Steam Engine Specifications: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
* Valve Gap - the amount of space open in the valves at top dead center. | * Valve Gap - the amount of space open in the valves at top dead center. | ||
** Initially, we shall use 1/8" (0.125"). This can be adjusted by changing the valve pin length. | |||
* I.D. of a half inch bolt - needed to determine valve spring holes and valve stem diameter. | * I.D. of a half inch bolt - needed to determine valve spring holes and valve stem diameter. | ||
* Cylinder clearance - space remaining in the bore at top dead center. | * Cylinder clearance - space remaining in the bore at top dead center. | ||
** "Steam Engines" recommends 3-8% of the piston displacement, which is 4". If we assume 6%, this is a clearance of 0.24, which we can round off to 0.25 (1/4 inch). | |||
* Exhaust port locations - near bottom dead center | * Exhaust port locations - near bottom dead center | ||
** We will use 3.6" from T.D.C as the left edge of the exhaust holes, which shall be 0.25" in diameter.. | |||
[[Category:Specifications]] | [[Category:Specifications]] | ||
[[Category:Steam Engine]] | [[Category:Steam Engine]] | ||
Revision as of 00:03, 26 May 2011
Main > Energy > Steam Engine
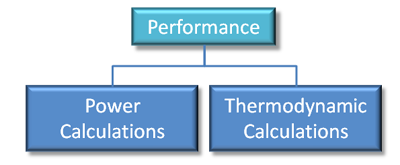
Summary
- Deliverable: a one cylinder prototype module with scalability, to constitute a single stage of a stageable system (compound or 3 stage) which uses the same module that is scaled to make other stages
- System consists of cyliner, crank arm, mechanical valve, automatically adjusted cutoff ratio, and constitutes a Steam Engine Construction Set
- Cutoff ratio controlled by closed loop electronic feedback with some type of linear actuator
- Applications to stationary, mobile, and solar power
Cost-Related Features
- Lowest materials cost for a given performance
- Simplest to fabricate, therefore lowest fabrication cost
- Advanced techniques of fabrication utilized only when necessary to achieve cost
- Fabrication tooling preferably simple, but secondary to fabrication cost
- Uses commonly available parts
- Replicable
- Materials cost of $50/hp
Materials Calculations
- 20 pounds of weigh per horsepower
Flexibility and Performance
- Scalable in power output from 1 - 100 hp by scaling or adding modules
- Power density of 1 hp/10 lb
- Pressure up to 500 psi
- Scalable cylinder dimensions, uncoupled staging, and tandem operation allows scaling of power and eficiency from 1-100 hp and up to 25% efficiency
- Multiple cylinder, in-line configuration is possible by bolting several cylinders together
See the following for steam engine calculations:
- Steam Engine Construction Set Calculations
- Steam Engine Efficiency Calculations
- Steam Engine Efficiency
Lifecycle
- Long lifetime under continuous use (50 years)
Ecology
- Compatible with stationary, solar, and mobile power applications
- LifeTrac power source
- Solar Power Generator heat engine
- CHP with space heating
Sources
- Steam Engine Specifications/Piston Ring Sources
- Steam Engine Specifications/Cylinder Liner Sources
- Steam Engine Specifications/Bearing Sources
- Steam Engine Specifications/Valve Spring Sources
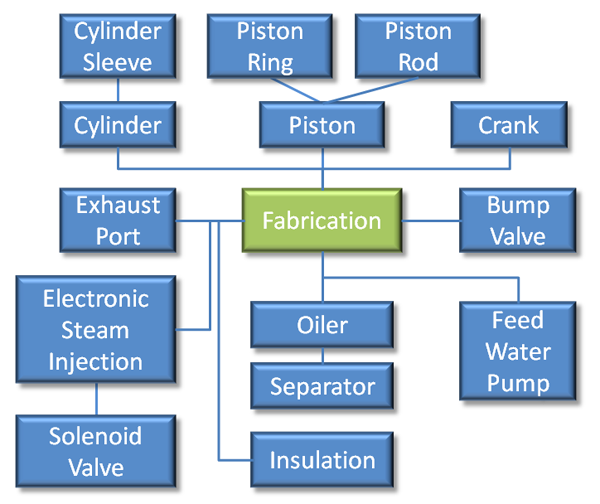
Fabrication
Steam Engine Elements:
- Elements to be Purchased
- Cylinder Assembly
- Cylinder Liner
- Cylinder Bolts (4) - 3 sizes
- Water Drain Plug
- Exhaust Plenum Bolts (4)
- Piston Assembly
- Piston Rings (2)
- Valve Assembly
- Valve Springs (2)
- Valve Spring Bolts (2)
- Base Plate Bolts (4)
- Cylinder Assembly
- Elements to be Fabricated
- Cylinder Assembly
- Cylinder
- Cylinder mounting bracket
- Cylinder end cap with valve seats
- Cylinder end cap and end mount
- Exhaust Plenum - 2 pieces
- Piston Assembly
- Piston Head
- Bump Valve Pins (2)
- Piston Connector Rod
- Valve Assembly
- Valves (2)
- Base Plate
- Oil Dribbler
- Cylinder Assembly
Crankshaft Elements:
- Crankshaft
- Shaft pieces (2)
- Offset plates (2)
- Crank piece (1)
- Couplers (2)
- Screws
- Crankshaft support assembly
- no welding in this design.
- does require tapping holes for machine screws.
- needs counterbalance to not vibrate.
Techniques and Stock:
- Casting used for body
- Stock parts wherever feasible
- Lathing for bore
Other:
Things to Spec
There are a few key dimensions that need to be specified before the full dimensions of the engine and it's parts are known. These include:
- Valve Gap - the amount of space open in the valves at top dead center.
- Initially, we shall use 1/8" (0.125"). This can be adjusted by changing the valve pin length.
- I.D. of a half inch bolt - needed to determine valve spring holes and valve stem diameter.
- Cylinder clearance - space remaining in the bore at top dead center.
- "Steam Engines" recommends 3-8% of the piston displacement, which is 4". If we assume 6%, this is a clearance of 0.24, which we can round off to 0.25 (1/4 inch).
- Exhaust port locations - near bottom dead center
- We will use 3.6" from T.D.C as the left edge of the exhaust holes, which shall be 0.25" in diameter..