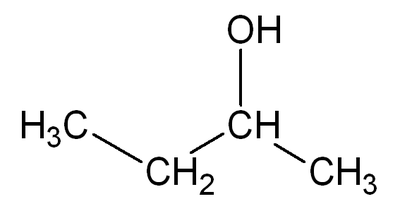
Butanol: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Added a Category to the Page) |
(Added some more information) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=Basics= | =Basics= | ||
* | *It can be used as a direct [[Gasoline Substitute]] in unmodified internal combustion engines | ||
*Butanol is far less corrosive than ethanol and can be shipped and distributed through existing pipelines and filling stations | *Butanol is far less corrosive than ethanol and can be shipped and distributed through existing pipelines and filling stations | ||
* | *It is an effective [[Hydrogen Carrier]] in a [[Hydrogen Economy]] ; Reformed butanol has four more hydrogen atoms than Ethanol, resulting in a higher energy density | ||
*Butanol is an industrial commodity, with a 370 million gallons per year market with a selling price of $3.75 per gallon. | |||
*Butanol is an industrial commodity, with a 370 million gallons per year market with a selling price of $3.75 per gallon. | *It can be, but does not have to be, blended (10 to 100 percent) with any fossil fuel. | ||
*It | |||
*Butanol can be transported through existing pipelines for distribution. | *Butanol can be transported through existing pipelines for distribution. | ||
*It can be blended with petrodiesel and with vegetable oils (where it also reduces the gel temperature point and the viscosity) to produce biodiesel. ? | *It can be blended with petrodiesel and with vegetable oils (where it also reduces the gel temperature point and the viscosity) to produce biodiesel. ? | ||
*It is a very versatile fuel and fuel extender in both gasoline and diesel engines. Octane? | *It is a very versatile fuel and fuel extender in both gasoline and diesel engines. Octane? | ||
=Production Routes= | |||
=Biological= | |||
==[[Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation]]== | |||
*Typically done via [[Clostridium acetobutylicum]] | |||
**Any genetically modified algae/e. coli/yeast etc? | |||
*This can be done with a starch or sugar based feedstock | |||
*It can also be done with syngas (See [[Syngas Fermentation]] ) | |||
=Catalytic= | |||
* | |||
=Internal Links= | =Internal Links= | ||
| Line 19: | Line 27: | ||
=External Links= | =External Links= | ||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Butanol The Wikipedia Page on Butanol] | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Butanol The Wikipedia Page on Butanol] | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Butanol_fuel The Wikipedia Page on Butanol Fuel] | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetone-butanol-ethanol_fermentation The Wikipedia Page on Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation] | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetone-butanol-ethanol_fermentation The Wikipedia Page on Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation] | ||
* | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Celtic_Renewables The Wikipedia Page on Celtic Renewables (A Company Making Bio-Butanol Fuel From Whiskey Wastes] | ||
* | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gevo,_Inc The Wikipedia Page on Gevo Inc] (Supposedly making this commercially viable (also not dead unlike 2/3 of these biofuel companies from the 2000's?) ( '''Make a page on them later''' ) | ||
**[https://gevo.com/agriculture/sustainable-farming/ Also advocates (at least somewhat; [[Low Till Farming]] / [[No Till Farming]] ) [[Sustainable Agriculture]] making it truely sustainable biomass based?] | |||
*PESwiki: [http://peswiki.com/index.php/Directory:Butanol Butanol] | |||
*Article: [http://tchie.uni.opole.pl/freeECE/S_18_1/Kaminski_18(S1).pdf BIOBUTANOL - PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION METHODS] | *Article: [http://tchie.uni.opole.pl/freeECE/S_18_1/Kaminski_18(S1).pdf BIOBUTANOL - PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION METHODS] | ||
*Company: [http://www.butanol.com/ Green Biologics] - a lot of proprietary stuff | *Company: [http://www.butanol.com/ Green Biologics] - a lot of proprietary stuff | ||
*[https://www.epa.gov/fuels-registration-reporting-and-compliance-help/epa-registers-isobutanol-blending-gasoline EPA Registry of Isobutanol for Blending into Gasoline] | |||
**Mentions “ Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC” | |||
**Dated 2018 | |||
**[https://advancedbiofuelsusa.info/the-development-of-butamax This article on “butamax” is dated 2010] | |||
**MIGHT just be [[Greenwashing]] , but that risk aside it does seem like it is at the [[Pilot Plant]] scale [[TRL]] wise as per [https://www.bp.com/en_us/united-states/home/news/press-releases/bp-and-dupont-joint-venture-butamax-acquisition-of-ethanol-facility-in-kansas.html This Article] | |||
*[https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/16/1/77 A 2022 Study in “Energies” Titled “ Effectiveness of Butanol and Deposit Control Additive in Fuel to Reduce Deposits of Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Injectors” ] | |||
**Re: | |||
***[[Deposit Control Additive]] / [[Fuel Detergency Additive]] | |||
***[[Gasoline Direct Injection]] / [[Direct Injection]] / [[Dual Injection]] | |||
[[Category:Biofuel]] [[Category:Bio-Petrochemistry]] | [[Category:Biofuel]] [[Category:Bio-Petrochemistry]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:32, 15 December 2025
Basics
- It can be used as a direct Gasoline Substitute in unmodified internal combustion engines
- Butanol is far less corrosive than ethanol and can be shipped and distributed through existing pipelines and filling stations
- It is an effective Hydrogen Carrier in a Hydrogen Economy ; Reformed butanol has four more hydrogen atoms than Ethanol, resulting in a higher energy density
- Butanol is an industrial commodity, with a 370 million gallons per year market with a selling price of $3.75 per gallon.
- It can be, but does not have to be, blended (10 to 100 percent) with any fossil fuel.
- Butanol can be transported through existing pipelines for distribution.
- It can be blended with petrodiesel and with vegetable oils (where it also reduces the gel temperature point and the viscosity) to produce biodiesel. ?
- It is a very versatile fuel and fuel extender in both gasoline and diesel engines. Octane?
Production Routes
Biological
Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation
- Typically done via Clostridium acetobutylicum
- Any genetically modified algae/e. coli/yeast etc?
- This can be done with a starch or sugar based feedstock
- It can also be done with syngas (See Syngas Fermentation )
Catalytic
Internal Links
External Links
- The Wikipedia Page on Butanol
- The Wikipedia Page on Butanol Fuel
- The Wikipedia Page on Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation
- The Wikipedia Page on Celtic Renewables (A Company Making Bio-Butanol Fuel From Whiskey Wastes
- The Wikipedia Page on Gevo Inc (Supposedly making this commercially viable (also not dead unlike 2/3 of these biofuel companies from the 2000's?) ( Make a page on them later )
- Also advocates (at least somewhat; Low Till Farming / No Till Farming ) Sustainable Agriculture making it truely sustainable biomass based?
- PESwiki: Butanol
- Article: BIOBUTANOL - PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION METHODS
- Company: Green Biologics - a lot of proprietary stuff
- EPA Registry of Isobutanol for Blending into Gasoline
- Mentions “ Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC”
- Dated 2018
- This article on “butamax” is dated 2010
- MIGHT just be Greenwashing , but that risk aside it does seem like it is at the Pilot Plant scale TRL wise as per This Article
- A 2022 Study in “Energies” Titled “ Effectiveness of Butanol and Deposit Control Additive in Fuel to Reduce Deposits of Gasoline Direct Injection Engine Injectors”