Power Cube/Manufacturing Instructions
| Power Cube | ||
|---|---|---|
| Home | Research & Development | Bill of Materials | Manufacturing Instructions | User's Manual | User Reviews | 
| |
| |||||||||||
Overview
Preparation
Tools
- Welder
- Cutting
- Bandsaw
- Chopsaw
- Torch
Assembly Instructions
Subassembly Fabrication
Many of the items listed in the Bill Of Materials require preparation before use in assembly of the Power Cube. This includes drilling and cutting steel up to 3/8” in thickness. These are the parts for assembling a Power Cube.
Engine mounts
- ¼” x 8” x 12” Plate
- ¼” x 8” x 9” Plate
- ¼” x 2” x 2” x 8” Angle
- ¼” x 2” x 2” x 29” Angle
Hydraulic pump mount
- ¼” x 8” x 8” Plate
Quick attach mounts
- [2] 3/8” x 4” x 27” Plates
Fuel tank
- [2] ¼” x 4” x 8” Plates
- 4” x 8” x 14 ½” Tube
- ¼” x 2” x 24” Plate
- All welds assembling the tank must be quality welds, as they must not leak. Be careful not to “over weld” the tank to the mount.
- Clean the inside of the ¼” x 4” x 8” tube and the two ¼” x 4” x 8” plates – anything left on these surfaces will end up in the gasoline and could clog the engine when started. Tack and weld the plates on each end of the tube, taking care to orient the top plate with the filler hole as shown in the diagram below.
- Weld the 1/4” tank flange to the smaller hole.
Oil Cooler Mount
- [2] ¼” x 2” x 24” Plates
- [2] ¼” x 2” x 22” Plates
- [2] ¼” x 2” x 1” Plates
Key Switches and Choke
- [3] 1/8” x 2” x 2” x 2” Angle
Electrical cables
- Note: The connectors can be purchased from an auto parts store – be aware that they usually require a crimper to attach to the cables. Alternatively, 3/8” copper tubing can be used in 1 ½” long pieces instead. Strip 1 ½” insulation from the cable, fully insert fully into 1 ½” copper tube, flatten end with a hammer and drill hole.
- [2] 11” 1 gauge
- 8 ½” 1 gauge
Battery Mount
- [2] ¼” x 2” x 2” x 4 3/4” Angle
- [2] ¼” x 2” x 5/8” Plate
Hydraulic reservoir
- [2] ¼” x 6” x 12”
- 6” x 12” x 27 ½” Tube
- 2” x 2 ¼” x 1/8” Tube
- All welds assembling the reservoir must be quality welds that do not leak. Be careful not to “over weld” the reservoir.
- Clean the inside of the tube and the two end plates – anything on these surfaces will end up in the hydraulic oil and could damage the pump or cylinders.
- Tack and weld the 6” x 12” plates to both ends of the 6” x 12” tube. Pay attention to the orientation of the plate with the filler hole and the side of the tube with other holes – see the diagram below.
- Tack and weld the strainer extension tube to the tank, centered around the strainer hole.
- Insert the strainer into the flange and insert it into the strainer extension tube – verify that it slides without binding or bottoming and that the flange is flush with the end of the tube. Remove the strainer from the flange, then tack and weld the flange to the tank.
CAUTION: Keep the strainer away from the welding, as its thin wires burn easily.
- Suction strainer, weld-in flange, 2” x 2 ¼” x 1/8” tube:
Assembly
Power Cube assembly requires all the parts listed in the Bill Of Materials to be available and prepared as detailed in the “Fabrication” section (above). Assembly requires a welder (electric or torch) capable of welding metal 3/8” thick.
A Power Cube Jig can be very useful during the welding stage.
Top / Bottom Rectangles
- Position two ¼” x 2” x 2” x 29” pieces angle iron on top of two 27” angle pieces as shown below. Check that all joints are square, then tack and weld joints.
- With one welded rectangle on the bottom, position the 24” pieces outside corner joints as shown below. Check that the angles are square, then tack and weld.
