Biochar/Brick Co-production System: Difference between revisions
(added illustration + text) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*Co-products in addition to bricks: [[biochar]], heat (can be turned into steam) | *Co-products in addition to bricks: [[biochar]], heat (can be turned into steam) | ||
==Technical challenges== | ==Technical challenges and other design considerations== | ||
Some reports suggest that high-quality [[biochar]] requires low reaction pressures, to allow all volatiles to evaporate and leave only the char behind. The simplest way to achieve this is the "open burn" approach as demonstrated by the [[Kon-Tiki Kiln]]. In contrast, if the the pyrolysis gas is captured, then this may result in higher pressures inside the pyrolysis zone, reducing the evaporation of volatiles. Potential solutions are: 1.) build higher smokestack to increase draft, 2.) forced draft system using electrical fans that pull out the exhaust, or 3.) blow CO2-rich exhaust gases into the pyrolysis zone to limit oxygen but still drive out the volatiles. | Some reports suggest that high-quality [[biochar]] requires low reaction pressures, to allow all volatiles to evaporate and leave only the char behind. The simplest way to achieve this is the "open burn" approach as demonstrated by the [[Kon-Tiki Kiln]]. In contrast, if the the pyrolysis gas is captured, then this may result in higher pressures inside the pyrolysis zone, reducing the evaporation of volatiles. Potential solutions are: 1.) build higher smokestack to increase draft, 2.) forced draft system using electrical fans that pull out the exhaust, or 3.) blow CO2-rich exhaust gases into the pyrolysis zone to limit oxygen but still drive out the volatiles. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
An entirely different approach would be to an open, complete burn as in the [[Kon-Tiki Kiln]] but only use it for heat, not for fuel. There would still have to be some fuel added to the brick shaft but perhaps at a somewhat (greatly?) reduced level. The air entering the VSBK from below would be pre-heated (heat exchanger?) before entering the burn zone. | An entirely different approach would be to an open, complete burn as in the [[Kon-Tiki Kiln]] but only use it for heat, not for fuel. There would still have to be some fuel added to the brick shaft but perhaps at a somewhat (greatly?) reduced level. The air entering the VSBK from below would be pre-heated (heat exchanger?) before entering the burn zone. | ||
Yet another approach would be to make the char but capture the pyrolysis gas (wood gas), condense it down to [[pyrolysis oil]] and then use that to co-fire a standard, unmodified VSBK. | |||
[[Category:Housing and construction]] | [[Category:Housing and construction]] | ||
[[Category:Materials]] | [[Category:Materials]] | ||
Revision as of 01:28, 25 April 2016
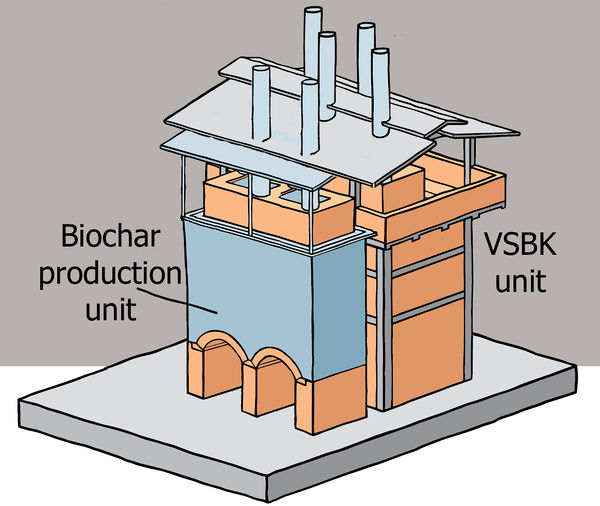
The concept is to couple the production of biochar with the production of fired bricks, analogous to the Biochar-Lime Co-production System. The pyrolysis gas generated during biochar production is not flared off but used to fire bricks in a Vertical Shaft Brick Kiln (VSBK). The process is carbon-negative, because part of the carbon (25-30%) is retained as recalcitrant biochar. This would need relatively close monitoring but there is potential for automation. Heat is another co-product that could be used for space heating, greenhouses, steam, even electricity, etc.
Related Pages
Development Proposal
- Proposal: carbon-negative VSBK fired with pyrolysis gas, with biochar as a co-product
- The typical VSBK is coal-fired, mostly using low-quality coal fines: pieces of coal are scattered onto the bricks from the top. The brick kiln could be re-designed as part of a pyrolysis system to run on pyrolysis gas.
- The emission exhaust system for the VSBK will require major adaptations (see below, technical challenges).
- This type of gas-fired kiln would have cleaner emissions than the coal-fired one (less soot/particulates, CO, NOx, heavy metals, organic pollutants, etc.).
- Co-products in addition to bricks: biochar, heat (can be turned into steam)
Technical challenges and other design considerations
Some reports suggest that high-quality biochar requires low reaction pressures, to allow all volatiles to evaporate and leave only the char behind. The simplest way to achieve this is the "open burn" approach as demonstrated by the Kon-Tiki Kiln. In contrast, if the the pyrolysis gas is captured, then this may result in higher pressures inside the pyrolysis zone, reducing the evaporation of volatiles. Potential solutions are: 1.) build higher smokestack to increase draft, 2.) forced draft system using electrical fans that pull out the exhaust, or 3.) blow CO2-rich exhaust gases into the pyrolysis zone to limit oxygen but still drive out the volatiles.
There is a potential conflict here in that the draft has to accommodate both the brick firing and the pyrolysis. This may make this whole concept not feasible. If the draft on the char is very high, then a larger percentage of the biomass will burn to ash (and the temperature may be above the optimal 450-550C range). If the draft is too low, then the temperature may be too low for good-quality biochar and also the amount of residual volatiles may be elevated. For the bricks, if the draft on them is too high or too low, quality will be affected. This can potentially be resolved in different ways. A throttle mechanism could be inserted between char and bricks. Also, an extra chimney could be added that is only for the char, to make sure that there is always enough draft. This would waste some heat but it could perhaps be captured for other purposes (e.g. steam production). Also, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, CO2-rich exhaust could be blown into the char which would have the advantage that it would pre-heat the newly added biomass. So this may be fixable but at the cost of having a more convoluted system.
An entirely different approach would be to an open, complete burn as in the Kon-Tiki Kiln but only use it for heat, not for fuel. There would still have to be some fuel added to the brick shaft but perhaps at a somewhat (greatly?) reduced level. The air entering the VSBK from below would be pre-heated (heat exchanger?) before entering the burn zone.
Yet another approach would be to make the char but capture the pyrolysis gas (wood gas), condense it down to pyrolysis oil and then use that to co-fire a standard, unmodified VSBK.