Hydrothermal Carbonization
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
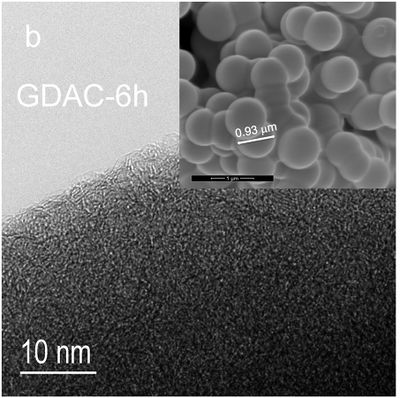

Carbon nanoballs made from glucose via hydrothermal carbonization, that have been processed with CO2 for 6 hours to change surface properties. SEM image from University of Tartu.
Basics
- Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC), also known as "hydrochar", is a form of thermal biomass conversion that involves moderate temperatures and pressures over an aqueous solution of biomass in a dilute acid for several hours.
- One advantage of the HTC process over conventional dry-thermal pre-treatments is the ability to handle wet feedstock without pre-drying.
- The resulting "biocoal" can be used as a Fuel or Chemical Feedstock, as a Soil Amendment (similar to biochar), and as a filtration media, among other things
- ’’’As with how Torrefaction is essentially partial Pyrolysis caused by calmer reaction conditions, HTC can be “tuned” to produce Pure Carbon, or something more akin to Lignite
Clarification on Carbon Produced
- ’’’Hydrochar’’’ shall be used as the term for (Near) Pure Amorphous Carbon which is similar to Charcoal , Carbon Black , or Petcoke and can be used as such
- ’’’Bio-Coal’’’ shall be used to refer to Oily Product intended for use as a Solid Fuel akin to Lignite / Bituminous Coal , or as a Chemical Feedstock for products such as Asphaultum (Useful for Japan Black , a durable Metal Coating called Japanning ) , Humic Acids , or potentially Wax akin to Cerasin Wax , Ozokerite , Motan Wax
Open Source Hardware Needs
- Pressure Vessel
Internal Links
- Biochar (The term used for using Charcoal / Bio- Petcoke or Hydrochar in soil as a Soil Additive such as in Synthetic Amazonian Black Earth )
- Torrefaction
- The Biochar Economy
External Links
- Paper: "A comparative review of biochar and hydrochar in terms of production, physico-chemical properties and applications"
- A Video by the YouTube Channel “ TerraNovaEnergy “ Titled “Hydrochar from Biomass” ( ‘’’~4 Minute Watch’’’ )
- A 2020 Study in “Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery” Titled “ Impact of hydrothermal carbonization on combustion properties of residual biomass”
- A 2024 Study Titled “Textile microfibers valorization by catalytic hydrothermal carbonization toward high-tech carbonaceous materials”