File:PowerCubeAssemblyFrame2.jpg
- Position the second rectangle as shown below, then tack and weld. Inspect all corners to verify secure welds.
File:PowerCubeAssemblyFrame3.jpg
Gas tank
- Screw the 1/4" hose barb into the 1/4 NPT flange welded into the gas tank.
- Perform a “soap bubble” test on the tank. Securely cover the larger hole (use something like strong tape), pressurize the tank using the smaller hole and cover the tank surface with soapy water. Look closely for new bubbles, mark any leaks and re-weld securely. Repeat soap bubble test if re-welded.
- Tack and weld the gas tank mount (¼” x 2” x 24” plate) to the frame.
- Tack and weld the gas tank to the gas tank mount as shown below.
- File:PowerCubeAssemblyGas2.jpg
Hydraulic tank
- Perform a “soap bubble” test on the tank by securely covering the larger hole (use something like strong tape), pressurizing the tank using the smaller hole and cover the tank surface with soapy water. Mark any leaks and re-weld securely. Repeat soap bubble test if re-welded.
- Weld it to the frame as shown with 4 1” welds. The tank is ¼” and it can be easily damaged by over-welding. Spacers may be needed on the sides near the top to keep everything snug.
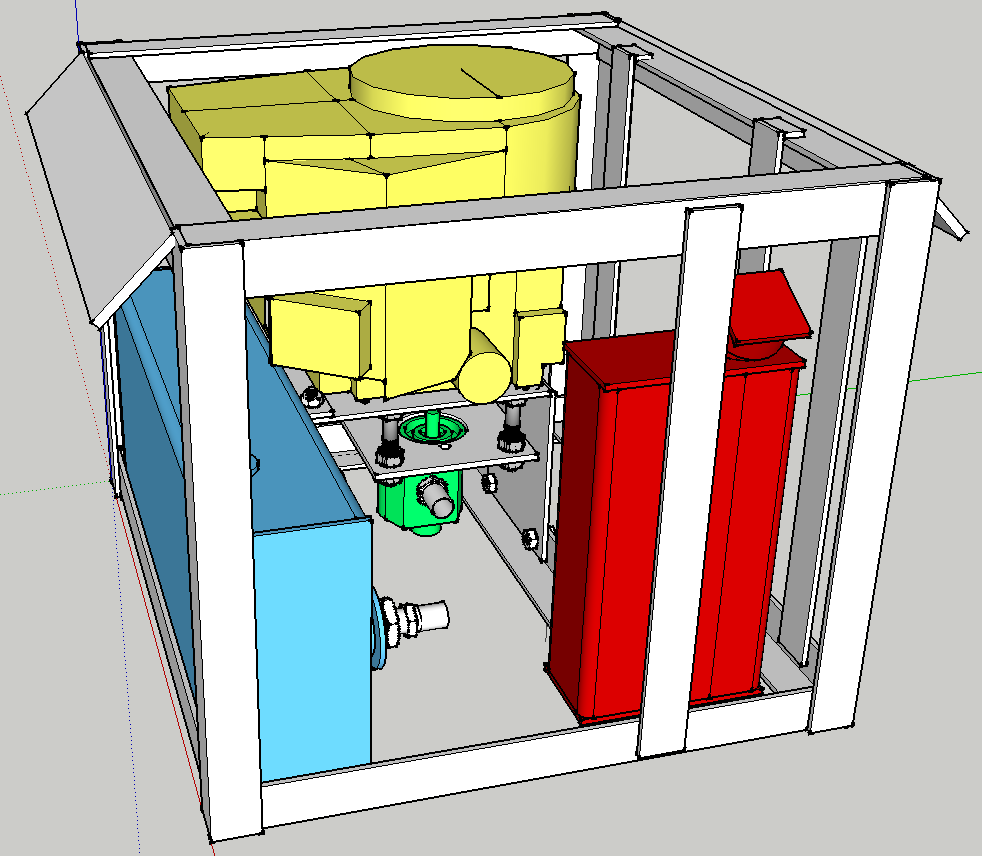
Engine Mounts and Hydraulic Motor Mount
- Position the ¼” x 2” x 2” x 29” angle 12 ½” from the hydraulic tank (see diagram below). Tack and weld it to the frame.
