Torrefaction: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
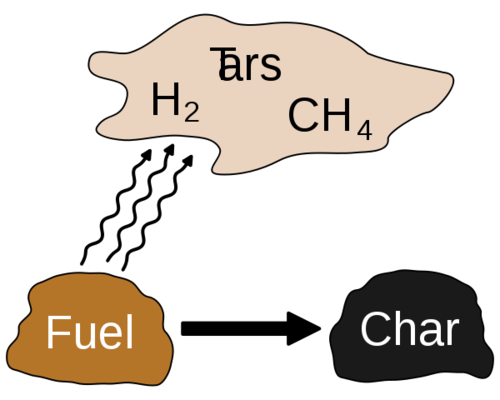
(Created page with "File:600px-Pyrolysis.svg.png|thumb|right|500px|Torrefaction removes moisture and some volatiles from wood. Further heating leads to carbonization, which mobilizes more volat...") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[[Category:Biofuel]] | [[Category:Biofuel]] | ||
[[Category:Energy]] | |||
Revision as of 03:30, 17 August 2016
Torrefaction of biomass, e.g., wood or grain, is a mild form of pyrolysis at temperatures typically between 200 and 320 °C. The calorific value of biomass can be greatly increased by torrefaction. Benefits are: higher energy density, more homogeneous composition, hydrophobic behavior, elimination of biological activity, improved grindability.