 15° |
| CA | 20° |
| E | 35° |
| Angular contact code for Tapered roller bearings | Meaning |
|---|---|
| B | Less than 17° |
| C | 20° |
| D | 28° 30' |
| DJ | 28° 48' 39" |
Internal clearance codes
| Internal Clearance code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| C2 | : Tight |
| C0 or CN | : Normal |
| C3 | : Loose |
| C4 | : Extra Loose |
| CM | : Radial internal clearance for electric motor use |
| /GL | : Light preload |
| /GN | : Normal preload |
| /GM | : Medium preload |
| /GH | : Heavy preload |
| Conditions when the machine is in operation | Examples | Optimal internal bearing clearance in C code |
|---|---|---|
| Significant shaft deflection | Semi-floating wheel bearings in cars | C5 or equivalent |
| Steam flow through hollow shaft or pressure rods exposed to high temperatures | The drying part of paper machines; | C3, C4; |
| Transport rollers in rolling mills | C3 | |
| High impact loads and vibrations or both the inner and outer ring have a press fit | Traction engines for trains | C4; |
| Vibrating sieves | C3, C4; | |
| Hydraulic connector | C4; | |
| Gearboxes for tractors | C4; | |
| Loose fitting inner and outer rings | Rolling pins for rolling mills | C2 or similar |
| Low noise and no vibrations | Small motors with special features | C1, C2, CM |
| Setting to prevent significant shaft deflection | Main spindle of lathes | CC9, CC1 |
Cage type codes
| Cage type code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| x | Manufacturer standard bearingcage |
| A | Steel pressed (land guided) |
| J | Steel pressed (ball guided) |
| F | Steelor iron,machined |
| y | Brass or bronze, pressed |
| B | Brass or bronze, pressed (land guided) |
| K | Brass or bronze, machined (land guided) |
| M | Brass or bronze, machined (ball guided) |
| H | Light alloy,machined |
| 0 | Non-metallic (land guided) |
| T | Non-metallic (ball guided) |
| v | Full complement bearingwithout cage |
External configuration codes
| External configuration code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| No code | Cylindrical inner ring bore |
| K | Tapered inner ring bore, taper ratio 1:12 |
| K30 | Tapered inner ring bore, taper ratio 1:30 |
| N | With snap ring groove |
| NR | With snap ring |
| D | With oil hole |
| D1 | Lubrication hole/lubrication groove |
| T | Non-metallic (ball guided) |
| v | Full complement bearing without cage |
Internal design codes
| Internal design codes | Meaning |
|---|---|
| U | Internationally interchangeable tapered roller bearings |
| R | Noninternationally interchangeable tapered roller bearings |
| ST | Low torque tapered roller bearings |
| HT | High axial load use cylindrical roller bearings |
Bearing arrangement codes
Bearing arrangement refers to how several bearings are arranged together to achieve characteristics in a product that are appropriate for the intended use or load condition. Details about bearing arrangement are found on this page: Bearing selection
| Bearing arrangement code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| DB | Back-to-back arrangement |
| DF | Face-to-face arrangement |
| DT | Tandem arrangement |
| D2 | Two matched, paired bearings |
| G | Flush ground |
Tolerance class codes
| Tolerance class code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| P6 | JIS Class 6 |
| P5 | JIS Class 5 |
| P4 | JIS Class 4 |
| P2 | JIS Class 2 |
| 2 | ABMA Class 2 |
| 3 | ABMA Class 3 |
| 0 | ABMA Class 0 |