Rammed Earth: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "*Nice overview - [http://webs.ashlandctc.org/jnapora/hum-faculty/syllabi/trad.html]") |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
*Nice overview - [http://webs.ashlandctc.org/jnapora/hum-faculty/syllabi/trad.html] | [[File:CEB2.jpg|540px|thumb|right|Rammed earth buildings at Escuela de Artes Visuales de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, México.]] | ||
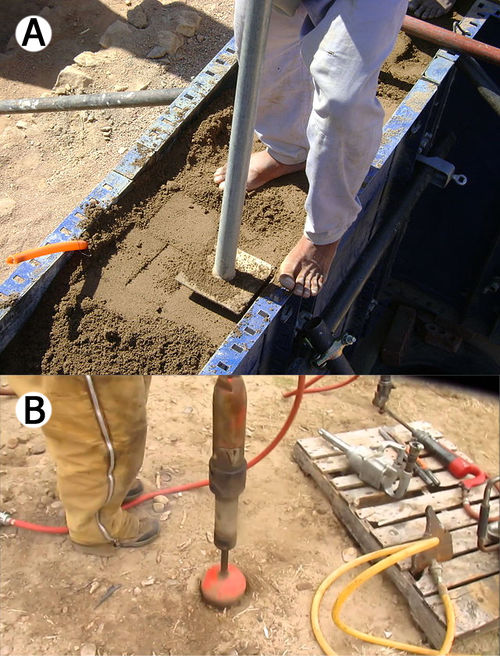
[[File:Tamp RammedEarth.jpg|500px|thumb|right|(A) Picture showing manual ramming of earth in metallic shutters. This technique is quite labor intensive (photo taken in Sinai, Egypt). (B) Pneumatic tamper.]] | |||
=Basics= | |||
*Rammed Earth is an ancient building method that has seen a revival in recent years | |||
*It produces noncombustible, thermally massive, strong, and durable buildings | |||
*However, walls can be labour-intensive to construct without machinery (powered tampers) | |||
*Structures are susceptible to water damage if not adequately protected or maintained. | |||
*Building a rammed-earth wall involves compressing a damp mixture of earth that has suitable proportions of sand, gravel and clay (sometimes with an added stabilizer (like with [[Stabalized CEBs]] ) into an externally supported frame or mould. The construction of an entire wall begins with a temporary frame, or formwork, similar to concrete | |||
* '''Essentially''' : | |||
**CEB is to Bricks/Concrete Blocks as | |||
**Rammed Earth is to Concrete | |||
=Open Source Hardware Needs= | |||
* powered (pneumatic) tamper; this may require an air compressor | |||
* temporary frame, i.e. formwork (usually wood, plywood, steel) | |||
* equipment for excavating subsoil, e.g. backhoe | |||
=Internal Links= | |||
* [[Lime]] may be used as a stabilizer, and in fact historically a lot of rammed earth construction has used lime | |||
* [[Lime]] plaster as an external covering for protection | |||
* [[Earthco Megablock]] - not actually rammed earth but a somewhat related technique | |||
* Reinforcement: [[hemp]] fibers, [[bamboo]], [[steel]], perhaps [[basalt fibers]] (unclear if this has been tried, but should work well) | |||
* with proper subsoil composition, the principles of [[geopolymers]] may be applied | |||
* [[$32k Rammed Earth House in India]] | |||
=External Links= | |||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rammed_earth Rammed earth] | |||
* Nice overview - [http://webs.ashlandctc.org/jnapora/hum-faculty/syllabi/trad.html] | |||
*[https://semmesco.com/our-methods/pise-rammed-earth/ A Page on this by " Semmes & Co. Builders, Inc" ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:54, 12 September 2022
Basics
- Rammed Earth is an ancient building method that has seen a revival in recent years
- It produces noncombustible, thermally massive, strong, and durable buildings
- However, walls can be labour-intensive to construct without machinery (powered tampers)
- Structures are susceptible to water damage if not adequately protected or maintained.
- Building a rammed-earth wall involves compressing a damp mixture of earth that has suitable proportions of sand, gravel and clay (sometimes with an added stabilizer (like with Stabalized CEBs ) into an externally supported frame or mould. The construction of an entire wall begins with a temporary frame, or formwork, similar to concrete
- Essentially :
- CEB is to Bricks/Concrete Blocks as
- Rammed Earth is to Concrete
Open Source Hardware Needs
- powered (pneumatic) tamper; this may require an air compressor
- temporary frame, i.e. formwork (usually wood, plywood, steel)
- equipment for excavating subsoil, e.g. backhoe
Internal Links
- Lime may be used as a stabilizer, and in fact historically a lot of rammed earth construction has used lime
- Lime plaster as an external covering for protection
- Earthco Megablock - not actually rammed earth but a somewhat related technique
- Reinforcement: hemp fibers, bamboo, steel, perhaps basalt fibers (unclear if this has been tried, but should work well)
- with proper subsoil composition, the principles of geopolymers may be applied
- $32k Rammed Earth House in India
External Links
- Rammed earth
- Nice overview - [1]
- A Page on this by " Semmes & Co. Builders, Inc"