File:PowerCubeAssemblyMounts1.jpg
- Place the ¼” x 8” x 8” plate on the angle iron and secure with two bolts.
- Place the ¼” x 2” x 2” x 8” angle on top of the ¼” x 8” x 12” plate, align the bolt holes and secure with two bolts. Align this assembly with the ¼” x 8” x 8” plate in the prior step and position the angle against the hydraulic tank, 3” below the tank top as in the diagram below, then tack and weld to tank.*<image>
- Tack and weld the corner formed by the two 8” plates.
- Examine the engine shaft – it should be 3” long. If longer, cut the shaft to 3” long.
- Place the engine on its mounting plate and verify that the shaft extends through the hole.
Battery mount
- Weld the ¼” x 2” x 5/8” plates to the ends of the ¼” x 2” x 2” x 4 3/4” plates as shown below.
File:PowerCubeAssemblyBatteryMount1.jpg
- Weld the two mounts to the angle iron and tank to form a rectangle for the battery as shown below.*<image>
- After the mount has cooled, lower the battery into the rectangle to verify it fits properly.
Oil cooler and fan mounts
- Position the two ¼” x 2” x 22” plates to the outside of the frame, adjust so the oil cooler mounting bolts match the holes in the plates and is positioned as in the diagram below. Tack and weld the mounts in to the frame. Verify that the oil cooler bolts match the holes in the mounts.
- Use the mounting holes in the fan shroud and the oil cooler width for positioning the mounting plates as shown in the diagram below. Position the four ¼” x 2” x 1” plates, then tack and weld. Position the two ¼” x 2” x 24” plates against the 1” plates, then tack and weld. Place the fan on the supports and mark the mounts with bolt hole positions. Place the bolt heads against the fan mounting plate and weld in place. Verify that the bolts match the holes in the fan. Inside the frame, adjust the fan position to to position fan shroud ¼” from oil cooler fins. Be careful with radiator as the delicate fins are easily bent and damaged.*
Solenoid Mounting and Installation
- Weld the solenoid mounting bolts to the hydraulic reservoir as shown below. Once cooled, secure the solenoid on the bolts with two nuts.
Keyswitch Brackets and installation
- Weld the 1/8” x 2” x2” x 2” angle brackets to the frame in the positions shown below. Note that the keyswitch brackets have larger holes than the choke bracket.
- Install the keyswitches in the brackets and wire as in the wiring illustration below.
Choke Bracket and installation
- Weld the 1/8” x 2” x2” x 2” angle bracket to the frame in the positions shown below.
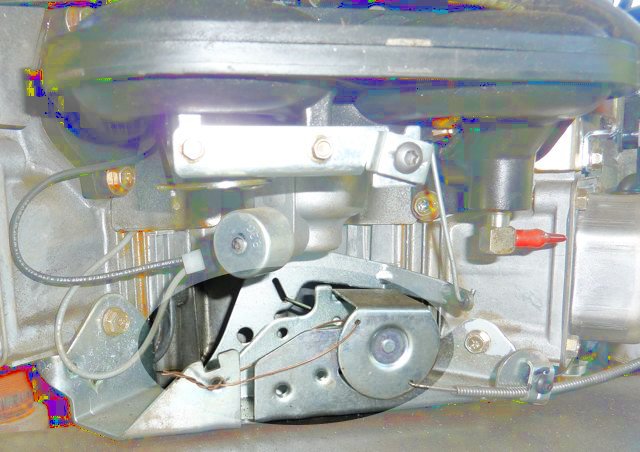
- Secure the engine choke knob as shown in the illustration below
Throttle Adjustment
- Use a wire to permanently set the throttle adjustment to full throttle as shown below
See Also
See also Power_Cube_Fabrication_Procedure for older model.
Work in progress by Tom Griffing - File:Powercube.odt