Staged pyrolysis: Difference between revisions
m (→See Also: rearranged) |
m (→See Also) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Pyrolysis | * [[Pyrolysis]] and [[Pyrolysis Oil]] | ||
* [[Biochemicals from Pyrolysis]] | * [[Biochemicals from Pyrolysis]] | ||
* [[Bioasphalt]] | * [[Biochar]] and [[Bioasphalt]] | ||
* [[Biofuels]] | * [[Biofuels]] | ||
* [[Vinegar as herbicide]] | * [[Vinegar as herbicide]] | ||
Revision as of 18:50, 13 October 2017
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic matter under an inert atmosphere. Ligno-cellulosic biomass is a common feedstock. The process produces non-condensable gas, bio-oil and biochar. The pyrolysis oil includes more than 300 valuable oxygenated compounds, such as furans, ketones, phenols and esters (see also: Biochemicals from Pyrolysis). Certain phenolic compounds are known for their insecticidal and fungicidal effects.
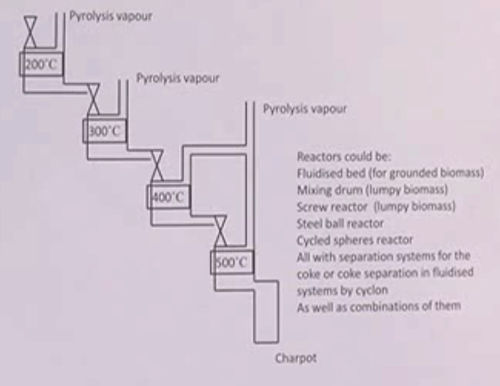
Different constituents of bio-oil can be difficult to separate. However, the composition of the off-gas is strongly influenced by temperature (see also: Wood Preservation by Carbonization). Therefore, when temperature is applied in different stages, different fractional components can be captured (hence: "staged pyrolysis").
Video