Guide to machine design: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "This guide explains how to design a machine. It includes the following: • Basic definitions • What standard components are included in machines (Machine elements) • How...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This guide explains how to design a machine. It includes the following: | This guide explains how to design a machine. It includes the following: | ||
*Basic definitions | |||
*What standard components are included in machines (Machine elements) | |||
*How to select the right components for machines | |||
=Basic definitions= | =Basic definitions= | ||
==Device== | ==Device== | ||
A device uses power as an | A device uses '''power''' as an Input to perform '''work''' as an Output. | ||
This includes smartphones or laptops, machines such as cars or robots, and appliances such as electric water boilers, etc. | This includes smartphones or laptops, machines such as cars or robots, and appliances such as electric water boilers, etc. | ||
==Machine== | ==Machine== | ||
A machine is a type of device that | A machine is a type of device that converts '''power''' into '''work in the form of motion'''. The term encompasses '''the entire physical system''' such as sensors, circuit boards, human interfaces, covers, etc. | ||
This includes tractors, conveyor belts, 3D printers, MRI scanners, etc. | This includes tractors, conveyor belts, 3D printers, MRI scanners, etc. | ||
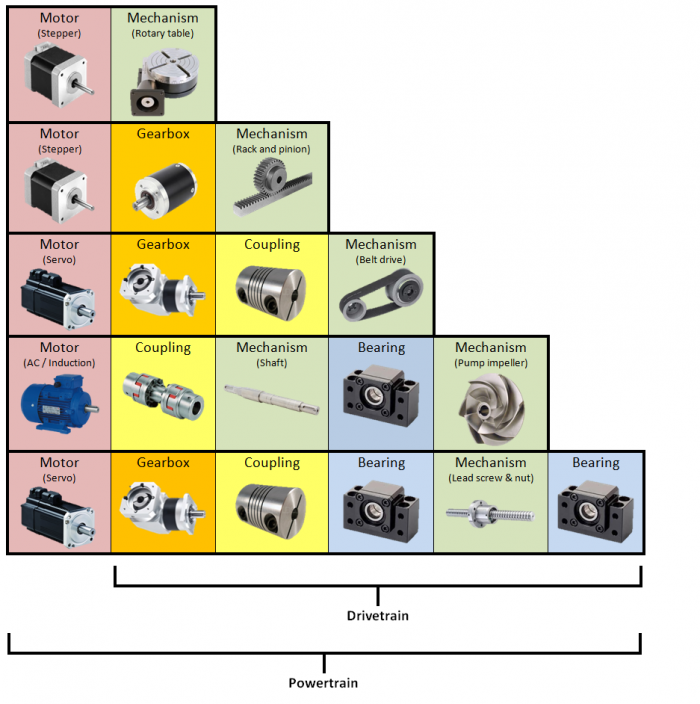
==Powertrain== | ==Powertrain== | ||
If you exclude the surrounding components of the machine and only focus on '''the chain of components that converts power into motion''', the part of the machine that you are left with is called a powertrain. | |||
In | In this ”chain” making up the powertrain, the first component (typically a motor) is connected to a power source (such as a wall socket) and the last component performs the intended motion as an Output. | ||
==Drivetrain== | ==Drivetrain== | ||
If you exclude the first component of a powertrain (such as a motor or engine) what you have left is called a | If you exclude the first component of a powertrain (such as a motor or engine) what you have left is called a drivetrain. | ||
==Drive mechanism== | ==Drive mechanism== | ||
The drive mechanism is the last part of the powertrain or drivetrain and the part of the machine that performs the output motion. | The drive mechanism is the last part of the powertrain or drivetrain and the part of the machine that performs the output motion. | ||
[[File:Powertrain, drivetrain.png|700px]] | |||
=Machine elements= | |||
A ''Machine element'' is a standard basic component of a machine. These elements consist of three types: | |||
* structural components such as frame members, bearings, couplings, axles, splines, fasteners, and seals, | |||
* mechanisms that control movement in various ways such as gear trains, belt or chain drives, linkages, cam and follower systems, including brakes and clutches, and | |||
* control components such as buttons, switches, indicators, sensors, actuators and computer controllers. | |||
==Machine element selection== | |||
See the articles below for selection guides, calculators, and general info pertaining to machine elements. | |||
*[[Drive mechanism selection]] | |||
*[[Bearing selection]] | |||
*[[OSE Bearing dimensioning calculator]] | |||
*[[Gear]] | |||
*[[OSE Gear calculator]] | |||
*[[Coupling Selection]] | |||
*[[Motor selection]] | |||
**[[AC motor/Induction motor dimensioning]] | |||
**[[DC motor dimensioning]] | |||
**[[Servomotor dimensioning]] | |||
**[[Stepper motor dimensioning]] | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[Basic Calculations#Machine_elements| Machine elements section under Basic calculations]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:44, 18 February 2023
This guide explains how to design a machine. It includes the following:
- Basic definitions
- What standard components are included in machines (Machine elements)
- How to select the right components for machines
Basic definitions
Device
A device uses power as an Input to perform work as an Output.
This includes smartphones or laptops, machines such as cars or robots, and appliances such as electric water boilers, etc.
Machine
A machine is a type of device that converts power into work in the form of motion. The term encompasses the entire physical system such as sensors, circuit boards, human interfaces, covers, etc.
This includes tractors, conveyor belts, 3D printers, MRI scanners, etc.
Powertrain
If you exclude the surrounding components of the machine and only focus on the chain of components that converts power into motion, the part of the machine that you are left with is called a powertrain.
In this ”chain” making up the powertrain, the first component (typically a motor) is connected to a power source (such as a wall socket) and the last component performs the intended motion as an Output.
Drivetrain
If you exclude the first component of a powertrain (such as a motor or engine) what you have left is called a drivetrain.
Drive mechanism
The drive mechanism is the last part of the powertrain or drivetrain and the part of the machine that performs the output motion.
Machine elements
A Machine element is a standard basic component of a machine. These elements consist of three types:
- structural components such as frame members, bearings, couplings, axles, splines, fasteners, and seals,
- mechanisms that control movement in various ways such as gear trains, belt or chain drives, linkages, cam and follower systems, including brakes and clutches, and
- control components such as buttons, switches, indicators, sensors, actuators and computer controllers.
Machine element selection
See the articles below for selection guides, calculators, and general info pertaining to machine elements.
- Drive mechanism selection
- Bearing selection
- OSE Bearing dimensioning calculator
- Gear
- OSE Gear calculator
- Coupling Selection
- Motor selection