Syngas Fermentation: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "400px|thumb|right|Microbial catalyst. syngas Syngas fermentation is a microbial process whereby syngas (i.e. a gasification-derived mixture of hyd...") |
m (added Wikipedia link) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* [[Open Source Biotechnology]] | * [[Open Source Biotechnology]] | ||
* [[Biorefinery]] | * [[Biorefinery]] | ||
* Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syngas_fermentation | |||
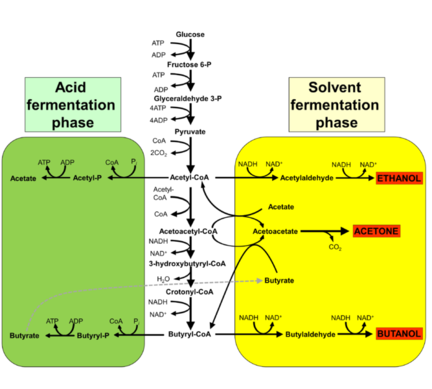
[[File:Acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation.png|432px|thumb|right|Syngas may be fed into the [[Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation]] pathway by ''Clostridia''.]] | [[File:Acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation.png|432px|thumb|right|Syngas may be fed into the [[Acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation]] pathway by ''Clostridia''.]] | ||
Revision as of 18:40, 13 October 2017
syngas Syngas fermentation is a microbial process whereby syngas (i.e. a gasification-derived mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide) is used as the source for carbon and energy for subsequent conversion into fuel and chemicals by microorganisms. The main products include ethanol, butanol, acetic acid, butyric acid, and methane.
This process has some advantages over the Fischer-Tropsch process, which include more flexibility in feedstock, high specificity of the microbial catalysts, reaction near ambient temperature and pressure, as well as other aspects.
Disadvantages include limitations in the gas-liquid mass transfer, impurities in syngas generated from biomass (may affect fermentation), as well as the sensitivity of microorganisms.
Related Pages
- Staged pyrolysis
- Biochemicals from Pyrolysis
- Open Source Biotechnology
- Biorefinery
- Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syngas_fermentation